Children are a life incentive for parents. The appearance of the baby in the family is a new breath for the couple. From the first day of the baby’s life, parents constantly watch him, monitor his development. The ability to communicate with the outside world is the first thing that manifests itself in a child. Over time, these abilities expand, and now the baby moves from communicating with mom to communicating with peers. This is clearly manifested even in infancy, when the baby literally reaches for children who pass by in a stroller. But what if the child is afraid of everything? In particular, he prefers to be alone, does not like to communicate with adults or peers? Is this normal and is it a
sign of autism?Let go of fearAutism is a complex psycho-emotional state. Defining it is quite simple - the baby avoids touch, has difficulty with motor skills, does not have the ability to act independently. In other words, you should have noticed in the first place that the baby is afraid of people, and it all starts with the mother - the baby pushes and twists during the first feedings. However, if there are no accompanying behavioral elements — problems with speech, obsession with certain actions — then your fears are groundless.
Childhood fears
According to children's psychologists, each child has an
instinct for self-preservation, which is supported by the genetic experience and the experience gained (fire burns, falling - it hurts). As a rule, a child’s fears of something disappear within a few weeks - he gets used to the idea, learns to manage this fear. However, if the child is obsessed with a certain fear, then this is already a neurotic problem that can persist for life. If a child is afraid of children on the first walk, the first lesson in kindergarten - this is normal. If this becomes a problem for a long time, - you notice that the kid eschews peers at school, prefers to play alone in the garden or the sandbox - then this problem needs to be solved. The type of this fear - neurotic or instinctive - can be determined by the accompanying signs. So, when a
child is afraid of children and at the same time he begins to have problems with speech (stuttering), with sleep, or he begins to urinate in bed (enuresis) - this is a problem that needs to be addressed.
Fighting the problem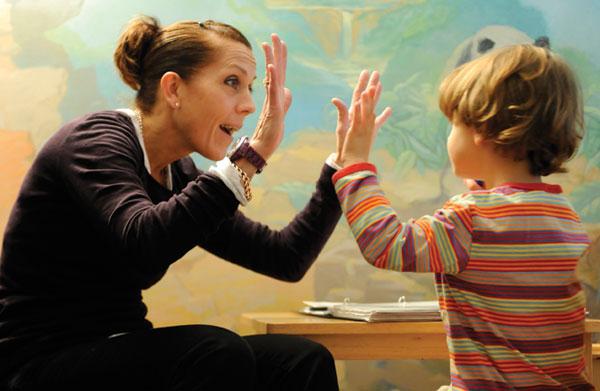
Four meanings for resolving a situation: affection, conversation, drawing, empathy. First of all, the parent for the baby has its own territory, its own man. Therefore, if you noticed that the child is afraid of children - sympathize with him. This can be shown in a conversation - it is necessary to question him in detail why he is afraid. The more often you do this, the faster the fear will dissipate. Do not forget that the baby expects sincerity from you - share your experience with him, tell us how you coped in such situations. You can focus on drawing - child psychologists have long identified drawing as a reflection of children's experiences. And, of course, all this must be accompanied by tactile sensations - stroking, kissing, speaking calmly and gently. On the street it is more often necessary to tell the child about other children, to talk about the benefits of communicating with them. After some time, you will notice that the child is less afraid of children, and in a month the fear will disappear altogether.