The performance parameters of the operating system in the form in which they are presented in Windows do not always properly provide the most comfortable work at the computer. This is understandable, because by default a lot of unnecessary services and background processes are included that slow down the functioning of the OS. Despite the fact that in Windows of any modification there is a corresponding section, it does not fully allow the most high-quality optimization to be performed. But some of the proposed settings can still be used.
Windows performance options: basic misconceptions in system optimization
To begin with, let's figure out what you can mean by system speed and what options affect it. Typically, in such cases, the absence of so-called braking is implied when performing certain operations or in the operation of installed devices.
In most cases, the main load falls on the central processor and RAM, however, similar components of graphic adapters may be partially involved, since they process all the software components. Accordingly, it is possible to increase performance by reducing the load on them. However, if we take into account only the performance parameters that are listed in a separate section, it is not always possible to establish the optimal options. The problem is that this section is more focused on setting up graphic effects and actions with some additional components. But deactivating all unnecessary system services will fail. By and large, to perform the optimization, only these settings are clearly not enough.
GUI Optimization
Apparently, there is no need to say that the developers of Windows-systems, initially using the methods of object-oriented programming, tried to pay maximum attention to the graphical interface, so that it was convenient for the user to work with the system and its basic functions. But all these embellishments just can quite heavily load system resources, and this especially manifests itself on those computers where integrated video cards belonging to the Video-on-Board class are installed, which are initially mounted on motherboards. With discrete video adapters, the situation is simpler, since it is their processors and dedicated memory that are responsible for processing the graphics, and not the central components.
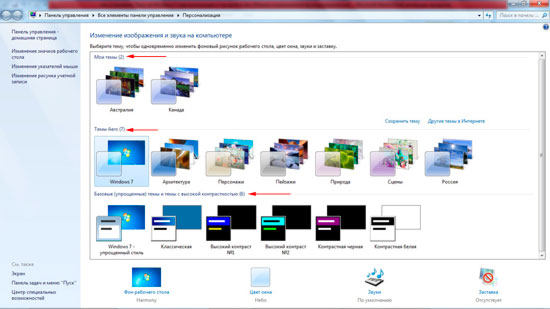
Thus, even without the involvement of specialized system settings, the performance parameters can be quite simply changed by setting in the personalization section, called from the context menu via RMB on the "Desktop", some simplified scheme in which resource-intensive graphic and video effects like design in Aero style for Windows 7. But this is not all that can be done.
Where are the performance options?
Now we proceed directly to the section of the described options. You can access these settings through the computer’s properties section on the “Desktop” (Windows 7 and below) or in “Explorer” (Windows 8 and 10). Here you need to go to additional options, and then on the opened general information tab, click the options button. It is easy to see that in the window that appears there are several main points that can be used for quick settings, and the main attention is paid to graphic effects.
To quickly increase productivity, you can immediately use the point of ensuring the best performance, when activated, all visual effects will be turned off, and the interface, depending on the installed modification of the operating system, can take on a classic look a la Windows 95.
How to make the best setup?
However, the performance parameters of Windows 7 or any other version of the system can be changed at your discretion, if you turn off absolutely all the visual effects there is no desire. In this case, we are talking about leaving only a certain minimum of them.
It is recommended to leave only the smoothing options for screen fonts and smooth scrolling lists. But everything else (animation, shadows, etc.) can be deactivated painlessly.
Additional settings
With the effects sorted out. Now let's see what performance parameters of Windows 10 or systems of a rank below are available as additional options.
On the data execution prevention tab (provided that this function is supported by the installed processor), it is recommended to activate the DEP service only for the main programs and system services, and not for everyone. It is not worthwhile to add exceptions to an ordinary user without special knowledge, since such actions can have unpredictable consequences.
Now the most important thing. On the additional options tab, it is better to set the optimization for programs, rather than for background processes, after which you can go on to configure the virtual memory settings, for which the swap file is responsible. To do this, click the button to change options. By default, the definition of the size of the paging file is provided to the operating system, but below there are values for the installed (current), minimum, and recommended size.
It is not worth changing these options without the need, however, if you notice a slowdown in the computer, or the system issues a warning about insufficient memory in the system tray, the size of this component can be increased to the recommended one or slightly higher. In general, although this is not recommended, the swap file can be completely disabled by setting the corresponding item active. True, such a solution can be applied only if there is a sufficiently large amount of RAM (8 GB and above).
Disabling can also be done on systems with a weaker configuration, if the computer does not provide for the use of resource-intensive applications. Too large a size is also not worth it, since the operating system will begin to access virtual memory, ignoring the RAM. And virtual memory is nothing but the reserved space of the hard disk where software components are unloaded. Accordingly, the speed of accessing the hard drive is lower than that of RAM. As a result, you get not a performance increase, but a decrease in performance.
Unused startup components and system services
Finally, a few words about the settings where the performance parameters available for change and described above are not involved. It is about disabling all those processes that start with the system and deactivating some unused services. In the first case, you should remove unnecessary startup items using the system configuration (msconfig) for access in Windows 7 and below or the "Task Manager" in later versions.
In the second case, you need to go to the programs and components section, and then disable unused services from the list that appears (for example, the print service if there is no printer installed).
Specialized Optimizer Programs
Of course, this is far from all that can directly affect the performance parameters of any Windows system. In some cases, it is advisable to optimize using utilities specially designed for this. This is not about removing garbage or cleaning the registry, but rather about disabling unnecessary processes.
The optimal application, it is believed, will be the Windows Manager program, several versions of which can be found for modification systems from the seventh to the tenth.