The right choice of product marketing strategy is a key factor in the development of the enterprise. An established distribution system allows you to expand the range of goods and services, increase the company's market share, assess the degree of customer satisfaction and receive financial profit.
What is a marketing strategy?
In the broad sense of the word, sales (or distribution) means the delivery of goods or services of an enterprise to a buyer or client. To organize a distribution system, it is necessary to create a logistics structure and distribution channels. The strategy should determine the number and type of intermediaries in the distribution network, the cost of wholesale and retail for the intermediate and final buyer, the need for additional services before and / or after the sale, as well as ways of management and communication between participants in the chain. Marketing methods are divided into intensive and exclusive. The first involves the sale of goods through an extensive network of distributors in order to broadly cover the market, the second - through a limited number of intermediaries or direct sales. With exclusive cooperation, the manufacturer has the right to put forward special requirements regarding the range, prices and design of goods.
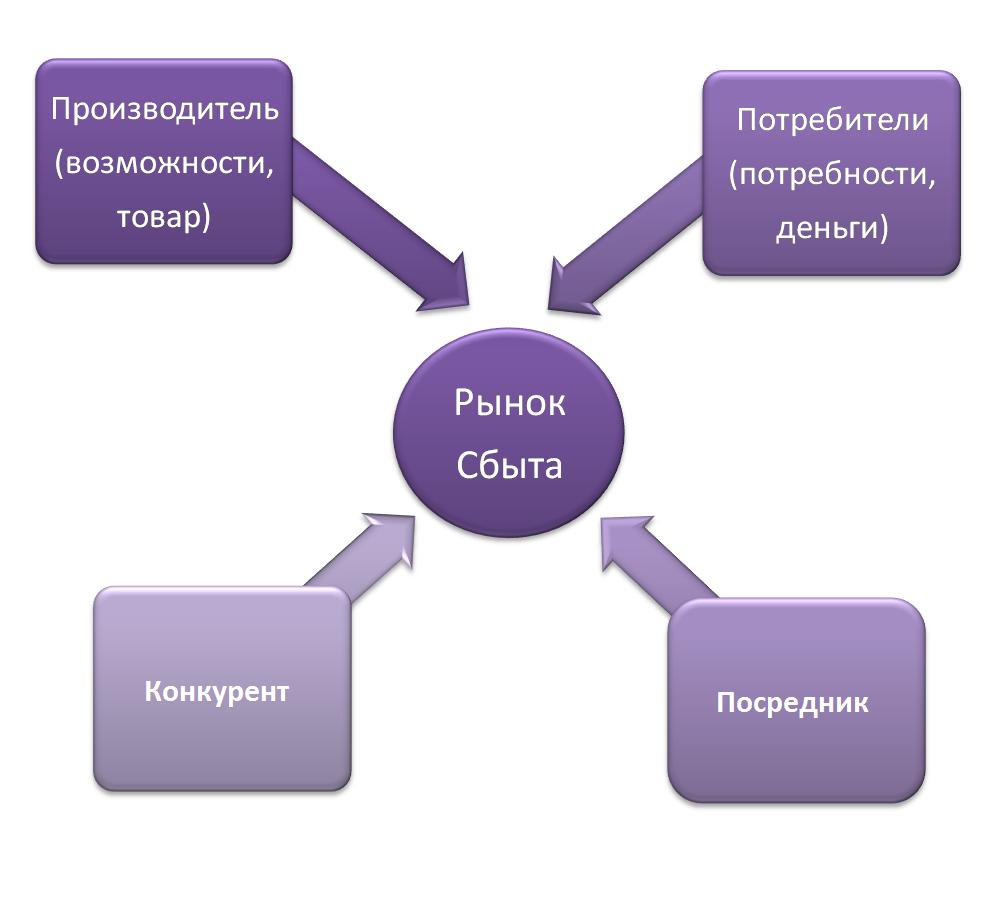
The choice of one or another marketing method depends on the coverage of the market, the goods belonging to a certain price segment, production volumes, financial capabilities of the enterprise and other factors. In marketing, marketing strategy is a key factor in the development of the enterprise. An established distribution system allows you to expand the range of goods and services, increase the company's market share, assess the degree of customer satisfaction and receive financial profit.
Sales Functions
The logistics and sales system should carry out a number of functions, some of which are undertaken by the manufacturing company, and the other by distributors (wholesalers and retailers).
Primary Planning Functions:
- Drawing up a plan of sales volumes based on the current market situation.
- The choice of distribution channels, transportation and storage systems.
- Definitions of the form of packaging and assortment.
- Calculation of distribution and sales costs.
Organizational Functions:
- Organization of logistics and storage of goods.
- Organization of a post- and pre-sales service department, training of sellers and other employees.
- Establishing contact with consumers and organizing sales.
- Organization of a management system and communication between participants in the distribution network.
Coordination and regulatory functions:
- Monitoring the implementation of sales and sales plans.
- Sales promotion.
- Assessment of statistics and accounting reports of intermediary enterprises.
- Marketing analysis of customer satisfaction.
Trading and financial functions:
- Stimulating demand, market segmentation to strengthen positions.
- Impact on market prices.
- Crowding out competitors.
- Receiving a profit.
Direct marketing method
Sales can be carried out without intermediaries, directly from the manufacturer. Such a structure is called a straight line. Sales can be carried out through an online store, a network of sales agents, from the company's warehouse (cash and carry), through subsidiaries and representative offices. Direct marketing is used when:
- sales volumes are high;
- the cost of goods is much lower than the cost of sales and income covers the costs of organizing your own marketing system;
- there are few main consumers, and they are located in a small territory;
- the goods need professional service or are made to order.
With a direct marketing marketing strategy, the manufacturer is faced with a number of costs for transportation, rental of warehouses and retail space, training materials for staff, telephone calls, etc. In addition, the creation of subsidiaries takes a lot of time and needs constant monitoring. However, this method of marketing helps to establish trusting relationships with customers, allows you to quickly respond to any changes in the market.
Indirect Sales Method
To increase sales efficiency, some manufacturers resort to a network of independent intermediaries. Such a multi-level system solves the problem of lack of finance for the organization of own marketing. The indirect method is used when:
- the group of potential consumers is vast;
- bulk deliveries needed;
- the market is geographically scattered;
- the difference between cost and final price is small.
If in direct marketing the manufacturer interacts directly with the buyer, in an indirect way the main work is carried out with an intermediary. In this case, it is much more difficult to maintain the image of the company or influence prices. The choice of intermediaries, their number and distribution of functions are the main stages in the formation of a marketing strategy.
Types of indirect sales channels
There are many options for implementing indirect distribution. The main intermediaries include:
- Agents and brokers are participants in the chain of sales of goods that help in transactions. The broker does not participate directly in sales, does not have his own rights to the goods, does not store his stocks and does not bear any risks. His task is to find a buyer and organize a deal. Agents conclude agreements with enterprises, which stipulate all their functions and tasks: the geographical territory of the customer search, the level of mark-ups on the goods, the provision of guarantees, delivery and service options, etc. Agents not only organize sales, but also participate in planning introducing a new product to the market, advising clients. The services of such intermediaries are used with a wide geographical spread of the market and sale in small batches.
- Dealers purchase the goods in the property from an agent or manufacturer, without obtaining the right to a trademark. As independent entrepreneurs, they have their own market, sell goods at retail and set a margin at their discretion. Dealers issue warranties and service.
- Consignees are intermediaries who organize the storage of producer goods in their own warehouses with subsequent sale. They do not buy goods in the property. Implementation is carried out in accordance with the contract with the supplier, which indicates the price of the goods, volumes and terms of sales.
- Distributors are engaged in the sale of goods on their own, concluding contracts with manufacturers and buyers. Such intermediaries set prices for goods, carry out promotions, engage in service and warranty services, have their own warehouses for storage and wholesale and retail outlets.
The sequence of formation of sales strategies
The selection of the most effective sales of goods begins with a market analysis. Assessment of market conditions implies consideration of a number of factors affecting sales: supply and demand, price level in various regions of activity, company market coverage, actions of competitors, etc. These factors determine the goals of a product marketing strategy.
The goals and objectives of the marketing of the enterprise should be consistent with the overall marketing strategy, as well as assortment policy and financial capabilities. Distribution objectives may be as follows:
- Transformation of existing sales methods, implementation of a new sales strategy in connection with the changing market situation.
- Increasing the company's market share.
- The increase in the number of goods sold.
- Expanding the product line and / or entering a new market.
- Adaptation to changes in the organization and policies of the intermediary company.
- Creating your own channels for the sale of goods.
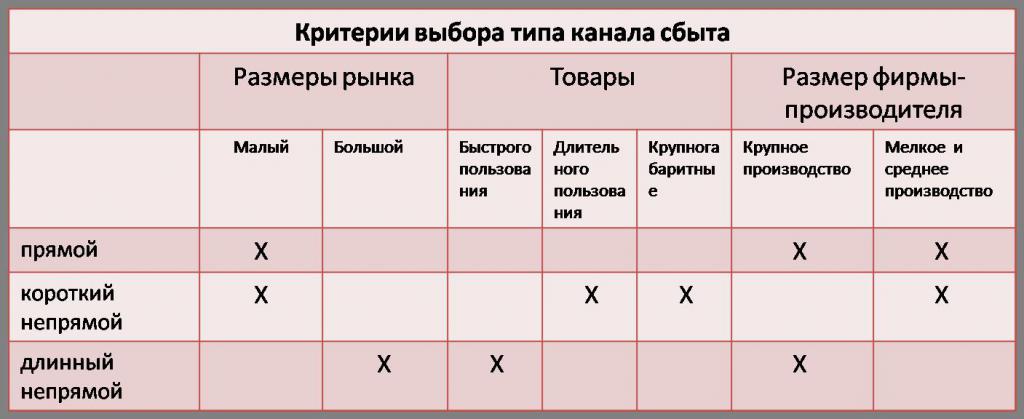
To carry out the stated tasks, it is necessary to analyze the forms and structures of sales. Based on the characteristics of the market and goods, they decide on direct, indirect or mixed sales.
Before involving intermediaries in cooperation, they evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise. Interaction with other companies compensates for the shortcomings. If the manufacturer is limited in financial resources or technical personnel, working with a large distributor and transferring part of the marketing functions to him will be a profitable decision. Thus, at the initial stages of creating a marketing strategy, the powers of intermediaries are determined. They can engage in after-sales service, local advertising, delivery, credit, etc., which will benefit both the manufacturer and the end customers. In addition, it is important to determine the range of goods sold by one or another distributor.
The number and type of intermediaries affect the demand for the product, the reputation of the company, customer contact, quality of service, etc. A large number of small distributors allows you to maintain control, quickly respond to changes in the market and ensure wide customer coverage. However, large intermediaries can store large stocks of goods and provide better service. A detailed classification of indirect marketing strategies, depending on the tasks and characteristics of the enterprise, defines all the benefits and risks of working with intermediaries.
After the approval of the strategy and sales channels, the company selects specific intermediaries, and also selects the structure of the organization of management and evaluation of work results.
Classification of Indirect Distribution Strategy Types
Methods of selling goods through intermediaries are divided according to the type of market coverage, orientation, communication with the end customer and the way sales are organized. Each type of classification has several forms that meet the objectives of the enterprise.
Market Coverage:
- Intensive, i.e., the maximum number of distributors of all types is used for a large market coverage. This form is used for everyday or impulsive goods, in order to increase brand awareness and increase the share of the enterprise. The disadvantages include difficulties in controlling pricing policies and implementing a common marketing strategy.
- Selective, i.e., work with a limited number of intermediaries. Suitable for pre-selection products and products requiring complex maintenance. Such cooperation limits the company's market share and makes the company dependent on intermediaries, however, it makes it possible to control prices, deliver goods in large quantities for sale, save on local advertising and improve the reputation of the brand.
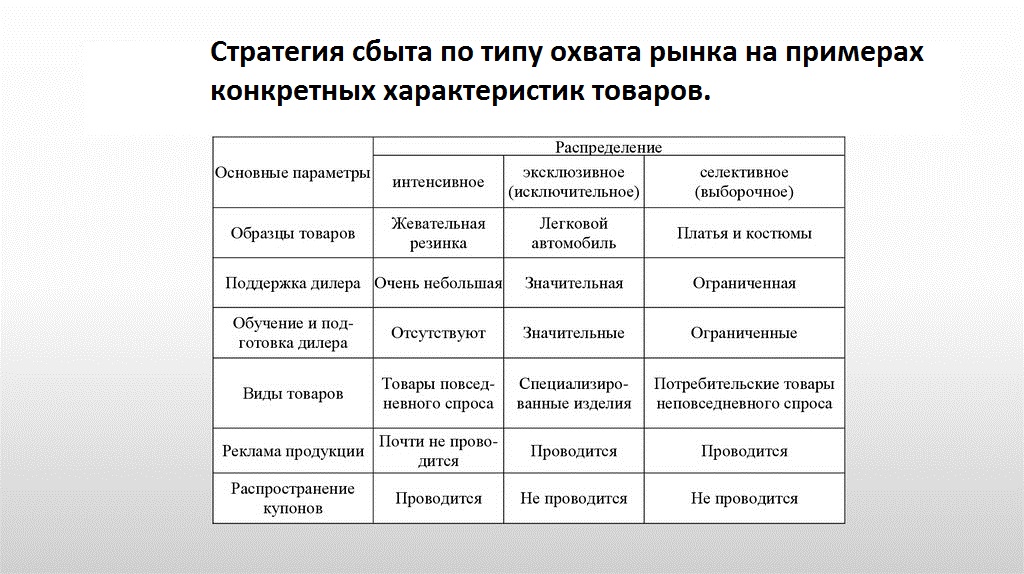
- Exceptional by one intermediary. It is used in sales of luxury goods requiring high-quality maintenance. Unprofitable for most manufacturers, because it limits the market share and makes the company completely dependent on the distributor.
- Franchise - a form of exceptional strategy in which the franchise holder transfers to the intermediary the right to use its own technology for the production and sale of goods. The franchiser saves money on the organization of production, receives cash inflows from the franchise and increases brand awareness in the market. However, this form has significant drawbacks, because the company's reputation depends entirely on the actions of an intermediary.
Sales Orientation:
- For buyers - involves assessing customer needs, then segmenting the market in accordance with them, increasing the range in accordance with changing needs.
- For goods - it consists in the active promotion of products, increasing brand awareness and the constant search for new ways of implementation.
Sales Method :
- Opportunistic, i.e. reduction or complete suspension of sales. It is used when defects are found in a product, there is a shortage in the market, a price change is expected, or a foreign intermediary has not completed the tasks and spoiled the company's reputation.
- Passive, not requiring special interaction with customers. It is used in the sale of low-cost consumer goods, in sales by large retail distributors or with the brand's wide popularity.
- Offensive, in which the manufacturer intensively promotes the product in all available ways. The method is popular when selling a product of passive demand, seasonal or overpriced goods.
- Expert, or customer-oriented. It is actively used in B2B sales, for long-cycle products and for frequent subsequent sales to the same customers. The manufacturer's activity is aimed at maintaining long-term mutually beneficial cooperation with customers.
Communication Method:
- “Pushing” implies an active influence on all intermediaries in the sales network to introduce more of their own goods into the partner's assortment. The ways of motivating and stimulating distributors are different: free training for intermediary staff, partial reimbursement of advertising costs, bonuses, cash rewards for sellers, tenders between outlets, etc.
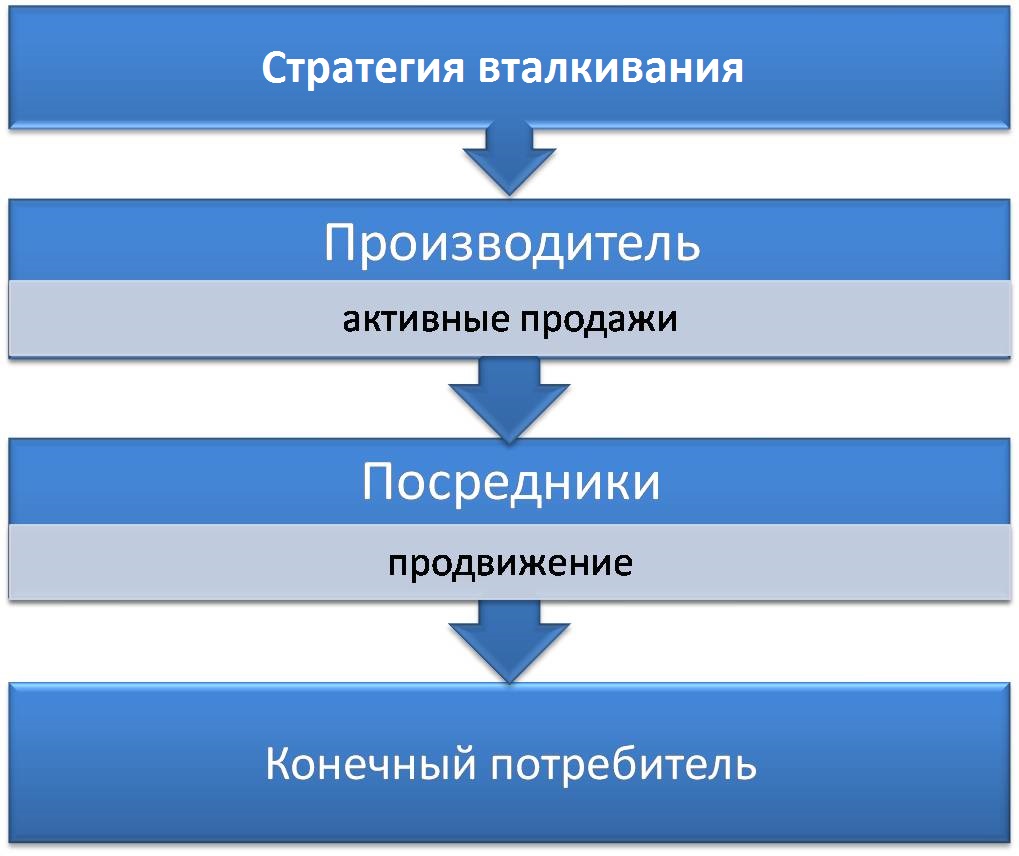
- “Retraction”, or focusing the manufacturer on the consumer. The company holds large-scale promotions in order to increase demand and customer interest, monitors the availability of goods at points of sale, organizes quality service and delivery. In this case, the intermediaries themselves are interested in cooperation in order to obtain a large revenue from sales. This strategy is often used by large enterprises, because it requires significant financial costs.
- A “combined” sales strategy combines the first two options. It is used only by large corporations that are able to bear the costs of strengthening relations with both customers and distributors.
The manufacturer can choose the type of distribution that matches its current capabilities. With expansion, a shift to more sophisticated sales promotion strategies usually occurs.
What to look for when selecting intermediaries?
Intermediaries are in direct contact with customers, which means that the reputation of the manufacturer depends on them. When developing sales strategies and selecting intermediaries, attention should be paid to the history of companies, their marketing policies, professional skills of staff, sales volumes and financial condition. If the manufacturer involves the transfer of certain functions to the partner, an analysis of the preparedness of employees and the availability of technical equipment is carried out in advance. Companies come to an agreement on financial and technical support, volumes of purchases, payment methods, pricing strategy and level of service. Then, organizational issues on communication methods and management are decided.
Sales organization
To work effectively with intermediaries, enterprises structure the sales department in accordance with the characteristics of the sales strategy, product properties, coverage and market size. Most often, the separation of duties of employees occurs according to the following principles:
- By market geography. In such a structure, each manager is responsible for a separate territory. The higher his position in the hierarchy, the greater the area of the territory for which he is responsible.
- By type of product. Each manager is responsible for a specific group of products in the assortment.
- By function. The sales department can be divided into customer service, sales, service, delivery, merchandising, etc.
- By types of customers. When a manufacturer trades standardized consumer goods, managers work separately with each consumer group.
- The mixed form of separation is used by small and medium-sized manufacturers and includes various services, depending on the characteristics of the sale.
Evaluation of the effectiveness of distribution policies
Analysis of the company's sales strategy includes checking the implementation of sales goals, the implementation of the sales plan, the level of income and profits. In addition, control over the activities of intermediaries related to the company's reputation is required: quality of service, effectiveness of advertising campaigns, timely delivery, and maintenance of inventory. Marketers conduct surveys and surveys to assess customer satisfaction. Large manufacturers are sending reseller trading reports with high sales to less successful distributors to stimulate better work.