Every year, the number of tumor diseases among the population is growing steadily. Every year, the world loses about eight million human lives.
For example, gastric carcinoid (a pathological formation, often of a benign nature, but capable of metastasis) is quite rare, but over the past five years, doctors have recorded more and more cases of the development of this disease.
Description
A carcinoid tumor is a formation of a neuroendocrine nature. It consists of mutated cells of the diffuse endocrine system.
A tumor forms on the mucous membrane of the stomach and begins the synthesis of biologically active substances (mediators of inflammation - prostaglandins, kinins, kallikrein). These compounds cause unpleasant symptoms. The more actively the tumor synthesizes them, the brighter the disease appears.
How aggressive is this tumor?
It is impossible to answer exactly this question, since carcinoid of the stomach can be either benign or a very high degree of malignant nature.
Types of Entities
Carcinoid foci may differ from each other in the level of tissue differentiation. The higher it is, the less malignant the process. There are several varieties:
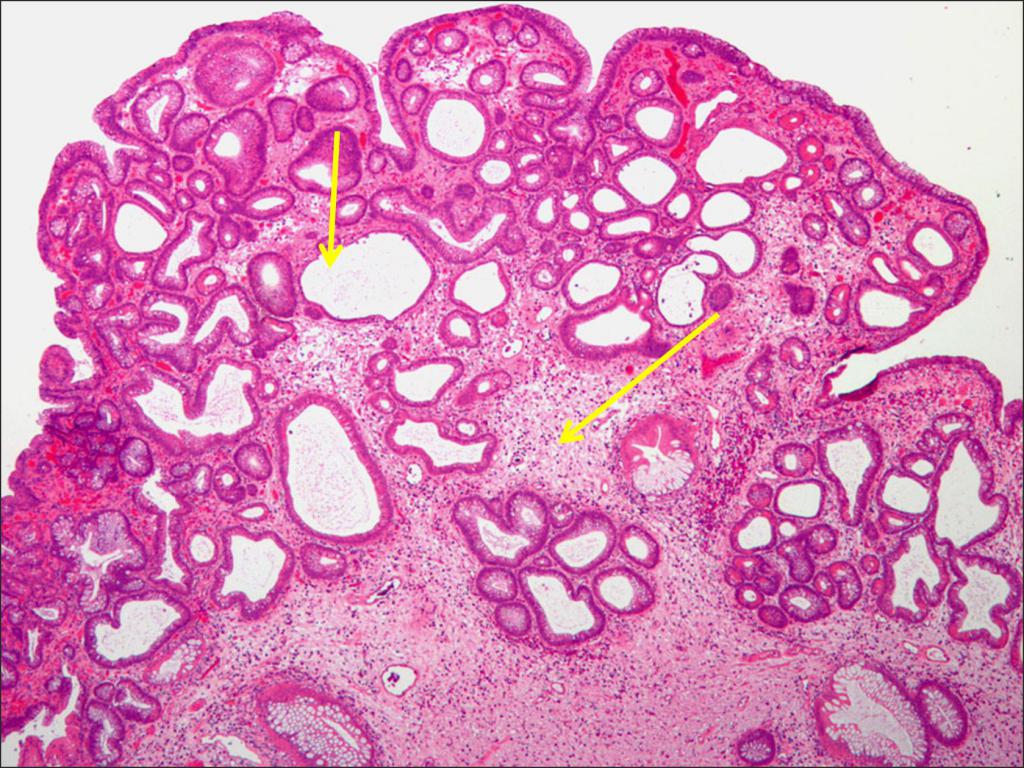
- The first type is characterized by a high level of cell differentiation. Education is a tumor in the stomach of a benign nature. It accounts for 70% of all carcinoid formations. Pathology develops due to a disease in which the synthesis of antibodies that destroy parietal cells occurs. Externally, a tumor is a group of several small tubercles on the gastric mucosa. In rare cases, they can grow inside the tissue. Sometimes penetration into neighboring organs (for example, the liver) is possible.
- The second type is characterized by a high level of differentiation and a low degree of malignancy. The second type accounts for about 8% of all gastric carcinoid tumors. It occurs as a result of endocrine neoplasia. Outwardly, it looks like an accumulation of small foci of inflammation protruding above the wall of the stomach. You can often notice that at the same time such formations occur in various glands (thyroid, adrenal glands, and so on).
- The third type is characterized by a low level of differentiation and a high degree of malignancy. The second name of this pathology is sporadic carcinoid of the stomach. The frequency of occurrence among all types of tumors is approximately 20%. At the same time, 80% of them are male patients. Externally, the tumor is a single formation about 3 cm in size. There are no signs of inflammation of the gastric mucosa.
Symptoms
Symptoms of this disease are easily confused with those of gastritis or gastric ulcer. Therefore, for a long time, the disease may go unnoticed.
The signs of the disease are as follows:
- Heartburn.
- Pain in the upper abdomen.
- Constant feeling that the stomach is full. This feeling does not go away even if a person is hungry.
- Nausea and vomiting may occur.
- Stool disorder: diarrhea alternates with constipation.
- As the disease progresses, there is a chance of developing obstruction of the stomach or intestines, as well as internal bleeding, which is characterized by blackening of feces and vomiting with blood.
- A distinctive feature of gastric carcinoid is myocardial damage.
- Dyspnea and redness of the skin are occasionally possible (against the background of the use of some gas-forming products).
- There is a risk of developing carcinoid syndrome - a disease that is characterized by excessive production of serotonin.
If at least one of the above symptoms is detected, you should immediately seek help from a specialist (general practitioner or gastroenterologist) who will listen to complaints, conduct a proper examination and prescribe the necessary examinations.
Diagnostics
The biggest problem in successfully treating the disease is its late diagnosis. The fact is that the pathology is quite rare, and its symptoms are mild. Therefore, approximately 1/4 of the diagnoses are made posthumously or by histological analysis of the tissue during surgery for another reason (for example, when appendicitis is removed).
All methods of diagnosing the disease can be divided into three large groups:
- Blood tests for elevated plasma levels of chromagranin A.
- Urinalysis for serotonin.
- Instrumental examination methods.
Blood test for chromagranin A
Chromagranin A is a polypeptide substance that is a non-specific oncological marker for malignant neoplasms in the gastrointestinal tract and organs of the endocrine system.
The biomaterial is blood from a vein, which is taken from a patient in the morning, on an empty stomach, in an amount of 5-10 ml. The duration of the analysis takes no more than four days.
Normally, the content of this protein should not exceed 10 nmol / liter. If these values are higher, then this allows you to suspect the development of a pathological process in the gastrointestinal tract or endocrine glands.
This method is relevant when making a diagnosis, evaluating the effectiveness of treatment, controlling the occurrence of relapses and the spread of metastases. However, based on a high test result alone, it is not possible to draw the final conclusion that the patient is ill with gastric carcinoid. This diagnostic method can only be used in combination with other options for making an accurate diagnosis.
This method is the simplest among all other diagnostic procedures. Therefore, many are interested in where to take tests for tumor markers? This can be done in any private laboratory.
Serotonin urine test
Serotonin is a hormone whose level in urine or blood directly reflects the state of the body as a whole, especially the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Its amount in urine indicates the number of monoamines that are synthesized by the cells of the gastric mucosa. For this reason, a high level of this substance in biological media allows the patient to suspect an oncological process in the stomach.
The material for analysis is daily urine. The normal value of the results is 3-15 mg / day. The duration of the analysis is from 1 to 5 days.
Hardware Survey Methods
- Gastroscopy. A method that allows you to determine any pathological lesions in the stomach. The first two types of carcinoid look like many small formations of a yellowish color, and type 3 tumors resemble single large polyps.
- Endoscopic ultrasound. This diagnostic method allows you to determine the depth of tumor penetration into the tissues of the stomach, and also to determine whether regional and distant lymph nodes are affected.
- CT scan (computed tomography). This is a special type of radiographic examination, giving a clearer picture of pathological education. The doctor receives information about the size of the tumor and its borders. Before the procedure, the patient should drink 200-400 ml of contrast medium. Sometimes it is administered intravenously. This will help to outline the stomach so that some parts of the internal organs are not mistaken for foreign formations. The duration of the examination is no more than half an hour. Please note that some people may develop an allergic reaction to a contrast medium. This usually manifests itself in the form of a rash and itching on the skin; in more severe cases, difficulty in the breathing process is possible. Another side effect is a sensation of heat on the skin, especially in the face. This usually disappears within 1-2 days after the CT scan.
- MRI At the moment, magnetic resonance imaging is the most effective method for the diagnosis of many tumor diseases, as it provides the most detailed information about the pathological formation. Thanks to MRI, the doctor receives information not only about the size and boundaries of the tumor, but also about its structural nature. In some cases, it may be necessary to inject contrast intravenously, but often the procedure is performed without it. In duration, it can take about 1 hour, and all this time the patient is forced to lie in a narrow pipe, under the knock of the device. For some people this is morally difficult. Especially for those who are afraid of a confined space.
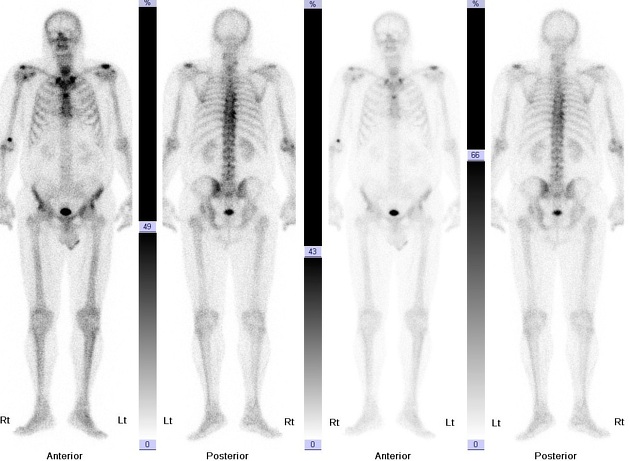
- To detect the possible spread of metastases, CT, MRI and bone scintigraphy are possible. Skeleton bone scintigraphy is a diagnostic method in which multiple bone scans and images are transmitted to a computer monitor. Previously, the patient receives an intravenous dose of a radioactive pharmaceutical drug that will stain bone tissue in the resulting images.
Treatment method: surgical method
The treatment technique directly depends on the type of tumor itself, as well as on the neglect of the process. Therefore, before starting the treatment of the disease, doctors should study the education in detail and make an accurate diagnosis.
In any case, surgery to remove the affected area (hemicolectomy) is the only treatment for carcinoid tumors. Only when removing part of the stomach will the patient be able to have the highest possible chance of recovery.
Carcinoid treatment
In type 1, treatment tactics depend on the stage of the process:
- If there are only a few small single tumors, then laparoscopy is indicated, in which the tumor and a small area of the mucous membrane are excised.
- If 3-6 polyps are found, then endoscopic removal of neoplasms is prescribed.
- If there are more than six, then, as a rule, a resection of the stomach is performed. Feedback from oncologists and patients suggests that this is the only sure way out of this situation.
It happens that the disease is diagnosed too late, and it is impossible to completely remove pathological tumors. Then the maximum possible excision of the affected areas and chemotherapy are indicated. About her in more detail below.
Treatment of carcinoid tumors of the stomach of the 2nd and 3rd types is usually carried out only by surgery. Such formations are almost completely resistant to chemotherapy.
Gastric carcinoid: chemotherapy
In addition, it should be noted that in the treatment of this type 1 pathology, the use of chemotherapeutic drugs is possible. Such as:
- Irinotecan;
- "Oxaliplatin";
- "Cisplatin";
- Leucovorin.
- "5-fluorouracil."
All of these funds have, due to their mechanism of action, a powerful antitumor effect. The instructions for use of "Cisplatin", for example, indicate that it is introduced into the DNA of a cancer cell, disrupting the division process. As a result of this, the tumor ceases to spread and dies.
"5-fluorouracil" is converted in the tissues of the body into an active metabolite, which replaces the enzyme necessary for the proper division of cancer cells.
This method of treatment cannot be the main one, but should be used as an adjunct in the treatment of gastric carcinoid. To increase the chances of recovery, oncologists usually prescribe a complex of two or more drugs.
According to the instructions for use of "Cisplatin", this drug is most effectively combined with "Leucovorin." Other combinations are allowed. So, it has an extremely effective effect in combination with Fluorouracil.
Symptomatic treatment
In addition, additional drugs are often used to stop the unpleasant signs of the disease. These include:
- Antacids, such as Almagel, Rennie, Gaviscon. They are used to eliminate heartburn.
- Antiemetics (Metoclopramide, Onandesterone-Teva) - relieve nausea.
- Means against spasms of the gastrointestinal tract (Duspatalin, No-shpa, Ganaton).
All of these drugs only alleviate the patient’s condition, but do not eliminate the cause of the disease.
Forecast
Stomach carcinoid is a dangerous disease. However, the survival rate in such patients is much higher than in other tumor diseases.
The prognosis of treatment success depends on the stage of the pathological process, and, most importantly, on the type of disease.
- With the first type of tumor, the prognosis is most favorable. The survival rate is 95%. This gives great hope for patients suffering from this type of carcinoid of the stomach.
- With the second type of tumor, the percentage of survival over the past five years drops to 80%. However, such indicators indicate a very positive outcome.
- The third type of tumor is the most aggressive, so patients suffering from this pathology have the lowest rates of life. The vast majority (60%) die in the first five years.
Conclusion
A carcinoid tumor of the stomach is a serious disease of the gastrointestinal tract. Some of its types are quite easy to treat. However, in the absence of timely treatment, it can lead to the development of carcinoid syndrome or death. To avoid this, it is extremely important to diagnose the disease in time and remove the pathological formations. Therefore, each person must regularly undergo mandatory medical examinations, medical examinations and, at the first unpleasant symptoms, seek help from specialists.