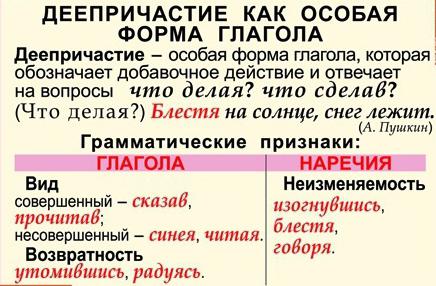
In the structure of the Russian language, along with independent and auxiliary parts of speech, there are so-called special forms of the verb, which many linguists argue about. Some of them say that according to morphological features of the sacrament and participle, they can be included in significant parts, while others say that the dependence of these forms on the verb itself is too great, and therefore there can be no talk of independence. One way or another, but in the school curriculum, participle is called a special unchanging form of the verb, which has the meaning of additional action and grammatical signs of the adverb and verb. To determine whether a particular word from the context is this very special form, you should know what questions the participle answers. In this case, this is “What are you doing?” or "What have you done?" It is worth noting that, in answering these questions, the word should complement the predicate, namely, indicate how the main action in the sentence is performed.
Verb Attributes
Since the participle is formed from the verb and is its special form, it also has morphological features inherent in this part of speech. Firstly, the view: it can be perfect and imperfect, depending on whether the completion of the action is indicated or not. For example: by looking (SV) and looking (NSV). Secondly, it is transitive: the participle, like the verb, in the transitive form can be used without an excuse together with the nominal parts of speech in the genitive case - when denied - and in the nominative and accusative case when approved. For example: building a relationship . And the intransitive participle, examples of which are often found in oral speech, is always used with pretexts. For example: in a hurry to help, rejoicing in the sun .
Signs of an adverb
In order to determine morphological features similar to the adverb, you need to remember what questions the participle answers. For example: I am standing at the window, peering into the distance (what am I doing? How?). It is clearly seen from the example that the word peering simultaneously means both an action and its sign, depends on the main verb and in the sentence acts as a circumstance. It does not have other morphological features characteristic of the independent part of speech, such as gender, face, time and number, as it is unchangeable.
Imperfect Communion
When studying this topic, special attention should be paid to what questions are answered by various kinds of participles. So, for example, imperfect germs have the meaning of simultaneously performing an additional action with the one indicated by the predicate and answering the question “What are you doing?”. For example: standing on a bench, he took a cup from the top shelf .
Such participles are formed on the basis of the verbs of the NSW in the present tense with the suffixes –– or –––. The exception is the word be , which is transformed into a special form through the suffix -uchi-. In other cases, “uchi-and-uchi” is used solely in order to get stylistically colored germs. Examples: being - being, playing - effortlessly .
It is worth noting that not all verbs of an imperfect form can become the basis for the participle. Lexical units with endings – –––– –– –– –– –––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––– ––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––––)) vocabulary; For example: bake, dry, write, drink.
Perfect Communion
It is important to know what questions the perfect participle answers and how it is formed, since it is these rules that will help to correctly form the desired form of the word. The question for the SV participles is: "What have you done?" Such words have the meaning of an action that occurred before the predicate indicated. For example: standing on a bench, he took a cup from the top shelf .
The given participle is generated from the stem of perfect verbs in the past tense by adding the following suffixes:
- -c-, if the stem of the verb ends with a vowel letter ( having done, having thrown off, having removed );
- -lice- if the verb is reflexive and its stem ends in a vowel ( looking, stroking, seeing );
- -shi- if the basis ends in a consonant ( having lost, hidden ).
Communion and participles: the difference
It is very important not to confuse the issues of communion and gerimony and learn to distinguish between these forms of verbs. In fact, there is nothing complicated here. In order to correctly determine in what form the word is used, it is necessary to remember which questions are in the participle (What have you done? What are you doing?), And which are with the sacrament (What is he doing? What has he done?). It should also be noted that these two forms have completely different morphological characters and significance. So, for example, participle means actions with pronounced signs of the adjective, while participle has the meaning of an additional action.
Morphological analysis of the participle
One of the main topics in the study of the Russian language section on participles is the morphological analysis of this form of the verb. Before proceeding with the analysis, the sentence should highlight the grammatical basis and find the participle. To do this, questions from the grammatical basis are posed. Nothing complicated so far. Knowing that the participle answers questions (examples are listed above) indicating the additional action of the subject or person referred to in the proposal, it is quite simple to determine. Then it is recorded and proceed to analysis.
Morphological analysis is carried out according to the following scheme:
- They write down the name of the part of speech, its grammatical meaning and indicate the question that can be posed to it from the main word.
- The initial form of the participle is recorded and its morphological characteristics are listed, namely: the form of the participle (perfect or imperfect) and its recurrence.
- It should further be indicated that the word being parsed is an unchanging form, and therefore does not have inconsistent morphological characters.
- In conclusion, they indicate which member of the sentence is the participle in this case.