Lymphoma is a disease in which lymphatic tissue is affected . In this case, the affected lymphocytes begin to intensively divide and provoke disruptions in the normal functioning of the internal organs of the human body. Such groups of the disease are distinguished: lymphogranulomatosis (or the so-called Hodgkin’s disease) and non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas (including follicular non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma).
Lymphatic system. What it is
Part of the body’s immune system is the lymphatic system, whose main function is to protect against all kinds of infections and other diseases. It is a network of channels through which a special fluid moves - lymph. In the course of the capillaries, lymph nodes are observed in which the lymph is enriched with special cells - lymphocytes. There are several subspecies. B-lymphocytes are responsible for acquired immunity to infectious diseases. Contacting with a pathogenic microorganism, they eliminate its action and keep it in their memory. B-lymphocytes are very important agents in the formation of a positive effect from vaccination. Most (80%) of the lymph are T-lymphocytes. They are responsible for the destruction of all kinds of viruses, bacteria. NK lymphocytes are found in lymph in a small amount (up to 10%). Their main function is the destruction of their own affected cells (including with a disease such as follicular lymphoma).
How does a malignant process develop in the lymphatic system
The tumor process begins to develop from the cells of the lymphatic system (B-lymphocytes). The disease is diagnosed mainly in the elderly, in children it occurs in isolated cases. Follicular lymphoma got its name due to the fact that the hair follicle is primarily affected. Very often, neoplasms are observed in the neck, armpits, and groin. A feature of such lymphoma is that patients seek help very late. Affected lymphocytes penetrate into all internal organs, disrupting their work. Although iiia follicular lymphoma responds well enough to therapy, the late diagnosis is not possible to completely get rid of the disease.
Possible causes of the disease
Experts cannot name the exact reasons that contribute to the development of cancer. However, there are a number of factors that increase the likelihood of malignancy. One of them is mutations of genes, chromosomes. Working in adverse conditions, constant contact with harmful chemicals can also be a catalyst for the development of a condition such as follicular lymphoma. The causes of the disease can also be: exposure to radiation, immunodeficiency weakening of the body, autoimmune diseases. Some experts identify factors such as smoking, taking certain medications, and even obesity.
Symptoms of Lymphoma
Follicular lymphoma symptoms are rather mild, especially the initial stages. First of all, a slight increase in lymph nodes can be noted . However, they remain painless. It is characteristic that a slight swelling periodically disappears, then reappears. This fact should especially alert. The nodes also increase inside the sternum. Outwardly, this can manifest as a cough, shortness of breath. A slight swelling of the face is possible. In some cases, the spleen also suffers. Follicular lymphoma symptoms can also be quite general: weight loss, general fatigue, weakness of the body. However, these signs are the exception rather than the rule; they are observed only in one out of ten patients. More severe stages of the disease are characterized by damage to the nervous system, in particular the bone marrow. At the same time, dizziness, nausea are noted, and loss of consciousness is possible.
Classification and stages of the course of cancer
There are several types of lymphomas. The first is follicular. The follicle content in this case is 75%. If from there are in the range of 25-75%, then this is a follicular-diffuse subspecies. With diffuse type, less than 25% of follicles are noted. Follicular lymphoma (iiia) proceeds in several stages. At the initial stage, only one area of the lymph nodes is affected . The second stage is characterized by the involvement of two or more sites (but on one side of the diaphragm) in the pathological process. In the third degree, areas on both sides of the diaphragm are affected. The most difficult fourth stage. Changes occur in internal organs and systems (bone marrow, liver, etc.). Sometimes the letters A or B are added to the numerical designation of the stage of lymphoma. This indicates whether follicular lymphoma has the following signs: “B” - a change in body temperature (periodic increase), weight loss, sweating at night. Lymphoma with the prefix "A" - these symptoms are absent.
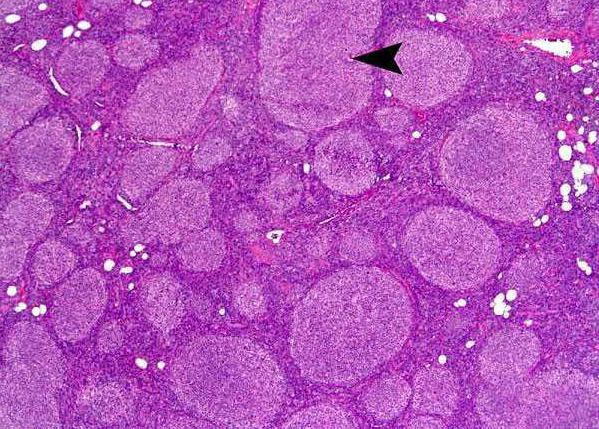
Method for the diagnosis of lymphoma
First of all, a specialist (onco-hematologist) conducts a visual examination of the patient. A histological examination of the sample is mandatory. For this, a biopsy is performed. A part of the affected lymph node is removed and examined under a microscope. It is worth noting three cytological types of the disease that require different treatment. The first type is characterized by the presence of up to five centroblasts in the field of view of the microscope, the second - up to 15 units. The second cytological type requires shock chemotherapy, as it is quite aggressive. Cytologic follicular lymphoma 3a has the most unfavorable prognoses. Extensive neoplasms can be seen in the field of view of the microscope. In addition, the patient needs to donate blood (tumor markers, general analysis), undergo an ultrasound examination of the internal organs, CT or MRI. In order to determine whether the central nervous system is affected, a spinal cord is taken for further examination for the presence of cancer cells.
Follicular lymphoma. Treatment
Recently, the number of patients with a similar diagnosis has increased significantly. As a rule, the earlier the neoplasms were noticed, the greater the patient's chances of preserving his health and life. Lymphoma is characterized by a fairly sluggish course, so in certain cases, doctors choose a wait-and-see position, observing all changes in the human body. This is due to the fact that both chemotherapy and surgery do not pass without a trace and have their negative sides. Remission of follicular lymphoma can last several years. If oncological disease begins to progress, then therapy should be carried out immediately. Among the main treatment methods, radiation, chemotherapy, and medications should be highlighted. Depending on the type of lymphoma, regional exposure can prevent possible relapses. At the first stage of the disease, prolonged remissions were recorded in most patients.
Chemotherapy
Aggressive chemotherapy (mainly using several drugs) in the early stages of lymphoma can significantly reduce the likelihood of relapse. For a long time, this method was considered the main in the treatment of cancer. Chemotherapy is aimed at the destruction of tumor cells during their reproduction. Combined drugs can affect the division process at different stages, so their use is more effective. However, chemotherapy has a destructive effect on other organs (skin, hair, etc.). The bone marrow also suffers from these drugs. During therapy, a person becomes more susceptible to infectious diseases, the appearance of multiple bruises, as well as bleeding. Often, drug treatment causes increased production of uric acid, which leads to the formation of kidney stones. However, all adverse events disappear a few weeks after the end of the course. It is worth noting that some chemotherapy drugs can lead to a decrease in the number of sperm in men, and provoke infertility in women.

Monoclonal antibody treatment
Follicular lymphoma is also treated with new drugs such as monoclonal antibodies. They purposefully destroy only lymphoma cells. This technique is especially effective in combination with chemotherapy. Monoclonal antibodies slightly reduce the toxicity of chemicals. Patients experience prolonged remission of follicular lymphoma. In some cases, an allergic reaction is possible, so the first injection of antibodies takes a rather long time. Before starting treatment, the patient needs a course of antiallergic drugs.
Relapses
This disease is characterized by slow progression in the early stages, the period of remission can last up to 20 years. Most often, recurrence of follicular lymphoma is observed with a 3a cytological type. In this case, stem cell transplantation may be necessary. A donor can be both a brother (sister) and a bloodless relative. The procedure is performed for patients not older than 70 years, who respond fairly well to chemotherapy and have a satisfactory state of health. After transplantation, improvement is observed in about half of the patients. Patient survival depends on many factors. First of all, the stage of the disease and the morphology of the changes are important (the prognosis of follicular lymphoma in the fourth stage is rather unfavorable). It should be noted that young people cope better with the disease. It is very important to recognize lymphoma on time, so you should not refuse preventive examinations from specialists.