The ships of this project could become the most massive in its class. They planned to launch them in huge quantities for our Navy. Fifty destroyers of the first rank - such an armada is enough to complete a fleet. In addition, multi-purpose intended to use them to solve a variety of problems. The lead destroyer "Sovremenny" (project 956) was laid down in 1975, the last ship of the series launched in late 1993. Out of the planned fifty units, 17 were received by the Navy of the USSR and Russia. Four more fly under the Chinese flag. Two ships were mothballed, two are under modernization, two more are in the combat strength of the Northern Fleet, the rest are decommissioned. What is the reason for such massive cutting of metal into old, by naval terms, units?
Why did the USSR need new destroyers
The reasons for the rejection of a large number of ships of the project 956 should be sought in the times already distant. It was then, in the mid-fifties, that an unfortunate phenomenon occurred, called by the sailors "Khrushchev’s rout". Intoxication with the success of domestic rocket scientists led to a major strategic miscalculation. The likelihood of a global conflict decreased due to the guarantee of mutual destruction, but this did not mean at all that there was no need for a regional presence of the Soviet Navy, and it was extremely difficult to ensure it without the presence of large ships in the arsenal. The operations of squadrons on combat duty in various remote sectors of the oceans were difficult (due to the small number of units forming their “core” and causing stability). Aircraft carriers in the USSR were not built due to their high cost, destroyers of early projects (Projects 30-2 and 78) and cruisers (Project 68), built under Stalin and “not cut back” by Khrushchev, were not only morally obsolete, but also worn out physically. The fleet demanded replenishment with modern ships of large displacement, equipped - along with missile launchers - with powerful artillery. This is what the newest destroyer of project 956 was conceived, the urgent need for which was fully realized after the large-scale exercises “Ocean”, held in the spring of 1970.
What is a destroyer and why is it needed
Destroyer squadron is a traditional concept rather than filled with real meaning. Of course, armament is not limited to mines, and by its purpose, the ship most likely corresponds to the class of frigates accepted in many fleets of the world, which, in turn, also have little in common with ancient sailboats. The destroyer of project 956 Sarych (that was the code) was intended to carry out a wide range of combat missions that might not be within the capabilities of the BOD (large anti-submarine ships), which formed the basis of the USSR Navy in the late sixties. Officially, its main mission was formulated as fire support for the landing, expressed in the suppression of small-sized ground targets, providing air defense and missile defense of the landing units and the destruction of boats of a potential enemy. It was also planned to be used jointly with the BOD (pr. 1155), which brought the effectiveness of such a pair closer to the combat capabilities of the most modern American frigates of the "Sprouts" at that time. Based on the tasks set, the destroyer of project 956 was created. The ship is expensive to the budget, it is built on the basis of a specific defense doctrine, especially when it comes to a large series.
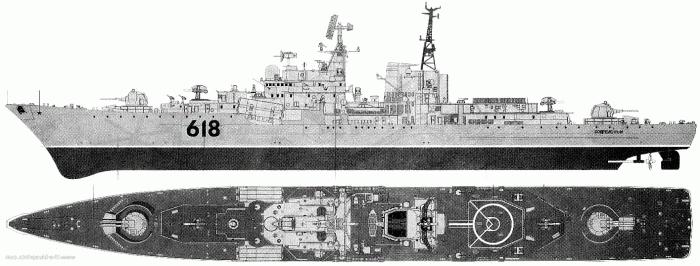
Appearance and propaganda of aesthetics
It is believed that the appearance of military equipment is not as important as its functionality, but this is not entirely true. The impression produced by it on a likely enemy often depends on how impressive the model is, that in the absence of war it can play an important role in the development of the conflict, and possibly prevent it. Based on this premise, the project 956 destroyer was also created. The model, the photo of which was presented to the IMF Commander-in-Chief Admiral S.G. Gorshkov at the end of 1971, was approved largely due to the formidable appearance of the ship, its ominous exterior and the propaganda effect that could produce its silhouette after the appearance of the ship in the ocean. The naval authorities liked the layout, built on a scale of 1:50: it fully corresponded to the foreign policy doctrine of the USSR and demonstrated progress in science and technology in the second half of the 20th century. But, of course, it was not only a matter of appearance - S. G. Gorshkov was not so simple as to evaluate the project 956 destroyer as a general impression. The characteristics of the ship were more important, and they spoke of very good seaworthiness.
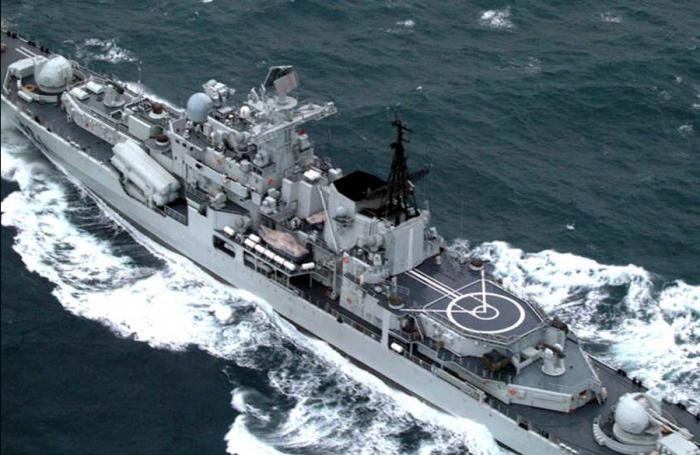

Shipbuilding Innovations
The shipbuilding specialist liked the preliminary project not only aesthetically. The main features of the appearance of the ship were the smooth-deck of the hull, the saddle of its bow, the successful placement of artillery weapons of the main caliber, the location of anti-aircraft systems on the sides (which provided excellent opportunities for staging fire) and the high elevation of the radar antennas (to improve location viewing). The length of the hull was limited by the capabilities of the shipyards of the plant named after A. A. Zhdanova and should not exceed 146 meters with a width of 17 m. When developing the general shipbuilding ideology of the ship, many technologies were first applied. The shape of the bow set the indefensibility (up to 7 points of excitement) by the oncoming wave, the side was made with a double fracture of the surface to reduce visibility. There were other features that distinguished the destroyer of project 956. Drawings of the decks were made in compliance with their strict horizontality regardless of contours, which greatly improved the manufacturability of the equipment installation. The case is divided into fifteen watertight compartments, the bow "bulb" underwater part not only reduces resistance, but also serves to accommodate the position of hydroacoustics (MGK-335MS, aka the Platinum complex). Rationally applied elements of power hardening in places of greatest stress.
Power plant
The disadvantages of the ships of this series, experts refer to the obviously outdated power plant. There were reasons for this. When choosing the type of turbine S. G. Gorshkov gave preference to the boiler circuit, rejecting the gas one. This was done under the influence of the Minister of Shipbuilding of the USSR B.E. Butoma, who argued that the large load of the South Turbine Plant and that the supply of fuel oil in a special period would be easier than diesel fuel. As a result, the project 956 destroyer was equipped with a twin boiler-turbine unit with a total capacity of 100 thousand liters. from. Today it is difficult to give a comprehensive assessment and speak out solely in favor of or against this decision. The fact is that in the beginning of the 70s there was an ambitious project to create technologically advanced once-through KTUs, which, if successful, promised to become unique, but it did not succeed. Ultimately, I had to stop at the usual outdated high-pressure boilers, proven and, in general, also not bad. And another argument in their favor was the relative cheapness of fuel oil. The world energy crisis also affected the USSR.

Cannon weapons
The underestimation of the role of artillery in the naval theater of operations over the past decades has prompted the Sevmash Design Bureau to equip the Sovremenniy destroyer (project 956) with two AK-130 twin units equipped with Lev-218 multi-channel control systems (MP-184). Guidance of the trunks is carried out on the basis of information received from the radar, rangefinder (laser) and television devices, and processed by a digital calculator of firing parameters. The supply of ammunition is mechanized, rate of fire reaches 90 rds / min, range exceeds 24 km. In terms of artillery power, the destroyer of project 956 is superior to battleships of the First World War, which had no other weapons except cannon. The weight of the shells delivered to the target (in one minute) exceeds six tons.
Anti-aircraft artillery means provide protection against complex targets (including cruise missiles) and are represented by two AK-630M 30-mm systems located side-by-side. These plants include six-barrel water-cooled systems controlled by Vympel automated control systems. They are capable of hitting high-speed targets at a distance of 4 km with a rate of fire of 4 thousand rounds per minute.
Rockets
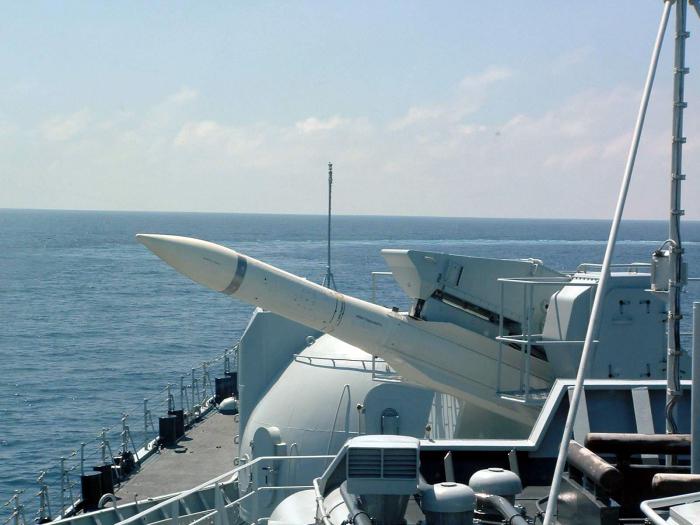
The missile weapons of the destroyer Sarych are designed to combat air and sea targets. The Hurricane complex (in later versions of the Hurricane Tornado) is equipped with single-beam launchers firing SAMs. In the ammunition of each of the two launchers - 48 guided missiles. “Hurricane” is a universal weapon, it is quite suitable for hitting small surface ships (for example, missile or torpedo boats). The number of targets followed and destroyed - up to six (at launch every 12 seconds).
Project 956 destroyer carries out specialized anti-ship defense by the Moskit complex (Moskit-M) equipped with ZM-82 missiles. Two installations, they are protected by reservation, each contains four shells. The combat radius of the complex is 120 km (170 at Moskita-M). Supersonic missiles (M = 3), the mass of explosives in the combat charging compartment is three centners. All eight ZM-82 can be fired within a half-minute salvo on command of the ship's control system.
Terms of Service
"Sarych" compares favorably with many Navy ships with improved habitability conditions. The destroyer is equipped with a single microclimate installation, providing a comfortable atmosphere at an outdoor temperature ranging from −25 ° C to +34 ° C. For rest of the rank-and-file crew there are 16 cubicles with a capacity of 10 to 25 people, with each sailor covering an area of more than 3 m². Michmansky (four-seater) and officer (single and double) cabins have an area of 10 square meters. m. Two spacious wardroom and three dining rooms serve for eating. On board there is everything necessary for life away from the hometown: a cinema hall, cable TV, a library, an internal radio system, comfortable showers, a sauna. In hot weather, by order of the commander of the ship, a pool can be assembled.
Inside the medical unit there is an outpatient clinic, a double insulator, an infirmary and an operating room.
The living and comfort conditions on the project 956 destroyers are not inferior to foreign standards, which affected the export potential of these ships.
Hard times
The project was created exclusively for internal use, and before the collapse of the USSR, there was not even a word about the sale of ships of this type. Fourteen destroyers became part of the USSR Navy in the period 1976-1881, each of them being built on average for four years. Ships arrived in the Northern (six) and Pacific (eight) fleets, took part in large-scale naval exercises, made long trips and friendly visits to foreign ports.
In the last Soviet years and immediately after the collapse of the USSR, the situation changed. State funding has fallen sharply. The maintenance of a warship is expensive. Over a decade, a dozen of them were decommissioned, five destroyers of this type remained in service, the rest were dismantled or mothballed. Ten years later (in 2011), the only destroyer of the project 956 Admiral Ushakov was in the Northern Fleet. "Persistent" was the flagship of the Baltic Fleet, and "Fast" was in the Pacific Ocean. There are only three active ships out of seventeen built.

By this time, most Sarych-class weapons systems are outdated. The planned modernization of project 956 destroyers involved the re-equipment of cruise missiles and new air defense and missile defense systems. The replacement of anti-submarine and anti-torpedo defense was required. At the same time, the running characteristics of the destroyers remained very good. The range of autonomous navigation of 4.5 thousand miles, high speed and powerful airborne artillery prompted the fleet command to refrain from the complete withdrawal of ships from the combat personnel.
Modernization and export supplies
Two unfinished ships, which were named “Important” and “Thoughtful” at the tab, and then renamed “Yekaterinburg” and “Alexander Nevsky”, were completed and sold to the PRC at the turn of the millennium. The export version of the project has undergone changes and received code 956 E. The names of the Chinese ships are “Hanzhou” and “Fuzhou”, they have been serving in the Eastern Fleet of the Navy of the People’s Liberation Army of China since 2000 to the present. The modernization of the destroyers of the project 956 series “E” (export) concerned only the power plant and some weapons systems.
The following two units intended for the Chinese fleet underwent more serious changes. The project destroyer 956EM differs from the E modification in size, Moskit-ME anti-ship missiles of extended range (they reach targets within a radius of 200 km) and the new Kashtan anti-aircraft missile and artillery modules. Aft gun mount replaced by a helicopter hangar. Under this project, two destroyers (Taizhou and Ningbo) were built in 2005 and 2006.
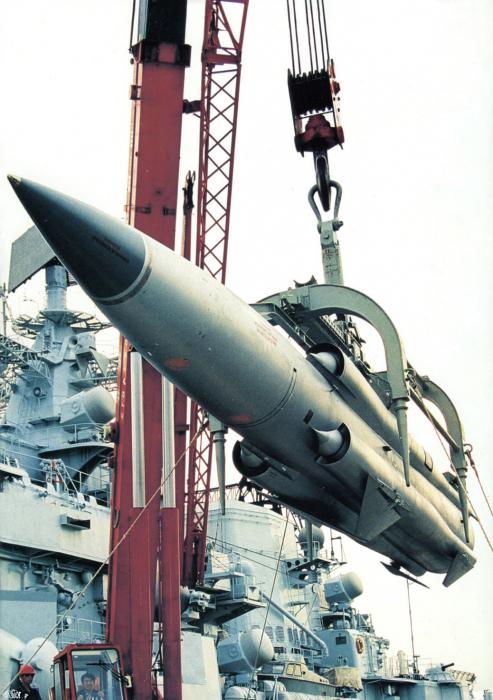

If the sale of the first two ships to China was explained mainly by the difficult financial situation of the initial post-Soviet period, the contract for the supply of the next pair can be called a successful foreign trade operation. In the middle of the first decade of the new century, a line was already outlined for systemic modernization of the Russian armed forces, including the fleet. At that time, ships were designed more advanced than the destroyer of project 956, the photo of which already evoked associations with the past era. Massive superstructures and numerous antennas corresponded to the appearance of the fleets of the last century. However, China did not fail, having bought powerful and reliable combat units that strengthened its Navy.