Skin carcinoma is a type of cancerous malignant tumor that develops from the cells of the epithelial tissue of various organs (mucous membranes, skin and various internal organs).
Skin cancer is a malignant skin tumor formation that occurs as a result of the atypical transformation of its cells and is characterized by a strong polymorphism. There are four main types of such oncology, basal cell, squamous, melanoma and adenocarcinoma, each of which has its own clinical forms.
Skin tumor
In the total number of malignant tumors, skin carcinoma is approximately ten percent. Dermatologists are currently talking about a trend towards an increase in the incidence rate with an average annual growth rate of 4.4%. This cancer most often develops in older people, regardless of gender. Particularly predisposed to the onset of the disease are fair-skinned people, as well as people who live in conditions of strong insolation (highlands and hot countries) and for a long time are outdoors.
Among the total number of phenomena of such oncology, it accounts for 11 to 25% of its squamous form and from 60 to 75% of basal cell carcinoma. Since the development of basal cell and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin is carried out from epidermal cells, such diseases are also referred to as malignant epitheliomas.
Causes of occurrence
Among the reasons that cause malignant transformation of skin cells, in the first place is excessive ultraviolet radiation. This proves the fact that about 90% of cases of skin tumors occur in open areas of the body (neck, face), which are most often exposed to radiation. For people with fair skin, the effect of ultraviolet rays becomes the most dangerous.
The appearance of skin carcinoma can be caused by exposure to certain chemicals that have a carcinogenic effect: lubricants, tar, particles of tobacco smoke and arsenic. Thermal and radioactive factors that act on the skin can also lead to cancer. For example, skin cancer can become a complication of radiation dermatitis or develop in the burn area. Frequent trauma to moles or scars can lead to their malignant transformation with the appearance of skin cancer.
Genetics
The occurrence of skin carcinomas can predispose the genetic characteristics of the body, which causes family cases of the disease. In addition, a number of skin diseases have the ability to undergo a malignant transformation into skin cancer over time. Similar pathologies are precancerous conditions. Their list includes Bowen's disease, erythroplasia, leukoplakia, xeroderma pigmentosa , dermal horn, keratoma senile, melanoma-dangerous nevus (Ota nevus, giant nevus, blue nevus, complex pigmented nevus), Dubreuil melanosis, inflammatory skin lesions of a chronic nature (SLE, with tuberculosis, trophic ulcers, etc.).
Classification
The following forms of this type of cancer exist:
- Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, or squamous cell tumor, the development of which occurs from flat cells of the epidermal surface layer.
- Cutaneous adenocarcinoma is a rare tumor of a malignant nature that develops from sweat or sebaceous glands.
- Basal cell carcinoma of the skin, or basal cell carcinoma, appears during the atypical transformation of epidermal basal cells located under flat cells and having rounded outlines. The classic, most commonly encountered variety is the nodular (micronodular) form, which accounts for up to 75% of cases of the disease. It is characterized by the formation of primary tumor elements - dense nodules up to 2-5 millimeters in diameter, which, as a result of a long period of existence, are interconnected. Thus, they form a tumor focus up to two centimeters in diameter. Micronodular basal cell carcinoma of the skin may be pigmented or ulcerative.
- Melanoma is a tumor of the skin that arises from its melanocytes, that is, pigment cells. Given a number of signs of melanoma, modern authors often identify the term “skin cancer” with non-melanoma cancer.
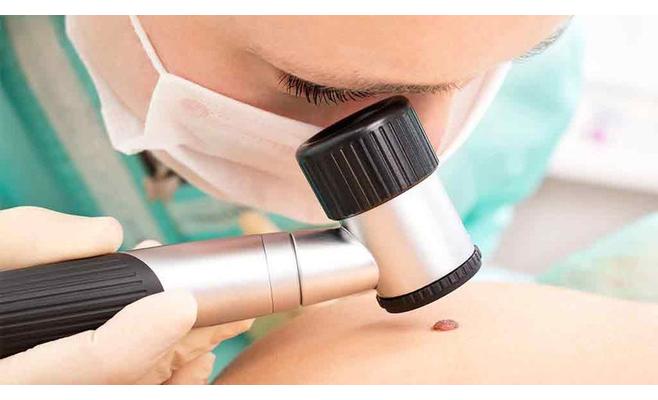
Symptoms of skin carcinoma
Squamous skin cancer is characterized by rapid spread and growth both in depth and on the surface of the epidermis. Germination of a tumor in tissues under the skin (cartilage, bone, muscle), or the attachment of an inflammatory process is accompanied by the occurrence of pain syndrome. Squamous cell carcinoma of the skin appears as a node, plaque or ulcer.
The ulcerative form of squamous skin cancer is externally a crater-shaped ulcer, which is surrounded, like a roller, with tight, raised and sharply breaking off edges. The ulcer has an uneven bottom, it is covered with crusts of dry bloody-serous exudate. It smells pretty unpleasant. Squamous cell carcinoma plaque has a bright red hue, a tuberous surface and a dense texture. Often it bleeds and increases rapidly.
With squamous cell carcinoma of the skin of the face, the coarse-knotted surface of the node makes its shape similar to a mushroom or cauliflower. Brown or bright red color, a high density of the tumor node are characteristic. Its surface may ulcerate or erosion.
Basal cell tumor
Basal cell tumor of the skin has a slower and more benign course compared with squamous. Only in advanced situations does it germinate in the tissues lying under it, becoming a cause of pain. As a rule, metastasis is absent. Basal cell carcinoma is characterized by a greater polymorphism, which can be represented by a turban, flat superficial, scleroderma, nodular, pigmented, scar-atrophic, perforating, warty and nodular-ulcerative forms. Most clinical types of basal cell carcinoma begin with the formation of a small single nodule on the skin. Neoplasms in some cases can be multiple.
Location
Carcinoma of the skin of the face mainly appears on areas that are covered with sebaceous and sweat glands. These include the inguinal region, axillae, folds under the mammary glands. Adenocarcinoma begins with the formation of a small papule or an isolated node. This rare type of skin cancer is characterized by slow growth. Only in some cases can large sizes be achieved (about eight centimeters in diameter) and germination in the fascia and muscles.
Pigmented or depigmented
In most cases, melanoma is a pigmented tumor that has a gray, brown or black color. But there are cases of depigmented melanoma. In the process of growth of a skin melanoma tumor, a vertical and horizontal phase are distinguished. Its clinical variants are represented by nodular, surface-spreading and lentigo-melanoma.
Diagnostics
People with a suspected carcinoma of the face and body skin should consult a dermatologist. A specialist examines the formation and other areas of the skin, conducts dermatoscopy and palpation of regional lymph nodes.
Establishment of the depth of the tumor, as well as the prevalence of the disease process is carried out by ultrasound. In addition, siascopy is prescribed for pigmented formations.
Only histological and cytological studies can finally refute or confirm the diagnosis of "skin tumor". A cytological study is performed using microscopy of specially stained fingerprints, smears made from erosion or surface of cancer ulcers.
Histological diagnosis
Histological diagnosis of a skin tumor is carried out on the material obtained after the elimination of the neoplasm or through a skin biopsy. If there is no violation of the integrity of the skin above the tumor node, the biopsy material is taken by the puncture method. If there is evidence, a lymph node biopsy is done. Thanks to histology, the presence of atypical cells, their origin (glandular, melanocytes, basal, flat) and the level of differentiation are determined.
In the process of diagnosing skin cancer, in some cases it is necessary to exclude its secondary origin, that is, the presence of a primary tumor in the internal organs. This is especially true for skin adenocarcinomas. For this, ultrasound of the peritoneal cavity organs, pulmonary radiography, CT of the kidneys, skeleton scintigraphy, contrast urography, CT and MRI of the brain of the head, etc. are performed. These examinations are required to diagnose situations of deep germination of a skin tumor or distant metastases.
How is cell carcinoma of the skin treated?
Treatment features
The treatment method is selected in accordance with the prevalence of the process, its type, level of differentiation of cancer cells. The patient's age and localization of the skin tumor are also taken into account.
The main goal in the treatment of skin carcinoma is radical removal. It is mainly performed surgically, by excision of tissues altered by pathology. Intervention is carried out with the capture of 1-2 cm of healthy-looking tissues. To carry out the operation, minimally capturing healthy tissue and maximally completely removing all cells of the skin cancer, makes it possible to perform intraoperative microscopic examination of the marginal zone of the area being eliminated. Excision of skin cancer can be carried out using a carbon dioxide or neodymium laser, which reduces bleeding during the intervention and gives an excellent cosmetic result.
Relatively small neoplasms (one to two centimeters) with an insignificant degree of tumor growth in the surrounding tissue, curettage, electrocoagulation, or laser removal can be used. If electrocoagulation is performed, it is advisable to capture healthy tissue by 5-10 millimeters. Superficial minimally invasive and highly differentiated forms of skin cancer may be subject to cryodestruction when healthy tissues are captured at 2-2.5 centimeters. Since cryodestruction does not allow histological examination of the removed material, it can only be done after a preliminary biopsy, when high differentiation and low prevalence of the tumor are confirmed.
Skin cancer that spans a small area can be cured effectively with close focus x-ray. To cure superficial and at the same time large neoplasms, they use irradiation with a beam of electricity. After the elimination of the tumor, radiation therapy is prescribed to people with an increased likelihood of metastasis and with relapse of skin cancer. It is also used to suppress metastases, as well as a palliative method for inoperable oncology.
The use of photodynamic treatment is allowed, the irradiation of which is carried out with the introduction of a photosensitizer. A positive effect in basal cell carcinoma allows local chemotherapy using cytostatics.
Forecast
With skin cancer, mortality is one of the lowest when compared with other oncological pathologies. This largely depends on the degree of differentiation of tumor cells and the type of cancer.
What is the prognosis for basal cell carcinoma of the skin? This form of oncology has a more benign course, there is no metastasis. If squamous cell carcinoma is treated on time, five-year survival is 95%. The most unfavorable prognosis in people with melanoma, this indicator is only 50%.