Missiles as a type of weaponry have existed for a very long time. The pioneers in this matter were the Chinese, as mentioned in the hymn of the Middle Kingdom of the early 19th century. “Red glare of missiles” - this is how it is sung. They were charged with gunpowder, invented, as you know, in the same China. But in order for the “red glare” to sparkle, and fire arrows fall on the heads of enemies, rocket engines, even the simplest ones, were needed. Everyone knows that gunpowder explodes, and for the flight requires intense combustion with directed gas evolution. So the composition of the fuel had to be changed. While in conventional explosives the ratio of ingredients is 75% nitrates, 15% carbon and 10% sulfur, rocket engines contained 72% nitrates, 24% carbon and 4% sulfur.
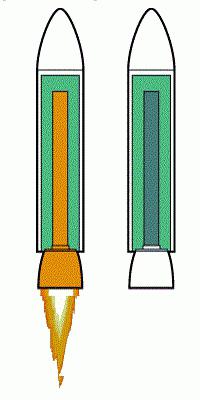
In modern solid-fuel rockets and accelerators, more complex mixtures are used as fuel, but the principle has remained the same, ancient Chinese. His merits are undeniable. This is simplicity, reliability, high speed of initiation, relative cheapness and ease of use. In order for the projectile to start, it is enough to ignite the solid combustible mixture, to ensure the flow of air - and that's it, it flew.
However, such a proven and reliable technology has its drawbacks. First, by initiating fuel combustion, it is already impossible to stop it, as well as changing the combustion mode. Secondly, oxygen is needed, but in rarefied or airless spaces it is not. Thirdly, combustion still occurs too quickly.
The solution sought by scientists in many countries for many years was finally found. Dr. Robert Goddard in 1926 tested the first liquid-propellant rocket engine. As fuel, he used gasoline mixed with liquid oxygen. In order for the system to work stably for at least two and a half seconds, Goddard had to solve a number of technical problems associated with pumping reagents, a cooling system, and steering mechanisms.

The principle by which all liquid-propellant rocket engines are built is extremely simple. Inside the body are two tanks. From one of them, through the mixing head, the oxidizing agent is fed into the decomposition chamber, where, in the presence of a catalyst, the fuel coming from the second tank goes into a gaseous state. A combustion reaction takes place , the hot gas passes first at the tapering subsonic zone of the nozzle, and then at the expanding supersonic zone, where fuel is also supplied. In reality, everything is much more complicated, the nozzle requires cooling, and the feed modes require a high degree of stability. Modern rocket engines can be powered by hydrogen as fuel, oxygen is an oxidizing agent. This mixture is extremely explosive, and the slightest violation of the operating mode of any system leads to an accident or disaster. Other substances that are no less dangerous can also be components of a fuel:
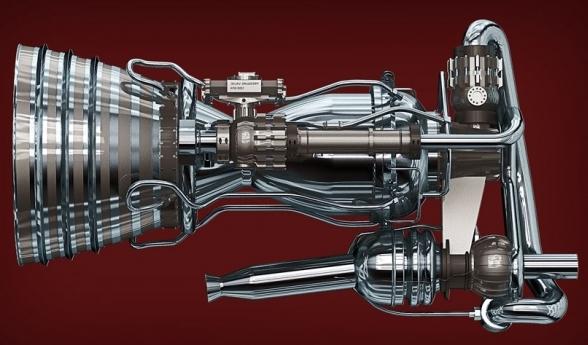
- kerosene and liquid oxygen - they were used at the first stage of the Saturn V carrier program in the Apollo program;
- alcohol and liquid oxygen - were involved in German V2 rockets and Soviet Vostok carriers;
- nitrogen tetraoxide - monomethyl - hydrazine - were used in Cassini engines.
Despite the complexity of the design, liquid rocket engines are the main means of delivery of space cargo. They are also used in intercontinental ballistic missiles. The modes of their work are amenable to precise regulation, modern technologies allow us to automate the processes taking place in their units and nodes.
However, solid propellant rocket engines also have not lost their significance. They are used in space technology as auxiliary. Great is their importance in the braking and rescue modules.