Probably, every user working with Windows systems of any generation has noticed more than once that immediately after the first installation, when the equipment installed on the computer fully meets the system requirements for Windows, it just “flies”, but after a while there is a clear slowdown. Here thoughts come about how to check the computer for performance and optimize its work. To do this, you can offer several universal methods that involve the use of system tools that are available in the Windows OS itself, and specialized narrowly targeted utilities, and general purpose optimizers from third-party developers.
How to test a computer for performance: the main directions of checks
To begin with, let's figure out what generally should be understood as performance, and also look at which particular components of the hardware-software complex need special attention. It is completely natural that, first of all, the central processor and random access memory come to mind, on which the maximum load is assigned.
Also, the main components of the computer hardware should include graphics adapters, since they, along with the CPU and RAM, also play one of the key roles in ensuring the correct functioning of the operating system. Installed in its application environment and directly involved even in the process of loading the OS.
Apparently, many paid attention to the appearance of blue screens, what was caused precisely by the malfunctioning of the video cards themselves and their drivers? The hard drive also plays an important role. The presence on it of errors, bad sectors, randomly scattered file fragments not only complicate its use, but also increase the time it takes for software components to access it to perform read / write processes.
It seems to be sorted out with the hardware. But where does the software part? Alas, even the components themselves in the form of various services and background processes of Windows can cause an increase in the load on system resources. In addition, many such processes are not needed by the average user at all.
Finally, there is another important component called the registry, which stores all the data about the system, installed programs and drivers, general and user settings, etc. The more records it contains, the slower Windows runs. She needs more time to scan the registry in search of a particular key. And this is often noticeable already at the loading stage. Thus, we will consider computer testing for performance in relation to the above components.
System performance testing
Now we proceed directly to the implementation of checks. If not all users, then very many people know that in all recent versions of Windows there is a special built-in tool that displays the so-called performance index. Alas, it is completely impossible to rely on the value that is provided to the user. This is due only to the fact that the total score is not even averaged, but is set based on the lowest score. Despite this, you can perform the most common visual test of a computer for performance. You can do this in any system in the standard "Task Manager", where you need to use the speed / performance tab. You can track indicators in real time by selecting the desired item among those presented.
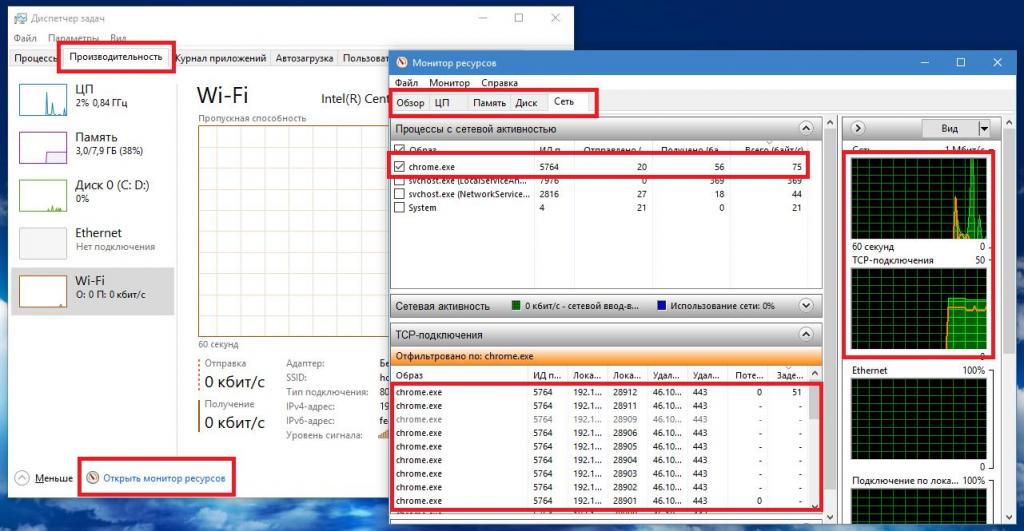
True, many forget that it is in this section that you can use an additional software tool called a performance monitor. It has a bit more information and capabilities, since you can choose a specific process and see how much it affects system resources. Unfortunately, with this tool you can only track the behavior of some processes, but you won’t be able to improve performance (even by forcing them to be completed, since many system services cannot be turned off, and some will start again after deactivation on their own).
How to improve computer performance on Windows 10 and below?
But on Windows, you can still achieve performance gains. At least the user himself can change some parameters even without being an administrator. Setting up a computer for performance that would fully satisfy your needs is done by changing the following options (only by the system):
- disabling unnecessary startup items;
- Deactivating unused components and services
- cleaning and optimization (defragmentation) of the hard drive;
- changing virtual memory settings.
All this together will allow you to offload system resources without using software from third-party developers. But what do you think exactly what can be turned off, and how to do it?
Check autoload
The first thing you need to pay attention to is this section, since the processes that start with Windows (both system and user) increase the boot time of the OS. In addition, at startup, along with the system, their components are constantly in RAM.
In the tenth and eighth versions of Windows, to access this section, you must use the "Task Manager" (taskmgr), and in the versions below it can be reached through the configuration (msconfig). It is in the G8 and G8 that you can disable everything that is on the list (of course, except for the services of a full-time antivirus). But in the seventh version and lower in the list, you must additionally leave the ctfmon applet responsible for the operation of the language panel and changing the language or layout (in Windows 10 and 8 this process is not displayed by default). Upon completion of the setup, the computer must be restarted.
Note: as additional actions, you can disable unnecessary services on the corresponding tab, but they will only be deactivated until the next reboot.
Disable unnecessary system components
Speaking about how to test a computer for performance and improve performance, you should separately dwell on the deactivation of some system components, which ordinary users often forget. You can view the list of active services through the standard section of installed programs, where you need to click on the link to enable or disable Windows components.
In the list, you can disable, say, Internet Explorer, if you have another browser installed as a program to access the Internet. You can also deactivate print services if you do not have a printer, or if you do not intend to use it at all. You can turn off the components of the Hyper-V module if you are not working with virtual machines or emulators, etc.
We delete unused and resource-intensive programs
By and large, you can get rid of unnecessary or rarely used applications. Some of them, even in the background, can load their own libraries into RAM or access the Internet. Pay special attention to the fact that very often when installing the main program in the appendage to it, some related applications are also installed. For example, when you install iTunes, you also get the Apple software update module, Bonjour synchronizer, etc.
The easiest solution is to uninstall such applications from the usual section of programs and components. But the native Windows uninstaller works extremely inefficiently, leaving a huge amount of garbage, so you need to remove unnecessary programs with other methods, which will be discussed separately.
Disable background services and processes
Now it's time to disable some system services that cannot be deactivated by the above methods. To view all services, use the corresponding section, called by the services.msc command through the Run console. But here you need to know what exactly can be deactivated. As a simple example, consider disabling the automatic installation of system updates. To do this, turn off the four components:
- Update Center itself;
- Windows Installer Service
- Update Installer Service
- delivery optimization.
Each component is double-clicked to call editing options, then the service is stopped by pressing the corresponding button, after which a disabled start is set in the startup type.
Clean and optimize your hard drive
To speed up access to the hard drive and increase its performance, you must constantly clean it from debris and regularly perform defragmentation.
In Windows, for starters, you can use your own tool to clean the selected partition, where it is desirable to use the removal of system files, which will get rid of files of the old system assembly, delete unnecessary saved update packages, clean the system cache, etc.
You can also use the built-in defragmentation tool, which works very, not bad, but for a long time.
Virtual memory
Finally, it’s time to dispel myths about the use of virtual memory and the swap file responsible for it. For some reason, many people think that it is best to set the maximum possible value. Alas, this will lead to the opposite effect, since instead of RAM, the components of the programs that start up will start loading just virtual memory, which is the reserved space on the hard drive, and the speed of accessing the hard drive is several times lower than that of RAM. But what volume to establish? It is generally accepted that with eight gigabytes of RAM, the use of the page file can be disabled altogether. Despite the recommendations of the system for setting the size of the swap file, this will give a noticeable increase in speed.
As practice shows, if you work only with office applications and documents, and the computer has a 2-core mid-range CPU and 2 GB of RAM, there’s nothing wrong with deactivating virtual memory.
Choosing the optimal graphics card operating mode
Finally, let's see how to improve computer performance by choosing the optimal graphics accelerator mode. In Windows, there are no proprietary tools to configure the necessary parameters. Therefore, it is best to use special diagnostic and configuration utilities from the manufacturers of video cards themselves (for example, ATI Catalyst, NVIDIA Control Panel or PhysX, etc.) Many such programs allow not only optimizing all the necessary parameters, but also monitor the timely update of drivers.
Note: management software update issues are relevant not only for graphic chips, but also for all installed hardware and even for some virtual components. For updates, it’s best to use automated programs like Driver Booster or something similar.
Testing performance with special programs
How to test the computer for performance and perform some steps to increase system performance using Windows, figured out. Now let's move on to third-party software products. To do this, you can use either applications belonging to the class of performance monitors or general-purpose optimizer programs. From the first type of applications, as is already clear, it is possible to achieve only the output of the relevant information on the functioning of certain software and hardware components, but in the optimizers you can perform very fine-tuning. That is why it is recommended to use them.
Complete removal of applications, Windows programs, extensions and browser panels
Now, with regard to checking the computer for performance and optimizing its operation, let us dwell on the removal of software components. In order to avoid garbage remaining in the system after removing the main elements of uninstalled applications in the form of files on the hard disk or registry entries, it is best to use special uninstallers, the most prominent of which are the iObit Uninstaller and Revo Uninstaller utilities.
Using these packages, you can even get rid of all installed panels and browser extensions, as well as remove unnecessary applets that are “wired” into the shell of the operating system itself. The program itself does not have a special effect on computer performance in terms of using computing resources, although it is sometimes advisable to disable the automatic update module.
How to improve system performance using optimizers?
In conclusion, we’ll look at how to test a computer for performance and increase speed if it is required using optimizers.
The initial test is best done in applications like Advanced SystemCare, but not yet including the automatic correction of problems found. But when a list appears with all detected errors, malfunctions, or with components that can be optimized, you can safely ask for troubleshooting. In such applications, you can independently enable the necessary modules, as well as use some additional settings or use constantly working means of unloading RAM.
The CCleaner utility is considered the most universal. The program has a beneficial effect on computer performance, allowing you to clean the registry, remove unnecessary applications, manage startup items and the Task Scheduler tasks, completely clear disk space, etc.
Also, applications like AVZ, Easy Service Optimizer or Windows Manager look good, in which you can additionally access important system parameters, and set the optimal parameters based on the recommended values, and it is absolutely safe for the operating system itself.