Probably there is no worse disease today than cancer. This ailment does not look at either age or status. He mercilessly mows everyone. Modern methods of treating tumors are quite effective if the disease was detected in the early stages. However, cancer treatment has a negative side. For example, radiation therapy, the side effects of which sometimes pose high health risks.
Benign and malignant tumors
A tumor is a pathological formation in tissues and organs that grows rapidly, causing fatal harm to organs and tissues. All neoplasms can be divided into benign and malignant.
Benign tumor cells are not much different from healthy cells. They grow slowly and do not spread beyond their focus. Treating them is much simpler and easier. For the body, they are not fatal.
The cells of malignant neoplasms in their structure are unlike normal healthy cells. Cancer grows rapidly, affecting other organs and tissues (metastasizes).
Benign tumors do not cause special discomfort to the patient. Malignant ones are accompanied by pain and general exhaustion of the body. The patient loses weight, appetite, interest in life.
Cancer develops in stages. The first and second stages have the most favorable prognosis. The third and fourth stages are the germination of the tumor in other organs and tissues, that is, the formation of metastases. Treatment at this stage is aimed at anesthetizing and prolonging the life of the patient.
No one is safe from a disease like cancer. At risk are people:
With a genetic predisposition.
Immunocompromised.
Leading the wrong way of life.
Working on harmful working conditions.
Received any mechanical injuries.
In order to prevent, you need to be examined by a therapist once a year and take tests. For those at risk, it is advisable to donate blood to tumor markers. This test helps you recognize cancer in the early stages.
How is cancer treated?
There are several ways to treat malignant tumors:
Surgery. The main method. It is used in cases when cancer formation is still not large enough, and also when there are no metastases (early stages of the disease). Radiation or chemotherapy may be preliminarily performed.
Radiation therapy of tumors. Irradiation of cancer cells using a special device. This method is used as an independent, as well as in combination with other methods.
Chemotherapy. Cancer treatment with chemicals. Used in combination with radiation therapy or with surgery to reduce the formation in size. It is also used to prevent metastasis.
Hormone therapy. Used to treat cancer of the ovaries, prostate, breast and thyroid gland.
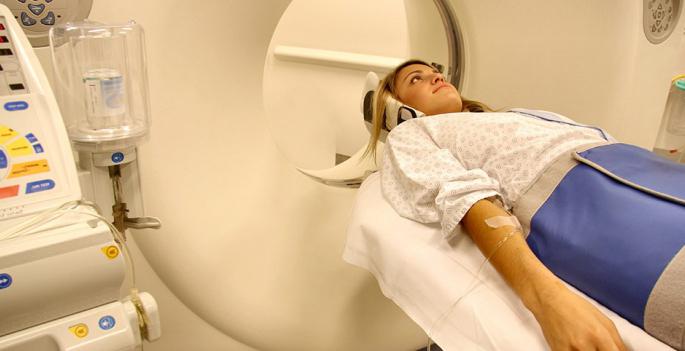
The most effective today is the surgical treatment of tumors. The operation has the fewest side effects and gives the patient a better chance of a healthy life. However, the application of the method is not always possible. In such cases, other methods of treatment are used. The most common of which is radiation therapy. Side effects after it, although they cause a lot of health problems, but the patient's chances of recovery are high.
Radiation therapy
It is also called radiotherapy. The method is based on the use of ionizing radiation, which absorbs a tumor and self-destructs. Unfortunately, not all cancer formations are sensitive to radiation. Therefore, the method of therapy should be chosen after a thorough examination and assessment of all risks for the patient.
Treatment with radiation therapy, although effective, has a number of side effects. The main one is the destruction of healthy tissues and cells. Radiation affects not only the tumor, but also neighboring organs. A method of radiation therapy is prescribed in cases where the benefit to the patient is high.
For radiation use radium, cobalt, iridium, cesium. Doses of radiation are compiled individually and depend on the characteristics of the tumor.
How is radiation therapy carried out?
Radiotherapy can be carried out in several ways:
Irradiation in the distance.
Contact exposure.
Intracavitary irradiation (a radioactive source is injected into the organ with a neoplasm).
Interstitial irradiation (a radioactive source is injected into the tumor itself).
Used radiation therapy:
after surgery (to remove cancer residues);
before surgery (to reduce the tumor in size);
during the development of metastases;
with relapses of the disease.
Thus, the method has three goals:
Radical - complete removal of the tumor.
Palliative - reduction of neoplasm in size.
Symptomatic - elimination of pain symptoms.
Radiation therapy helps to cure many malignant tumors. With its help, you can ease the suffering of the patient. And also extend his life when healing is impossible. For example, radiation therapy of the brain provides the patient with legal capacity, relieves pain and other unpleasant symptoms.
Who is contraindicated in radiation?
As a cancer control method, radiation therapy is not for everyone. It is prescribed only in cases where the benefit to the patient is higher than the risk of complications. Radiotherapy is generally contraindicated for a separate group of people. These include patients in whom:
Severe anemia, cachexia (a sharp decline in strength and exhaustion).
There are diseases of the heart, blood vessels.
Radiation therapy of the lungs with cancer pleurisy is contraindicated.
There is renal failure, diabetes mellitus.
There are bleeding associated with the tumor.
There are multiple metastases with deep germination in organs and tissues.
The blood contains a low number of leukocytes and platelets.
Intolerance to radiation (radiation sickness).
For such patients, the course of radiation therapy is replaced by other methods - chemotherapy, surgery (if possible).
It should be noted that those who are shown radiation may subsequently suffer from its side effects. Since ionizing rays damage not only the structure of
cancer cells, but also healthy cells.
Side effects of radiation therapy
Radiation therapy is the strongest exposure of the body to radioactive substances. Besides the fact that this method is very effective in the fight against cancer, it has a whole bunch of side effects.
Radiation therapy patient reviews are very different. In some, side effects appear after just a few treatments, while in others they have almost none. One way or another, any unpleasant phenomena will disappear after the end of the course of radiotherapy.
The most common consequences of the method:
Weakness, headache, dizziness, chills, fever.
Disrupted digestive system - nausea, diarrhea, constipation, vomiting.
A change in blood composition, a decrease in platelets and white blood cells.
Increased heart rate.
Edema, dry skin, rashes in places of application of radiation.
Hair loss, hearing loss, vision.
Small blood loss, provoked by fragility of blood vessels.
This is with regard to the main negative points. After radiation therapy (complete completion of the course), the work of all organs and systems is restored.
Nutrition and body renewal after irradiation
During the treatment of tumors, no matter what way, you need to eat properly and balanced. So you can avoid many unpleasant symptoms of the disease (nausea and vomiting), especially if a course of radiation therapy or chemistry is prescribed.
So:
Food should be taken often in small portions.
Food should be varied, rich and fortified.
For a while, you should refuse food that contains preservatives, as well as salted, smoked and fatty foods.
It is necessary to limit the use of dairy products due to possible lactose intolerance.
Carbonated and alcoholic drinks are prohibited.
Preference should be given to fresh vegetables and fruits.
In addition to proper nutrition, the patient should adhere to such rules:
Have more rest, especially after the irradiation procedures themselves.
Do not take a hot bath, do not use hard sponges, toothbrushes, decorative cosmetics.
Spend more time outdoors.
Lead a healthy lifestyle.
Radiation therapy patient reviews are very different. However, without it, successful cancer treatment is not possible. By following simple rules, you can avoid many unpleasant consequences.
What diseases are prescribed RT?
Radiotherapy is widely used in medicine to treat cancer and some other diseases. The dose of radiation depends on the severity of the disease and can be divided into a week or more. One session lasts from 1 to 5 minutes. Radiation is used in the fight against tumors that do not contain fluid or cysts (skin cancer, cancer of the cervix, prostate and breast, brain cancer, lungs, as well as leukemia and lymphomas).
Most often, radiation therapy is prescribed after surgery or before it in order to reduce the tumor in size, as well as kill the remains of cancer cells. In addition to malignant tumors, radioactive diseases also treat diseases of the nervous system, bones, and some others. Doses in such cases differ from oncological doses.
Repeat radiation therapy
Irradiation of cancer cells is accompanied by simultaneous irradiation of healthy cells. Side effects after RT are not a pleasant phenomenon. Of course, after canceling the course, the body recovers some time later. However, having received a single dose of radiation, healthy tissues are not able to tolerate repeated irradiation. In the case of relapse of the tumor, the use of radiotherapy for the second time is possible in emergency cases and at lower doses. The procedure is prescribed when the benefit to the patient exceeds the risks and complications for his health.
If repeated exposure is contraindicated, the oncologist may prescribe hormone therapy or chemistry.
Radiation therapy in advanced cancer
The method of radiotherapy is used not only to treat cancer, but also to prolong the patient's life in the last stages of cancer, as well as to alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
When a tumor spreads to other tissues and organs (metastasizes), there is no chance of recovery. The only thing left is to reconcile and wait for that “doomsday”. In this case, radiotherapy:
Reduces, and sometimes completely relieves pain attacks.
Reduces pressure on the nervous system, on bones, supports legal capacity.
Reduces blood loss, if any.
Irradiation with metastases is prescribed only at the places of their spread. It should be remembered that radiation therapy side effects are very different. Therefore, if the patient has a sharp depletion of the body and he can not withstand doses of radiation, this method is not practiced.
Conclusion
The worst disease is cancer. All the insidiousness of the disease lies in the fact that it can not manifest itself in any way for many years and in just a couple of months can lead a person to death. Therefore, for the purpose of prevention, it is important to periodically be examined by a specialist. The detection of the disease in the early stages always ends with complete healing. One of the most effective cancer control methods is radiation therapy. Side effects, although unpleasant, however, completely disappear after the abolition of the course.