The cyst of the spermatic cord in a boy (the reasons may be in the wrong development in the womb) is an isolated dropsy of the testicle. This disease involves the accumulation of fluid. The size of the cyst can be different - from very small, which are almost invisible, to those that disrupt the entire reproductive system of the boy.
What is the spermatic cord
The spermatic cord is one of the organs of the reproductive system that is paired. It consists of nerves, lymphatic and blood vessels, vas deferens, the remains of the outgrowth of the peritoneum.
A funiculocele is a benign hollow tumor in the spermatic cord that can be congenital or acquired. It is quite easy to identify this pathology during a manual examination of the child, but it is better to entrust it to a doctor who will make a diagnosis on the basis of a comprehensive examination.
Manifestation forms
Cyst of the spermatic cord in a boy (reasons, photos are presented in this article) can be:
- Congenital. In this case, there is only one explanation - disruptions in embryonic development. A congenital cyst of the spermatic cord in a boy is manifested with incomplete growth in the abdominal cavity of the vaginal process, which is why hollow neoplasms form in the spermatic cord. Most often, this form of pathology is spermatogenic and consists only of a clear fluid without sperm.
- Acquired. This form most often develops as a result of the inflammatory process of the scrotum or its injury. The ducts that were damaged in one way or another cease to function, due to which there is an overlap, which means that the outflow of sperm cells stops. In addition, there is a blockage of the secret itself, which pulls some sections of the seminal ducts. It is precisely because of this that hollow neoplasms, cysts are formed. Unlike congenital pathology, in this case, the fluid is also filled with sperm bodies, and they can be already destroyed or even fresh.
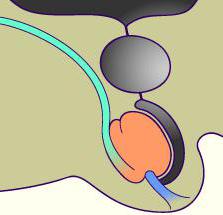
It is worth noting that the boy’s congenital cyst of the spermatic cord, the reasons for which lies in the peculiarities of embryonic development, does not pose a threat to life, however, when the first symptoms appear, it is recommended to consult a urologist immediately. This is due to the fact that funicular can only be a symptom of another serious disease. For example, a cancerous tumor may develop with the same symptoms. That is why any neoplasm needs a complete study.
The main causes of pathology
In addition to pathologies of embryonic development, a cyst of the spermatic cord in a boy, the causes, treatment and diagnosis of which are discussed in the article, may occur due to:
- blockage of the duct of the spermatic cord or interruptions in the circulation of interstitial fluid (retention cyst) ;
- mechanical damage, inflammation or other pathology of the spermatic cord (remission cyst).
Most often, this disease is congenital in nature and is formed as follows: in the womb, the testicle normally lowers into the scrotum, moving along the inguinal canal, and the outgrowth of the peritoneum, which subsequently forms the inner shell of the testicle , also falls . It is this outgrowth that is called the vaginal process.
Normally, this process overgrows during the first months of life, as a result of which a thin cord forms, and the area of contact of the testicle with the peritoneum disappears. This prevents the passage of peritoneal fluid to the location of the testicle. The lower part of the process forms a kind of cavity around the testicle, which serves as a reservoir for fluid in the cyst of the spermatic cord. The main reason for this condition is that the area of contact of the testicle with the peritoneum does not disappear. It is through this opening that the abdominal fluid penetrates the testicle.
What does a cyst look like?
Outwardly, this disease has its manifestations. In particular, the cyst of the spermatic cord in a boy, an operation on which is inevitable, is manifested by swelling or rounded formations in the inguinal region. This education has the ability to vary in size. This indicates that there is a message with the abdominal cavity.
A cyst develops for a long time, so it is almost impossible to notice any functional malfunctions in the body. A neoplasm can be noticeable when palpating, but it is very rarely disturbing. If the boy already knows how to walk, discomfort may occur during movement, but this symptom is quite rare. In addition, pain may be observed.
It is usually possible to detect a neoplasm during a routine examination or after a cyst reaches a certain size (usually they are within 1-3 cm).
It is worth remembering that the cyst of the spermatic cord in a boy, the reasons for which were described above, regardless of its size, can exert pressure on neighboring elements, resulting in poor nutrition of the testicle. That is why in any case, an operation is required, which is performed at the age of 1.5-2 years.
Diagnostic Features
Only an andrologist can diagnose a spermatic cord cyst in a boy based on the results of the study. The following procedures may be required:
- Ultrasound scrotum. This method is the most informative and accurate for research. Using it, a cyst of the spermatic cord is diagnosed. This research method allows you to determine the exact size of the neoplasm, as well as its location. On ultrasound, this pathology has the appearance of a homogeneous formation, which has a thin wall. In addition, even internal and external contours are clearly visible on the screen. However, ultrasound does not detect the presence of sperm in the fluid.
- Diaphanoscopy. This method involves the scintillation of the scrotum in the rays of light of a certain length. During this, the cyst (usually the size does not exceed 2.5 cm) can be seen as light yellow transparent contents. A cyst has the ability to completely transmit light, in contrast to tissue seals.
- Computed tomography and MRI are performed only when the doctor suspects the presence of a tumor process.
An important role in the diagnosis is the manual examination of a suspicious area. It is on the basis of the results of palpation that it is possible to establish the presence of pathology.
Cyst treatment methods
This pathology is not a deadly threat to the body. A feature is that the cyst of the spermatic cord is easily treatable. However, in the presence of serious pain, as well as with a fast growth rate of the cyst, the necessary measures should be taken as soon as possible, since slowness can lead to the development of serious complications, such as a hernia. Also, this neoplasm can press on neighboring tissues, because of which they are deformed, and their functionality is impaired.
If a boy is diagnosed with spermatic cord cyst, surgery (doctors' reviews only confirm this) is the only possible treatment method. For its implementation, local anesthesia is used. After the operation, the patient in the hospital spends another day, and already on the tenth day, almost all restrictions are removed.
Stages of Surgery
The operation itself is carried out in several stages:
- A minor incision.
- Detailed dissection of all tissues on the way to the cyst. The basic rule of this stage of the operation: the skin of the appendages should be injured as little as possible. If this rule is neglected, there may be difficulties with the reproductive function of the patient in the future.
- Removal of a cyst.
- Suturing of the tissues of the epididymis. If this stage is missed, some time after surgery, scars may appear that will adversely affect the process of sperm production and transportation.
To reduce the negative consequences after surgery, modern surgeons use special microsurgical instruments, as well as optical magnification. This allows you to make the smallest seam possible. The scar will be almost invisible, which means it will not interfere. After all surgical procedures have been performed, cold is applied to the sore spot to avoid the formation of a hematoma.
Cyst of the spermatic cord in a boy: operation, specific consequences
After surgery, there may be both specific and non-specific complications. The first group includes:
- hemorrhages in the place in which the operation was directly performed;
- suppuration of the wound;
- discrepancy of seams.
As a rule, these consequences can be avoided if the operation was carried out according to all the rules.
Nonspecific effects
As for non-specific complications, a pronounced cicatricial process refers to them, as a result of which the outflow of seminal fluid is disturbed (this complication can lead to the development of infertility). In order to avoid such a violation, surgical intervention is recommended to be carried out only on indications, which are:
- severe symptoms of pathology, for example severe pain or a constant feeling of heaviness in the groin area;
- an increase in the size of the cyst;
- too large neoplasms, resulting in deformation of surrounding tissues.
With small sizes, cysts choose the so-called expectant tactics.
Given the numerous reviews of mothers whose children were operated on, we can conclude that any consequences after surgery are extremely rare and largely depend on the individual characteristics of the body. However, experienced specialists take this into account before the operation, during a full examination. Also, patients say that the use of local anesthesia significantly accelerates the rehabilitation period, and in a day you can return to your previous lifestyle. And this is an important argument, given the speed of modern life.
Is conservative treatment possible?
Many people have a question: "If a cyst of the spermatic cord is diagnosed in a boy, can the Helev preparations help to avoid surgery or not?" The answer is unequivocal: no, they cannot. Neither tablets nor ointments are able to rid a congenital or acquired cyst of the spermatic cord, since this is an anatomical formation that cannot resolve on its own. That is why only the surgical method is used to solve this problem.
Do not self-medicate, as in some cases, procrastination can be dangerous. A timely diagnosis of a funicular can minimize complications. That is why it is recommended that the parents of the boy conduct a regular examination of the inguinal area of the child.