Technogenic hazards are risks associated with the technosphere. They are found most often in modern life. Such dangers are associated with pollution of the world. Energy flows, waste, harmful emissions - all these are elements of the technosphere that create risks for society.
general information
For man, technological hazards are most often circumstances, conditions of his work, where there are saturated streams of energy or some kind of matter. Such risks are inherent in areas where communications, transport resources, economic, industrial facilities are actively used. The level of risk depends on the duration of the influence of an aggressive factor, the nature of its action on a person. Sound vibrations are harmful, various compounds are dangerous, dangers are associated with vibration and electromagnetic radiation, radiation and others. Perhaps a combined effect on the person - at the same time several factors may be present in one place.
Zones of influence are areas of the technosphere and nature nearby. Risks are inherent in economic, industrial facilities, premises inside them, and territories nearby. Dangers are inherent in residential, urban areas and places used for transport. In some cases, the risks extend to the whole region. Examples of global hazards are known.
Causes and effects
Man-made hazards are phenomena caused by the operation of technological objects. The reasons for the emergence of risks are explained by human activity - primarily the people responsible for the maintenance of a particular site. The impact on a person at his workplace is analyzed taking into account the nature of the impact and such a phenomenon itself. Special regulations have been introduced that limit the maximum degree of impact. From the documentation follows the division of all risks into psychological and physiological, into biological, chemical, physical, mechanical.
Mechanics and physics
Mechanical technological hazards are caused by malfunctioning factors of a certain system or the presence of a defect in it, as well as incorrect operation. Malfunction of equipment, careless observance of operating modes provoke the appearance of situations leading to injuries. Such factors are spontaneous, short-term, relevant for a limited area. They are formed if an accident occurs, something explodes, collapses if a disaster occurs.
Physical factors are a complex group of several subgroups. Risks create heating of surfaces, air parameters, level of ionization, saturation with dust and harmful gases. Physical factors include noise, vibration, ultra-, infrasound, electromagnetic radiation, electricity, field strength (magnetic, electric). Among the physical factors are the closure of the electrical circuit to a person, the level and brightness of light, brilliance, light pulsation, level of contrast. This category includes radiation: ultraviolet, infrared.
Chemistry and more
Technogenic hazards are created due to the influence of chemical aggressive factors on the human body. It is customary to distinguish several groups. There are common toxic substances, there are irritating and increasing sensitization, as well as provoking mutations, malignant processes. There are chemical factors that change the reproductive qualities of a person. Based on the characteristics of penetration into the human body, they introduced a classification system. According to it, all dangerous substances are divided into those that enter through the skin, with breathing and through the digestive tract.
Biological - these are objects whose influence provokes diseases and injuries. Among the dangerous belong various microscopic life forms. Biohazard is associated with bacteria, fungi, but also with various animals and plants.
Some technological hazards are caused by psychophysical factors. Such are physical overloads, lack of motor activity and overload of the neuropsychic type. The latter is observed if the employee is confronted with mental strain, works monotonously, and because of work, his emotional state is unstable.
Where is the most dangerous?
From statistical studies it is known that the risks in question are most characteristic of the oil, gas, coal industry, chemical facilities. They are not uncommon in metallurgy, geological exploration, and boiler surveillance. Hazards are associated with transport, hoisting vehicles. Especially dangerous are accidents, disasters occurring at chemical production sites, as well as affecting the field of nuclear energy.
What regulates?
So that the main technological hazards are met somewhat less often, in our country regulatory acts have been adopted that regulate aspects of work. To determine the comfort of the environment in which people work, it is necessary to analyze the conditions, taking into account the provisions of GOST, published under the number 12.1.005-88. It lists the general regulatory requirements for hygiene, sanitation of the air. To determine the standards of illumination, SanPin was adopted - it was published under the number 23-05-95. The microclimate in the workplace must meet certain optimal parameters. If satisfaction is observed, the zone is characterized as the highest comfort. If conditions are acceptable, the terrain is described as uncomfortable. In the first case, the functioning of the human body proceeds without any malfunctions, there is no tension of thermoregulatory mechanisms. Permissible climate conditions require a certain strain, while the person’s health does not suffer.
The normalized value of air heating, its saturation with moisture, as well as the level of air exchange rate - all this is determined based on the characteristics of the work. Some values are necessary for the normal functioning of one who works easily, another is necessary for a person who is forced to work medium or hard. To control climatic conditions, workplaces are equipped with thermo-, hygro-, acti-, psycho-, anemo-, katermometers. All these devices are responsible for the visualization and numerical display of some qualities of the environment. In order to avoid the influence of aggressive factors on the people involved in the work in the industrial zone, specialized industrial ventilation and heating systems are installed.
Local hazards
It is no secret that it is precisely technogenic risks - those that people face most often. There are constant locally active risks. These are usually explained by too strong currents - energy or some substance. Connections may be thrown, noise, vibration flows are possible. Such happen at a specific local area where equipment is operated, including communications, a variety of vehicles. The influence of such factors is continuous. A combination of several types of technological hazards is possible.
Very often there are risks associated with malicious connections. This includes any substances that provoke diseases when interacting with the human body and in the long term, including future generations. Hazard is characterized as the risk of adverse effects on health in a work environment or other situations where it is necessary to resort to a compound.
About substances in more detail
In relation to harmful substances, the classification of technogenic hazards is due to the belonging of such compounds to a particular group, as well as the nuances of practical application. Chemical agents are industrial poisons that are used in production. These are coloring components, fuel, solvents. There are chemical poisonous substances for agriculture, household chemicals, household poisonous compounds of animal, plant origin, present in mushrooms, in some insects and other wildlife. To this category belong toxic substances - mustard gas, sarin, and others. Poisonous properties are inherent in almost any substance, but the probability and strength of their manifestation are determined by volumes. Poisons classify compounds whose harmful effects on humans are observed in everyday conditions, in a small dosage.
Since harmful substances are a source of technogenic danger, they have introduced a system for dividing these compounds into four groups. The main classification parameter is the nature of the effect on the person. There are substances that provoke mutations, malignant processes, as well as teratogens, toxins. The former initiate hereditary damage. The second group activates genetic programs and leads to the formation of malignant tumor diseases. Teratogens disrupt genetic systems, which causes malformations. The last group is substances that negatively affect the human body, physiology, but do not correct genetic characteristics. Of the above, only toxins give an immediate effect, the effect of others is observed with a delay, and its duration is unpredictable and can reach several generations.
Everything has its own assessment
To assess how strongly the factors of technogenic danger affect a person, they introduced a toxicometry system. It is used to characterize the toxic effect of harmful compounds. The system offers the division of all compounds into exclusively poisonous, high, moderate, low toxicity. The effect is determined by the volume of the compound penetrated into the human body. Much depends on the physical properties, the duration of the penetration of the compound, chemism in biological media.
The influence of a number of toxic compounds is determined by gender, age, and individual qualities of a particular person. Much depends on penetration and methods of removing compounds, nuances of distribution, meteorological conditions. Perhaps the influence of other related phenomena. The toxic effects of the poison can provoke functional malfunctions, death. Among the factors determining the outcome of a case are the concentration of a substance and its dosage.
About poisoning
Since the risks associated with toxic compounds are related to technological hazards, in regulatory and scientific work, attention was paid to poisoning. This condition is acute, subacute, can occur in the form of a chronicle. Acute develops with a single, repeated time-limited exposure to a hazardous substance. Typically, the duration of exposure is not more than a few days. Subacute poisoning develops with interrupted, constant exposure to a hazardous substance. The duration of influence reaches three months. Chronic is observed due to prolonged, often counting years of contact with the poisonous compound.
An analysis of cases that make it possible to understand that often technogenic hazards arise as a result of an unpredictable release of a poisonous compound, demonstrates: acute poisoning is often group. It is explained by an accident, breakdown, non-observance of the rules of operation in a rough form, neglect of safety aspects of work. More often in such cases, hazardous compounds are briefly affected by human organisms, the temporary duration of contact does not exceed the shift. Poisoning is possible if the person mistakenly takes poison, when inhaled poisonous air, and skin contamination. From practice, in particular, cases of hydrogen sulfide poisoning are known. If gas pollutes the atmosphere, the concentration is high, intoxication occurs quite quickly. It can cause death due to paralysis of the center responsible for breathing. Nitric oxides are a no less dangerous poisonous substance. Examples are known from practice where such compounds provoked coma, convulsions, and a decrease in blood pressure.
More about poisoning
Such a nature of the occurrence of anthropogenic hazard can differ in the lasting effect on the human body. Chronic poisoning is a gradually forming condition due to the prolonged penetration of small doses of poison into the human body. It is possible poisoning due to the accumulation of a critical volume of a dangerous compound in the body. Cases of chronic poisoning affecting the respiratory system are frequent. This is possible due to acute poisoning, once or several times previously. In the form of chronicles, poisoning is possible if a person works with benzene, comes into contact with gasoline, is forced to interact with chlorinated hydrocarbons.
Risks are formed if the limit concentration exceeds normal. The documents set the maximum permissible contents of various hazardous compounds in the environment. Declaration of parameters due to the analysis of natural-technological hazards, cases of poisoning by various compounds. When calculating MPCs, they were guided by information about the local one-time effect of a hazardous compound on a person, prolonged exposure, including spreading to subsequent generations.
Ionizing radiation
Perhaps the public has heard the most about this origin of man-made danger. Radiation is not only technogenic, but also natural. To analyze the level of risks, you need to know the quality of radiation and the nuances of the effect on organics. Unstable atomic nuclei transform, emitting small particles - this process is called radiation. Radioactivity is alpha and beta decay, proton, as well as spontaneous nuclear fission. Ionizing radiation are particles that are emitted during a reaction. The energy transferred to the substance, on average, is spent on excitation, and the other half on ionization. To evaluate the radiation environment, it is necessary to measure the radiation. For this, special units are used - x-rays. One x-ray means that 2.082 * 108 ion pairs are generated in a cubic centimeter of air. In life, the situation is often measured in milli-microroentgens. To assess the impact on the person, analyze the amount of absorbed radiation. The unit of absorbed dose is Gray. Less commonly used are welcome. In one Gray - a hundred happy. The absorbed dose does not show radiation, but its effect.
Since ionizing radiation is a technogenic hazard, it traditionally attracts special attention of the public; mechanisms for its study have been identified. Man-caused radfon is generated and depends on pollution sources. Such appear due to the explosion, industrial activity, weapons cycles. Possible radiation hazardous accidents. Such happen not only in industry, but also in transport. Radiation technology is used by scientists, researchers, doctors. It also forms a background. To some extent, it depends on the presence of radioactive waste and how it is handled.
Is it dangerous or not?
Traditionally regarded as sources of man-made hazards of nuclear power plants with adequate, normal functioning, although they create certain risks, they are relatively insignificant. In particular, studies were conducted at the international level to evaluate technogenic exposure. It amounted to about one percent of the natural, and in some cases even less. This is typical for the absence of accidents at nuclear power plants.
Where else does danger come from?
Another source of technological hazards in the form of radiation is medical devices used for some specialized procedures. Technological control is sometimes also implemented through radioisotope techniques. Medical examinations are most often an X-ray examination of the patient’s body condition. During the event, the equivalent dose is greater than when using radioisotope methods.
In a residential building, the radiation level is determined by the materials used for the construction of the facility. Higher level in the house, built of cinder blocks, reinforced concrete, bricks, and in a wooden - lower. A gas stove is a source of combustion products and radon. The degree of radioactivity in the kitchen is higher if the stove is working. Radon affects a person primarily in a room that is not ventilated. This substance is released from the crust of our planet. On the upper floors of buildings, the concentration of the compound is lower than near the foundation.
How does it work?
, , . , , , – . . , - . , . 6 , . – 100%.
– . , - . – . 237 . 1-16 . 29 . – 90% . . .
:
Of course, I would like society to never know about the extraordinary technological dangers, but our life is such that every day there is a risk of some extremely risky situation. In our country, an emergency classification has been introduced, taking into account what caused the event. SPS is traffic wrecks, fire, accidents, emissions, collapses.
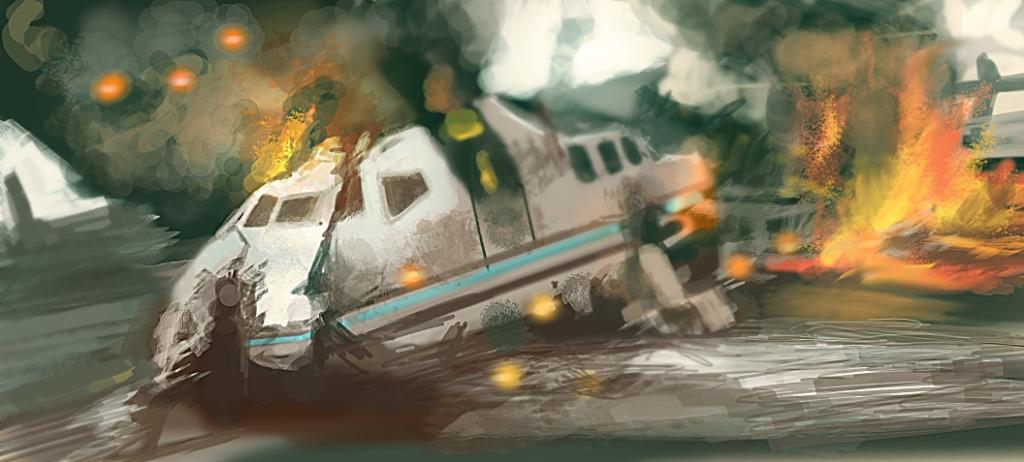
Transport happen on water, in the railway system, on pipelines. Fire, explosion are possible in buildings, vehicles, communications, technological facilities. In such a situation, an extreme technological hazard is associated with the possibility of contamination with radioactive, chemically aggressive, biological harmful compounds. Sudden collapse can affect production facilities, communication transport, household and residential. Emergencies are possible on electric power, purification, and municipal systems responsible for life support. Hydrodynamic emergencies are known. Such happen if a dam is broken, a breakthrough wave appears, the flooding is catastrophic. Breakthrough flood may occur.
Emergency: need attention
The characterization of the technological hazards caused by the emergency is made taking into account the factors that provoked the case, the peculiarities of its impact on the world, and man. Emergencies of a technogenic character are due to industry. Such an accident is often accompanied by pollution. The most dangerous are transport accidents, explosions, fire, radiation, chemical emissions.
Yesterday Today Tomorrow
The danger of SST in our country is increasing. This is due to an increase in the number of enterprises. Many industrial facilities have exhausted their resources by 70% or more. Cases of detection during the inspection of the pre-emergency level are frequent. Other unfavorable factors affect, including a low professional level due to the lack of specialized educational institutions. Production methods are often lagging behind, and safe technologies are being introduced too slowly. The risk at potentially hazardous facilities in our country is greater than what is considered normal at the international level.

In total, in our country there are at least 45 thousand potentially risky objects, of which more than three and a half thousand in the event of an accident will become sources of chemical emissions. More than eight thousand objects are dangerous in terms of the possibility of explosion, fire. There are industrial energy, research nuclear installations, as well as plants responsible for working with radioactive waste. All these objects are potential sources of technological danger. If a catastrophe occurs, an accident occurs, negative consequences are possible that will reach up to 10 million people. Chemical contamination in the event of an accident can cover territories with more than 60 million people.