One of the varieties of pigment metabolism disorders is the rare syndrome of “piebaldism”. It is characterized by nesting bleaching of hair on the head. This is not a harmless cosmetic defect, but a symptom of a large number of serious diseases.
This article will take a closer look at “piebaldism”. Causes, symptoms, diagnosis, treatment will also be described.
Causes of hair bleaching
Disorder of pigment metabolism occurs in the form of depigmentation - loss of pigment, hyperpigmentation - increased staining.
In the color of the hair, 2 pigments are important - eumelinin, pheomelanin. They are located in the cortex of the hair. Eumelanin gives the hair a black-brown color, pheomelanin - yellow-red. The combination of these pigments in an individual amount and interaction with air gives the hair a certain color. Hair color is genetically programmed.
How often is the syndrome of "piebaldism", what is this disease?
In case of violation of the work of melanocytes synthesizing hair pigments, gray hair develops with age. If this condition begins at a young age - this indicates a genetic pathology, or serious diseases.
Diseases in which pigment metabolism suffers
Why does the syndrome of “piebaldism” arise, what kind of deviation is it?
In case of violation of the work of melanocytes, the following conditions develop:
- piebaldism in isolated form;
- albinism;
- piebaldism in combination with damage to the eyes, hearing organs, skin, nervous system, musculoskeletal system.
Clinical picture
How exactly does the “piebaldism” syndrome manifest itself, what does this mean?
Loss of pigment in the hair in the form of the appearance of a white curl on the head can occur from birth and into adulthood.
The earlier there is a violation of pigment metabolism, the more serious its cause, the worse the consequences.
Isolated discoloration of the curl is combined with a discoloration area on the forehead. It is accompanied by the appearance of foci of hyperpigmentation, i.e., nesting darkening of the skin on the front surface of the abdomen, hips, legs, chest, arms, sizes from 1 mm to 6 cm.
Diseases Behind Piebaldism
There is a large group of diseases and developmental abnormalities that combine, along with hair bleaching, serious damage to organs and systems. Timely revealed pathology will save the life of the child and save parents from many problems.
Waardenburg-Klein Syndrome
The disease has an autosomal dominant type of inheritance, i.e., it occurs equally often in boys and girls. A genetic defect can be inherited from any of the parents.
Along with the bleaching of hair strands, general and ocular manifestations of the disease are observed.
Eye symptoms of this disease:
- underdevelopment of eyelashes;
- gray hair on the inner areas of the eyebrows;
- narrow palpebral fissure;
- eyes of different colors;
- farsightedness;
- eyes wide apart.
General manifestations can be of varying degrees of severity:
- partial albinism;
- wide back of the nose;
- short stature;
- tooth abnormalities;
- deaf-mute or isolated hearing loss;
- anomalies in the development of internal organs;
- resizing the skull.
Given that at first the severity of the disease is minimal and is manifested only by piebaldism, it is necessary to undergo an examination to exclude serious pathology. This is what piebaldism is.
Wolfe Syndrome
Isolated heterochromia, i.e., different eye color is found mainly in animals. In humans, the frequency among the entire population is 1%.
Famous people with different eye colors: Mila Kunis ("Oz: The Great and the Terrible", "Blood Ties", "Rise of Jupiter"), the English actress Jane Seymour, famous for the film "Live and Let Die", David Bowie - British rock singer, songwriter, producer, sound engineer, artist, actor.
Isolated heterochrony is a disease, and in combination with piebaldism is called Wolfe's syndrome and leads to rapidly developing deafness.
It is necessary to differentiate this ailment with retinitis pigmentosa - dystrophy of the pigment epithelium of the eye. There is a variant of the course of this disease - retinitis pigmentosa without pigment.
Mom and Daughter with Piebaldism Syndrome
The disease has recessive inheritance linked to the female chromosome. A woman passes this gene to her son, and he develops a disease. The daughters of these men are healthy if their mother is healthy. The only manifestation will be piebaldism.
If the mother is clinically healthy, but is the carrier of this gene, then the daughter will be sick.
To diagnose this disease, ophthalmoscopy is used, which reveals pigmented spots on the fundus, similar to moth eaten.
Hypomelanosis Ito
The disease develops from birth. Children of both sexes suffer equally often. His hereditary transmission from parents to offspring has not been proven, but the disease is always combined with congenital defects in the development of internal organs.
The diagnosis is made clinically based on the following symptoms:
- pigmented areas of a bizarre shape appear in the form of curls, snowflakes on the skin;
- on the palmar, plantar surfaces and mucous membranes of such changes do not happen;
- in the temporal region, the area of bleached hair is piebaldism;
- depigmentation sites become less noticeable with age;
- damage to the nervous system is always present, manifested by mental retardation, convulsive syndrome, decreased muscle tone;
- eye pathology is manifested by strabismus of varying severity;
- accompanied by scoliosis, deformation of the chest, limbs in 25% of cases;
- with a frequency of 10% combined with heart defects.
This disease must be differentiated from a condition called pigment incontinence. They have similar clinical symptoms, but the latter is inherited.
Pigment incontinence
Is the rare piebaldism syndrome transmitted?
The disease is transmitted from mother to daughter. Depending on the severity of the clinical picture, the following symptoms are manifested:
- Rashes on the skin in the form of long stripes, which after drying and removing crusts leave areas of pigmentation. Rashes have a wave-like course with the periodic appearance of new skin elements. As a child grows up, these areas lose their pigment and become pale.
- Violation of the growth and configuration of teeth, nails, hair in the form of nesting depigmentation and baldness.
- Neurological disorders are manifested by delayed psycho-speech development, increased intracranial pressure, cramps, weakness in the arms and legs.
- Eye disorders are intermittent and are manifested by strabismus, nystagmus, cataracts, decreased vision, blindness.
Griscelli syndrome
This is a group of diseases that can occur in three types, the main similarity of which is the presence of bleached areas of hair on the head. The following manifestations are available:
- Neurological disorders with hypopigmentation.
- The most dangerous type of disease in which the syndrome of "piebaldism" is combined with impaired hematopoiesis. Clinical manifestations: moderately elevated body temperature, not amenable to explanation and treatment. The severity of the fever gradually increases, an increase in the liver, spleen, a decrease in red blood cells, white blood cells, platelets, fibrinogen in the blood joins. The latter is involved in the process of the nervous system.
- Hypopigmentation of the skin and hair of varying severity, which for the time being proceeds without damage to blood cells and the nervous system. For the timely diagnosis of this dangerous pathology, a consultation with a hematologist, a dermatologist, and genetics is necessary. Be sure to take into account the presence in the family of various disorders of pigment metabolism, an analysis is carried out to exclude gene mutations.
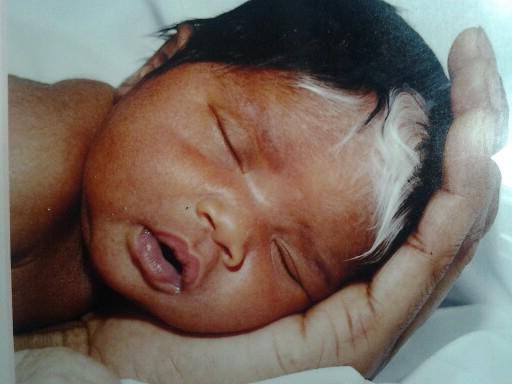
The relevance and danger of this disease is explained by the high frequency of its combination with Down syndrome, Edwards, Shereshevsky-Turner.
Skin and hair depigmentation can be detected at birth, but the presence of Shereshevsky-Turner syndrome can be established only as a person grows up, when short stature, lymphostasis, heart defects, increased blood pressure, underdevelopment of the mammary glands, low location of the nipples, replacement of the internal genital organs of the connective cloth. Intelligence in these patients practically does not suffer, the mood background is almost always increased, there is some positive euphoria, which explains the good social adaptation of these patients.
Conclusion
In humans, the gene for normal skin pigmentation is always dominant in relation to the gene responsible for impaired pigment metabolism.
The main significance of pigmentation problems is that they are markers of dangerous chromosomal diseases, multiple congenital malformations.
For any disturbance in the exchange of pigment of the skin, mucous membranes, hair, specialist consultation is necessary. We examined the syndrome of "piebaldism." What is it, it became clear.