What is a Bodo Code? Baudot code is one of the first telecommunication binary encodings from a machine. Baudot encryption uses a five-bit coding alphabet and two character sets (usually one for letters and one for numbers and punctuation). The coding alphabet depends on the device used (type Baudot).
Encryption of Morse code and Bodo code is to decrypt the message characters. There are two keys for switching between character sets: ⇩ and ⇧.
What is the advantage of Bodo code?
The Baudot encoding invented by Emil Bodo is a character set preceding EBCDIC and ASCII. Bodo's telegraphic code was the forerunner of the International Telegraphic Alphabet No. 2 (ITA2), the teleprinter cipher that was used before ASCII. Each character in the alphabet is represented by a series of five bits transmitted over a communication channel, for example, a telegraph wire or a radio signal. A symbol’s speed measurement is known as a baud by the name of a scientist.
History
Technically, five-bit encodings appeared in the 16th century, when Francis Bacon developed the cipher, which is now called the Bacon cipher. This technology was not created for machine telecommunications. Although theoretically this cipher could be adapted for this purpose, it covered only 24 of the 26 letters of the English alphabet (two sets of letters - I / J and U / V - were expressed with the same code) and did not contain any punctuation marks, spaces, numbers or control characters, which made it unused.
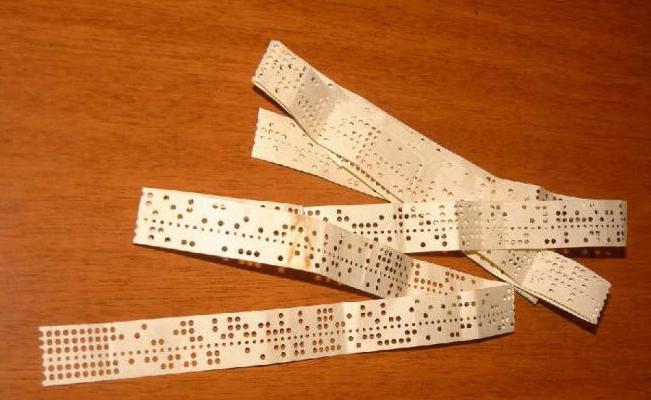
Emil Bodo invented his original code in 1870 and patented it in 1874. It was a 5-bit code with equal on and off intervals, which made it possible to transmit the Latin alphabet and punctuation and control marks by telegraph. The cipher was based on an earlier code developed by Karl Friedrich Gaus and Wilhelm Weber in 1834. It was Gray's encoding (when vowels and consonants are sorted alphabetically). This code was not patented (only the machine), since the French patent law does not allow patenting concepts.
What is a Bodo Code?
Baudot's source code was adapted for sending from a hand-held keyboard, but specialized equipment that could use it in its original form did not exist at that time. The code was entered from the keyboard with five keys - two fingers of the left hand and three fingers of the right hand.
As soon as the keys were pressed, they were blocked until the mechanical contacts in the distribution block passed through the sector connected to this particular keyboard when it was unlocked. Operators had to maintain a steady rhythm, and the usual speed was 30 words per minute.
Murray Code
In 1901, the Bodo telegraph code was modified by Donald Murray (1865-1945) after developing his own typewriter. Murray’s system used an intermediate step and a keyboard punch, which allowed the operator to punch a paper tape and a tape transmitter to send a message from a punch tape. At the receiving end of the line, the printing mechanism transmitted information to a paper tape. A rotary hammer was used to make a perforated copy of the message.
Since there was no longer any connection between the movement of the operator’s hand and the transmitted bits, there were no restrictions on how to organize the code to minimize operator fatigue. Instead, Murray developed a cipher capable of minimizing mechanism wear by assigning code combinations with the smallest punched holes to the most commonly used characters.
Western Union
What is Bodo Code and how did it evolve? Western Union - teleprinter keyboard using Bodo encoding (US version) with Shift and LTRS keys. Murray's code was adopted by the Western Union, which used it until the 1950s with a few changes, which consisted in the fact that some characters were skipped and more control codes were added.
An explicit SPC character (space) was entered instead of BLANK / NULL, and a new BEL cipher triggered a call or sound in the receiver. In addition, a code was introduced that caused the receiving machine to send the identity stream to the sender in the reverse order.
ITA2
In 1924, the CCITT introduced the International Telegraphic Alphabet Code No. 2 (ITA2) as an international standard, which was based on the Western Union code with some minor modifications.
The US standardized a version of ITA2 called US Teletype Code (US TTY), which was the basis for 5-bit teletype codes before the debut of 7-bit ASCII in 1963. Some code points have been reserved for national use.
Nomenclature
Almost all of the 20th century teleprinter equipment used Western Union, ITA2 or its variants. In the US, the implementation of Baudot code may differ in the addition of several characters, such as #, & at the FIGS level.
What is the Bodo code in Cyrillic? The Russian version of the Bodo code (MTK-2) used three shift modes. Cyrillic letter mode activated symbol (00000). Due to the larger number of characters in the Cyrillic alphabet, the characters!, &, £ have been omitted and replaced with the Cyrillic alphabet. By the way, BEL has the same code as the Cyrillic letter Y.