Any material body has such a characteristic as heat, which can increase and decrease. Heat is not a material substance: as a part of the internal energy of a substance, it arises as a result of the movement and interaction of molecules. Since the heat of different substances may differ, a process of heat transfer from a warmer substance to a substance with less heat occurs. This process is called heat transfer. The main types of heat transfer and the mechanisms of their action we will consider in this article.
Heat transfer
Heat transfer, or the process of temperature transfer, can occur both within matter and from one substance to another. At the same time, the heat transfer intensity largely depends on the physical properties of matter, the temperature of substances (if several substances are involved in heat transfer) and the laws of physics. Heat transfer is a process that always proceeds unilaterally. The main principle of heat transfer is that the most heated body always gives off heat to an object with a lower temperature. For example, when ironing clothes, a hot iron gives off heat to trousers, and not vice versa. Heat transfer is a time-dependent phenomenon that characterizes the irreversible distribution of heat in space.
Heat transfer mechanisms
The mechanisms of thermal interaction of substances can take various forms. Three types of heat transfer in nature are known:
- Thermal conductivity is a mechanism of intermolecular heat transfer from one part of the body to another or to another object. The property is based on the inhomogeneity of temperature in the substances under consideration.
- Convection - heat transfer between fluids (liquid, air).
- Radiation exposure is the transfer of heat from bodies (sources) heated and heated due to their energy in the form of electromagnetic waves with a constant spectrum.
Consider the listed types of heat transfer in more detail.
Thermal conductivity
Most often, thermal conductivity is observed in solids. If under the influence of any factors the same substance has areas with different temperatures, then the thermal energy from the more heated area will go to the cold. In some cases, a similar phenomenon can be observed even visually. For example, if we take a metal rod, say, a needle, and heat it over a fire, then after some time we will see how thermal energy is transmitted through the needle, forming a glow in a certain area. Moreover, in a place where the temperature is higher, the glow is brighter and, conversely, where t is lower, it is darker. Thermal conductivity can also be observed between two bodies (a mug of hot tea and a hand)
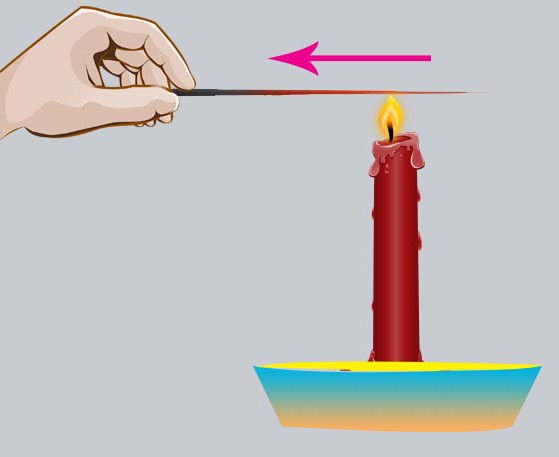
The intensity of heat flux transmission depends on many factors, the ratio of which was revealed by the French mathematician Fourier. These factors primarily include the temperature gradient (the ratio of the temperature difference at the ends of the rod to the distance from one end to the other), the cross-sectional area of the body, and the thermal conductivity coefficient (it is different for all substances, but the highest is observed for metals). The most significant thermal conductivity is observed for copper and aluminum. It is not surprising that these two metals are more often used in the manufacture of electrical wires. Following the Fourier law, the heat flux can be increased or decreased by changing one of these parameters.
Convection types of heat transfer
Convection, which is characteristic mainly for gases and liquids, has two components: intermolecular thermal conductivity and motion (propagation) of the medium. The mechanism of action of convection is as follows: with increasing temperature of the fluid substance, its molecules begin to move more actively and in the absence of spatial restrictions, the volume of the substance increases. The consequence of this process will be a decrease in the density of the substance and its upward movement. A striking example of convection is the movement of air heated by a radiator from a battery to the ceiling.
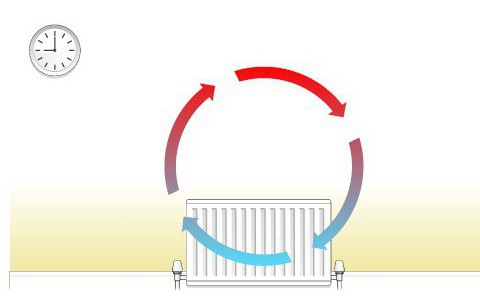
Distinguish between free and forced convective types of heat transfer. The heat transfer and mass movement in the free type occurs due to the inhomogeneity of the substance, that is, the hot liquid rises above the cold naturally without the influence of external forces (for example, heating a room through central heating). In forced convection, mass movement occurs under the influence of external forces, for example, stirring tea with a spoon.
Radiant heat transfer
Radiant or radiation heat transfer can occur without contact with another object or substance, therefore it is possible even in airless space (vacuum). Radiation heat transfer is inherent in all bodies to a greater or lesser extent and manifests itself in the form of electromagnetic waves with a continuous spectrum. A striking example of this is the sun's rays. The mechanism of action is as follows: the body continuously radiates a certain amount of heat into the space surrounding it. When this energy falls on another object or substance, part of it is absorbed, the second part passes through, and the third is reflected in the environment. Any object can both radiate heat and absorb, while dark substances can absorb more heat than light ones.
Combined heat transfer mechanisms
In nature, types of heat transfer processes are rarely found separately. More often they can be observed in the aggregate. In thermodynamics, these combinations even have the names, say, thermal conductivity + convection - this is convective heat transfer, and thermal conductivity + thermal radiation is called radiation-conductive heat transfer. In addition, such combined types of heat exchange are distinguished as:
- Heat transfer is the movement of thermal energy between a gas or liquid and a solid.
- Heat transfer is the transfer of t from one matter to another through a mechanical obstacle.
- Convective radiant heat transfer is formed by combining convection and thermal radiation.
Types of heat transfer in nature (examples)
Heat transfer in nature plays a huge role and is not limited to heating the globe with sun rays. Extensive convection currents, such as the movement of air masses, largely determine the weather on our planet.
The thermal conductivity of the Earth's core leads to the appearance of geysers and the eruption of volcanic rocks. These are just a few of the examples of heat transfer on a global scale. Together, they form types of convective heat transfer and radiation-conductive types of heat transfer necessary to maintain life on our planet.
The use of heat transfer in anthropological activities
Heat is an important component of almost all production processes. It is difficult to say what type of heat transfer is used most by man in the national economy. Probably all three at the same time. Thanks to heat transfer processes, metals are smelted, and a huge amount of goods is produced, from everyday objects to space ships.
Extremely important for civilization are thermal aggregates capable of converting thermal energy into usable force. Among them are gasoline, diesel, compressor, turbine units. For their work, they use various types of heat transfer.