Hard disks, or, as they are also called, hard drives, are one of the most important components of a computer system. Everyone knows about it. But far from every modern user, even in principle, guesses how the hard disk works. The principle of work, in general, is quite simple for a basic understanding, but there are some nuances here, which will be discussed later.
Questions about the purpose and classification of hard drives?
The question of destination, of course, is rhetorical. Any user, even at the most entry-level level, will immediately reply that the hard drive (aka hard disk, aka Hard Drive or HDD) will immediately reply that it serves to store information.
In general, it is true. Do not forget that on the hard disk, in addition to the operating system and user files, there are boot sectors created by the OS, thanks to which it starts, as well as some labels by which you can quickly find the information you need on the disk.
Modern models are quite diverse: ordinary HDDs, external hard drives, high-speed solid-state drives SSD, although they are not usually assigned to hard drives. It is further proposed to consider the device and the principle of operation of the hard disk, if not in full, then at least in such a way that it is sufficient to understand the basic terms and processes.
Please note that there is a special classification of modern HDDs according to some basic criteria, among which are the following:
- way to store information;
- media type;
- way to organize access to information.
Why is a hard drive called a hard drive?
Today, many users are thinking about why hard drives are called small arms hard drives . It would seem that what could be common between these two devices?
The term itself appeared back in 1973, when the world's first HDD appeared on the market, the design of which consisted of two separate compartments in one sealed container. The capacity of each compartment was 30 MB, which is why the engineers gave the disc the code name “30-30”, which was fully consonant with the brand of the “30-30 Winchester” popular at that time. True, in the early 90s in America and Europe, this name was almost out of use, but it still remains popular in the post-Soviet space.
The device and principle of operation of the hard drive
But we were distracted. The principle of operation of a hard disk can be briefly described as the processes of reading or writing information. But how is this going? In order to understand the principle of operation of a magnetic hard disk, first of all, it is necessary to study how it works.
The hard drive itself is a set of plates, the number of which can range from four to nine, interconnected by a shaft (axis), called a spindle. The plates are located one above the other. Most often, the material for their manufacture is aluminum, brass, ceramics, glass, etc. The plates themselves have a special magnetic coating in the form of a material called platter, based on gamma-ferrite oxide, chromium oxide, barium ferrite, etc. Each such plate is about 2 mm thick.
Radial heads (one for each plate) are responsible for writing and reading information, and both surfaces are used in the plates. Two electric motors are responsible for the rotation of the spindle, the speed of which can be from 3600 to 7200 rpm, and the movement of the heads.
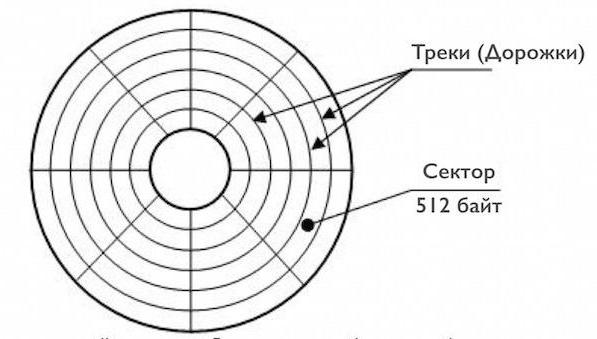
At the same time, the basic principle of the computer’s hard drive is that the information is not recorded anywhere, but in strictly defined locations, called sectors, which are located on concentric tracks or tracks. To avoid confusion, uniform rules apply. It is understood that the principles of operation of hard disk drives, from the point of view of their logical structure, are universal. So, for example, the size of one sector, adopted as a single standard throughout the world, is 512 bytes. In turn, sectors are divided into clusters, which are sequences of adjacent sectors. And the features of the principle of operation of the hard drive in this regard are that the exchange of information is carried out by entire clusters (an integer number of chains of sectors).
But how is reading information? The principles of operation of a hard disk drive are as follows: using a special bracket, the read head in the radial (spiral) direction moves to the desired track and, when rotated, is positioned above a given sector, all heads can be moved simultaneously, reading the same information not only from different tracks , but also from different disks (plates). All tracks with the same serial numbers are usually called cylinders.
At the same time, one more principle of hard disk operation can be distinguished: the closer the read head is to the magnetic surface (but does not touch it), the higher the recording density.
How is information recorded and read?
Hard disks, or hard drives, were therefore called magnetic because they use the laws of the physics of magnetism, formulated by Faraday and Maxwell.
As already mentioned, a magnetic coating is applied to plates of non-magnetosensitive material, the thickness of which is only a few micrometers. In the process, a magnetic field appears, having a so-called domain structure.
The magnetic domain is a magnetized region of a ferroalloy strictly limited by boundaries. Further, the principle of operation of a hard disk can be briefly described as follows: when an external magnetic field is applied, the disk’s own field begins to be oriented strictly along the magnetic lines, and when the exposure is stopped, zones of remanent magnetization appear in which the information that was previously contained in the main field is stored .
The read head is responsible for creating an external field during recording, and when reading the zone of residual magnetization, being opposite the head, creates an electromotive force or EMF. Further, everything is simple: changing the EMF corresponds to one in binary code, and its absence or termination to zero. The time of EMF change is called a bit element.
In addition, the magnetic surface can be associated purely for computer science, as a kind of point sequence of bits of information. But, since the location of such points is absolutely impossible to calculate, you need to install some pre-defined marks on the disk that helped determine the desired location. Creating such labels is called formatting (roughly speaking, breaking a disk into tracks and sectors clustered).
The logical structure and principle of operation of the hard disk in terms of formatting
As for the logical organization of the HDD, it is formatting that comes to the fore in which two main types are distinguished: low-level (physical) and high-level (logical). Without these steps, there is no need to talk about any bringing the hard drive to working condition. How to initialize a new hard drive will be discussed separately.

Low-level formatting involves a physical effect on the surface of the HDD, which creates sectors along the tracks. It is interesting that the principle of operation of the hard disk is such that each sector created has its own unique address, including the number of the sector itself, the number of the track on which it is located, and the number of the side of the plate. Thus, when organizing direct access, the same random access memory accesses directly to the specified address, and does not search for the necessary information on the entire surface, due to which speed is achieved (although this is not the most important thing). Please note that when performing low-level formatting, absolutely all information is erased, and in most cases it cannot be restored.
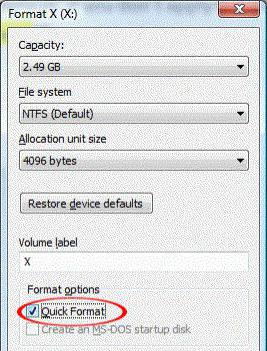
Logical formatting is another matter (in Windows-systems it is quick formatting or Quick format). In addition, these processes are applicable to the creation of logical partitions, which are a certain area of the main hard disk that works on the same principles.
Logical formatting primarily affects the system area, which consists of the boot sector and partition tables (boot record Boot record), file allocation tables (FAT, NTFS, etc.) and the root directory (Root Directory).
Information is recorded in sectors through a cluster in several parts, and in one cluster two identical objects (files) cannot be contained. Actually, the creation of a logical partition, as it were, separates it from the main system partition, as a result of which the information stored on it is not subject to change or deletion when errors or failures occur.
HDD Main Features
It seems that in general terms the principle of operation of the hard drive is a little understandable. Now let's move on to the main characteristics, which give a complete picture of all the possibilities (or disadvantages) of modern hard drives.
The principle of operation of the hard disk and the main characteristics can be completely different. To understand what is at stake, we will single out the most basic parameters that characterize all currently known information storage devices:
- capacity (volume);
- performance (data access speed, reading and writing information);
- interface (connection method, type of controller).
Capacity is the total amount of information that can be recorded and stored on the hard drive. The HDD industry is developing so fast that today hard drives with volumes of about 2 TB and above are already in use. And, as it is believed, this is not the limit.
Interface is the most significant feature. It determines how the device is connected to the motherboard, which controller is used, how to read and write, etc. The main and most common interfaces are IDE, SATA and SCSI.
Disks with an IDE interface are not expensive, but the main drawbacks are a limited number of simultaneously connected devices (maximum four) and a low data transfer rate (even if it supports direct access to Ultra DMA memory or Ultra ATA protocols (Mode 2 and Mode 4). Although it is believed that their use allows to increase the read / write speed to 16 Mb / s, but in reality the speed is much lower. In addition, to use the UDMA mode, you need to install a special driver, which, in theory, it should be bundled with the motherboard.
Speaking about what constitutes the principle of operation of the hard drive and the characteristics, you can not ignore the SATA interface, which is the successor to the IDA ATA version. The advantage of this technology is that the read / write speed can be increased up to 100 Mb / s due to the use of the high-speed Fireware IEEE-1394 bus.
Finally, the SCSI interface is the most flexible and fastest in comparison with the previous two (write / read speed reaches 160 Mb / s and higher). But such hard drives are almost twice as expensive. But the number of simultaneously connected information storage devices is from seven to fifteen, the connection can be made without disconnecting the computer, and the cable length can be about 15-30 meters. Actually, this type of HDD is mostly used not on user PCs, but on servers.
The speed characterizing the transmission speed and I / O throughput is usually expressed by the transmission time and the amount of transmitted sequential data and is expressed in Mb / s.
Some advanced options
Speaking about what constitutes the principle of operation of a hard disk and what parameters affect its functioning, one cannot ignore some additional characteristics that can affect the speed or even the life of the device.
Here, in the first place is the rotation speed, which directly affects the search and initialization (recognition) time of the desired sector. This is the so-called hidden search time - the interval during which the necessary sector is rotated towards the read head. Today, several standards are adopted for spindle speed, expressed in revolutions per minute with a delay time in milliseconds:
- 3600 - 8.33;
- 4,500-6.67;
- 5400 - 5.56;
- 7200 - 4.17.
It is easy to notice that the higher the speed, the less time is spent searching for sectors, and in the physical plane - on the disk revolution before setting the desired positioning point for the plate for the head.
Another parameter is the internal transfer rate. On external tracks, it is minimal, but increases with a gradual transition to internal tracks. Thus, the same defragmentation process, which is the movement of frequently used data to the fastest areas of the disk, is nothing more than transferring them to the internal track with a higher read speed. External speed has fixed values and directly depends on the interface used.
Finally, one of the important points is related to the presence of a hard disk of its own cache memory or buffer. In fact, the principle of operation of a hard disk in terms of using a buffer is somewhat similar to RAM or virtual memory. The larger the cache (128-256 Kb), the faster the hard drive will work.
Key HDD Requirements
The basic requirements that are in most cases presented to hard drives are not so many. The main thing is a long service life and reliability.
The main standard for most HDDs is the service life of about 5-7 years with an operating time of at least five hundred thousand hours, but for high-end hard drives this figure is at least a million hours.
As for reliability, the SMART self-test function is responsible for this, which monitors the status of individual elements of the hard drive, constantly monitoring. Based on the collected data, even a certain forecast of the appearance of possible malfunctions in the future can be formed.
It goes without saying that the user should not be left out. So, for example, when working with the HDD, it is extremely important to observe the optimum temperature regime (0 - 50 ± 10 degrees Celsius), avoid shocks, bumps and drops of the hard drive, dust or other small particles getting into it, etc. By the way, many will it is interesting to know that the same particles of tobacco smoke are approximately two times the distance between the read head and the magnetic surface of the hard drive, and human hair is 5-10 times.
Initialization issues in the system when replacing a hard drive
Now a few words about what actions should be taken if, for some reason, the user changed the hard drive or installed an additional one.
We will not fully describe this process, but dwell only on the main stages. First, you need to connect the hard drive and see in the BIOS settings whether the new hardware has been determined, initialize and create a boot record in the disk administration section, create a simple volume, assign it an identifier (letter) and perform formatting with the choice of the file system. Only after that a new “screw” will be completely ready for work.
Conclusion
That, in fact, is all that briefly touches on the basics of the functioning and characteristics of modern hard drives. The principle of operation of an external hard drive was not considered in principle here, since it is practically no different from that used for stationary HDDs. The only difference is only in the method of connecting an additional drive to a computer or laptop. The most common is a USB connection, which is directly connected to the motherboard. At the same time, if you want to ensure maximum performance, it is better to use the USB 3.0 standard (the port inside is colored blue), of course, provided that the external HDD itself supports it.
For the rest, it seems, many at least a little understood how a hard drive of any type functions.Perhaps, too much technical information was given above , especially even from the school course in physics, nevertheless, without this, it will not be possible to fully understand all the basic principles and methods laid down in the technologies for the production and use of HDD.