Several decades ago, it was believed that the affinity of languages speaks of the obligatory consanguinity of peoples, while the Aryan race and the corresponding languages did not attract too much public attention. Some time passed, and in Oppert's works, ideas were voiced that Aryan languages exist, but such a race does not exist in principle. What is it about?
general information
Today, some people believe that Aryan is a word that can describe something linguistic, but it does not have a special connection with ethnicity. All such dialects are supposedly of the same root, but the peoples speaking them are not native by blood. At the same time, it is recognized: at first one race was to appear, which began to use it. It is she who probably applies such languages to this day. Who could it be? Linguists, philologists, historians began to search for the answer to this question.
Before the separation, the Aryans, that is, the peoples who used languages from the Indo-European family, were probably shepherds, led a nomadic lifestyle, and therefore spread over large areas. Gradually, the number of people increased, nationality included different tribes. The Aryan dialect came to others and changed at the merger. Studies by archaeologists and anthropologists suggest that at least two of the four European races of the Neolithic are not associated with the Aryans. If we analyze the two remaining, we can assume that the Aryans were the so-called short-headed, who lived in central European areas.
Types and forms
If you ask a linguist what languages are currently in the Indo-European group, he will mention nine major families. These are Indians and Greeks, Slavic and Lithuanian people, as well as living in Armenia, Italy. The Celts, Teutons, Letts belong to the same group. Previously, there were many more families. Over the centuries, they have completely disappeared. Thracians are among those who have disappeared. No less illustrative examples are Dacians, Phrygians. Relations between some families are closer, so they can be grouped into blocks. This combination allows you to get six main categories out of nine: Indo-Iranian, Lithuanian-Slavic, Celtic-Italian. In addition to them, the Greeks, Armenians, Teutons are distinguished.
An analysis of the features of Sanskrit, Zenda showed an amazing similarity between these two dialects. The results of research work have suggested the presence of some producing, common for these adverbs, language. In science, it was designated Indo-Iranian. Subsequent studies on the Slavs proved the closeness of the Lithuanian dialects and languages of the Slavic peoples. At the same time, an abundance of the common language of the Lithuanians and the Teutonic dialect is recognized. A study of classical philological works made it possible to determine that previously there were only two types of literature related to Aryan dialect. It was suggested that the two main languages for the classics (Latin, Greek) were related, literally fraternal languages, between which there are many connections. Such calculations have now found opposition in the form of a belief in a closer relationship between the Celts and Italians. But the language inherent in the Greek people from the Indo-European family, according to the linguists of our day, is closer to the language spoken by the Armenians, as well as to the Indo-Iranian.
Terms and Definitions
To understand which languages belong to the Indo-European, it is necessary to recall the ethnic groups that lived on the territory in ancient times occupied by India, Iran. In those days, people in these lands called themselves "Arya", and it was from this word that the name "Aryan" was formed. The Indo-Iranian group is a specific branch, which is inherent in matching vocabulary, grammar systems to Iranian dialects, Indo-Aryan. For these languages, the constancy of the ratio of sounds is characteristic. The Vedas, Avesta, cuneiform writing of the ancient Persians prove the similarity of dialects, which today are included in the Indo-European group. The Indo-Iranian language, which became the ancestor of the later ones, eventually split into two branches: Iranian, Indian. So there were new proto-languages. They are the foundation of those separate languages that will become known to us later.
Focusing on information about ethnic groups speaking Indo-European languages, they tried to form a single idea of the cultural condition of Indo-Iranian people. For the first time, Spiegel, who was known as the leading Iranian of his time, took up this. He formulated a list of terms characteristic of Indo-Iranian dialects. They are mainly used to refer to divine entities, images from mythology, as well as military activities. The proximity of the languages forming this group is so unique that the original theory was almost never criticized.
How many, how many
To understand in the Indo-European family which languages belong to the number of Indo-Iranian, one should turn to the eastern lands. The Indo-European language tree is a unique, enormous entity, and the Indo-Iranian is only one of its many branches. It is customary to divide into Iranian, Indo-Aryan sub-branches. In total, the Indo-Iranian group is currently a language unit used for communication by approximately 850 million people. Among all the groups that make up the Indo-European tree, it is rightfully considered the most numerous.
The Indian dialects used today are New Indian languages. They are used in the central Indian regions, in the north of the country. They are common among Pakistanis and Nepalis; Bangladeshis, inhabitants of the Maldives, Sri Lanka use them to explain. Modern linguists recognize the complexity of the current language situation in such powers. The Indian south are occupied by people who speak different variations of the Indo-Aryan, here they use the dialects referred to the Dravidian group with might and main. New Indian dialects include Hindi, Urdu. The first is used by the Indians, the second is used by Pakistanis and the inhabitants of some parts of India. The Hindu script is based on the Devanagari system, but for the adherents of Urdu, Arabic characters and rules are the basis for writing.
Different and not so
Modern linguists know well which languages of the Indo-European group are close to each other. In particular, considering Hindi, Urdu, they note an amazing similarity. Literary variants of adverbs are similar to each other almost like two drops of water. The key difference is the chosen form for writing words. By analyzing colloquial forms of language, Hindustani is evaluated. The dialect used by Muslims is practically indistinguishable from that used by Hindus.
Bhili, Bengali, Nepali and many others are included in the same group of languages. New Indian languages included in the same family include a gypsy dialect. It can be found not only within the territories where Indo-Aryan dialect is used, but also beyond. Our country is no exception.
Historical context
The Indo-European language family belongs to ancient groups uniting a huge number of people. Literary linguistic forms characteristic of the Indian people are distinguished by a rich historical past. It is known that the most ancient version of writing is Vedic, the language of the Vedas. It is on it, as historians know for certain, that sacred songs were recorded, spells were recorded. It was used to record religious hymns. Linguists praise the knowledge of the Rig Veda, that is, the leading of hymns. This collection was first created around the end of the second millennium before the start of the current era.
The Vedic dialect was replaced by Sanskrit over time. This language is characterized by two main forms. The epic was used to create the Ramayana. The authors of the Mahabharata used the same form of language. Both poems are famous all over the world because of their huge size. The same Sanskrit was used to fix classical literature. Creations are predominantly voluminous. They are characterized by a wide variety of genres. Surprisingly, even brilliantly, the performance of works. The language of the Vedas, Sanskrit in total is an ancient Indian dialect. Sanskrit grammar was first recorded in the fourth century before the beginning of the current era, the author of the collection is Panini. To this day, this creation is a model for any description in the field of linguistics.
Times and Terrain
Indo-European languages include not only new and ancient languages. Between them, along the timeline, are Central Indian. There are a lot of such dialects. They are called prakrit. The word is derived from the term "natural", written in Sanskrit. Near the end of the 18th century, European scholars appreciated and were surprised at the qualities of Sanskrit - a strict and very beautiful language. Then they noticed for the first time how much it has in common with European dialects. In many ways, these observations turned out to be the basis for further linguistics. In this area of science, a new direction has appeared devoted to the comparison of different languages and the analysis of their changes and mutual relations, taking into account the historical context.
Iranian languages
Indo-European languages and Aryan peoples are also the Iranian language group. Among all the other groups included in the family, Iranian ones are the most numerous in number. These dialects can be heard these days, being not only in Iran, but also in Afghanistan, as well as performed by Turks, Iraqis, Pakistanis, and Indians. Some ethnic groups of the Caucasus and Central Asian residents communicate in Iranian languages. The Iranian group unites not only a huge number of live communication options, but also an abundance of already exhausted, extinct ones. There are such with writing, but there are those whose carriers have never been able to write. To reconstruct such dialects, modern linguists, philologists use indirect evidence. Of particular interest to scientists, however, are literary languages, and first of all the one that was used for fixing on solid material "Avesta", a collection of holy texts of Zoroastrians. Modern scholars know this dialect as Avestan.
Of the languages that did not know writing, Scythian is curious. It was spoken in the lands adjacent to the Black Sea from the north, it was also used by people who lived on modern South Ukrainian lands. Scythian was previously used by Caucasian residents. It is believed that the language died out about one and a half millennia ago. As some scientists are sure, the linguistic heritage can be seen among the inhabitants of North Ossetia.
Among the peoples belonging to the Indo-European family of languages, Iranians deserve attention. The ancient Iranians are Scythians and Sarmatians. These peoples lived next door to Slavic tribes, regularly contacted with their representatives. The result was an abundance of borrowing. These include the words familiar to us - a hut, an ax. From Aryan languages pants and boots came to us as words. The fact that the Iranians lived in lands close to the Black Sea, toponyms say. In particular, it was they who came up with the names Don, Danube. From here came the names Dniester, Dnieper.
Similarities and differences
Linguist Schmidt, studying the ancient Aryan languages and the peculiarities of the dialects, came to the conclusion that there are hundreds of words between Indo-Iranian and Greek common. If we compare Latin with Greek, then we can find 32 similar words. Such partially are words associated with the designation of vegetation, representatives of the animal world, as well as general terms from the themes of civilization. It makes sense to assume that they came from both of these languages from somewhere else. If you pay attention to the connection of languages, you also have to admit that such specific features as increment, doubling, aorist are the hallmarks of Indo-Iranian, Greek. These same ways of speaking have their own unique non-final moods. The six divine names known to the Greeks are well explained by Sanskrit, but only three have similarities with the words used in Latin.
An analysis of the dialects belonging to the Indo-European family of languages, peoples and the features of their life recorded in these dialects allows us to note curious features, similarities and differences. For example, the terms used to designate objects, phenomena related to the life of shepherds, farmers at a time when such a direction was only developing, are quite similar in Latin and the Greek language. But the terminology associated with military affairs in these languages is fundamentally different. The words used by the Greeks often coincide with Sanskrit, while the Latin ones are as close as possible to the Celts used. Certain conclusions about language connections follow from the analysis of numerals. In ancient times, the Aryans knew only a score within a hundred. The term thousand is the same among the Greeks in Sanskrit, but differs in Latin. Latin, the Celtic language, has a similar word to describe a thousand. In this aspect, there is a similarity between the Germanic languages and the one used by the Lithuanians.
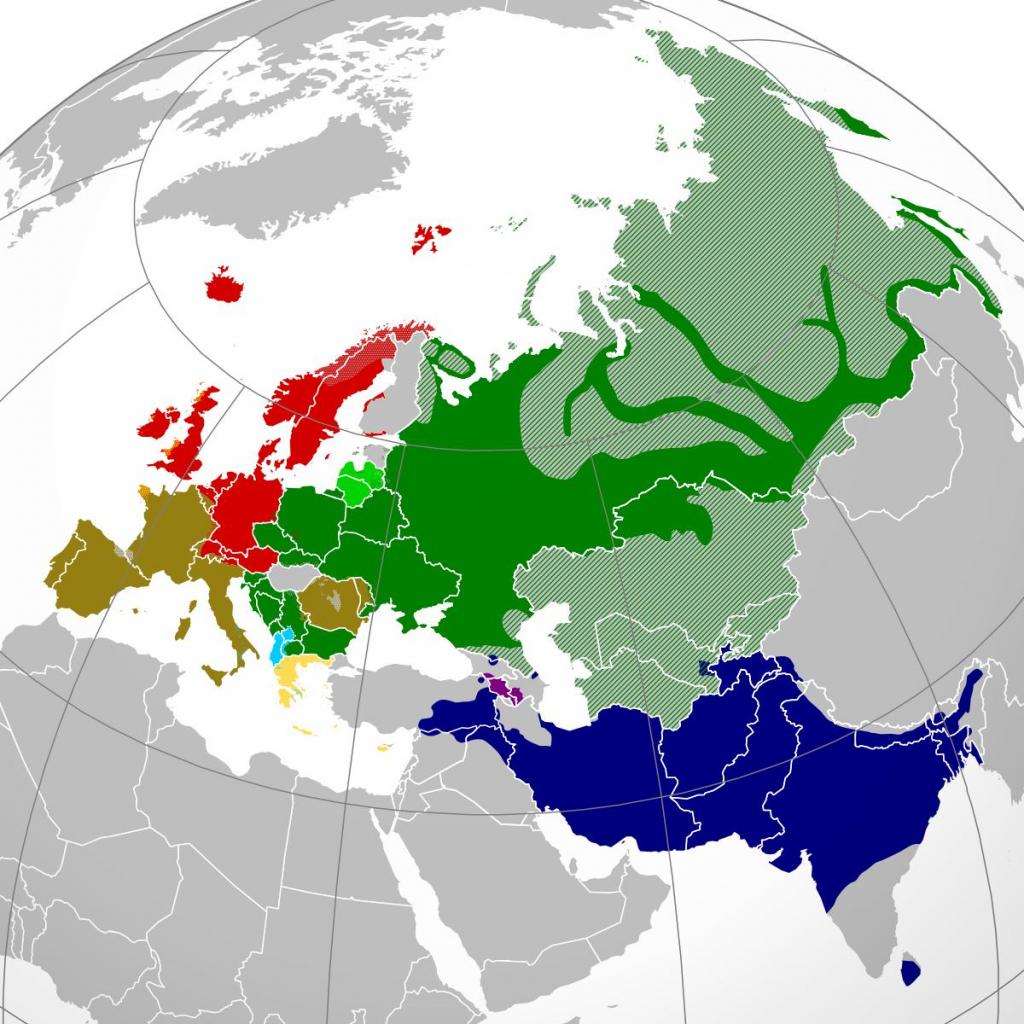
What does it mean?
Based on these facts, it can be assumed that Greek, Latin have been divided for a long time. Similarly, the separation of Latin and Lithuanian happened early. At the same time, Latin and the Celtic language were divided relatively recently. Also, at a fairly late period, Indo-Iranian, Greek separated. Not so long ago, apparently, there was a separation of Lithuanians and German nationalities.
History and Travel
In order to correctly assess what the Aryan group of languages is, it makes sense to turn to history, which makes it possible to understand at what point the Indo-Iranian groups lived in the modern Russian south. Presumably, the decay into separate branches occurred in 5-4 millennia before the beginning of the current era. In those days, the ancestors of the Balts and Slavs probably lived next door to Indo-Iranian peoples. At the end of the fourth or beginning of the third millennium BC, Indo-Iranian tribes moved to the eastern lands, passing the northern regions near the Black Sea. The Kuban lands were replenished with Maikop culture, the Novobvodninsky component appeared, which modern historians also associate with the Indo-Iranian peoples. Probably, here comes the mound culture. From the north, nationalities coexisted with the Balts, which in previous centuries were much more widespread than today. This fact is confirmed by the fact that the word "Moscow" also has an etymology of the Baltics.
In the second millennium BC, the Aryans planted log cabins in the steppe areas up to the Altai territories. Some believe that they were spread even further east. In the southern lands, they spread to Afghanistan. In these places in those days, the spread of the Andronovo Aryan language and the culture corresponding to it was observed. Currently, scientists know that the centers of Andronovo culture were Arkaim, Sintashta. The culture is associated with Indo-Aryan people, although some compare that it is due to the influence of proto-Iranians. The latest hypotheses suggest considering Andronovites as the third Aryan branch. Presumably, such a nation had its own, fundamentally different language. This branch possessed features of both Iranian dialects and similarities with Indo-Aryan dialects.
Grammatical progress
Researchers who devoted themselves to the peculiarities of the development of the Aryan group of languages found that for this type of dialect one of the oldest changes in morphology was that it allowed to stand out from the Celts and Italians. There was a passive voice, new options for designating the future. Formed new grammatical ways to reflect the past perfect. Modern linguists, philologists, analyzing information about these grammar features, suggest that the Celtic-Italian variants of speaking stood out from the general group at a time when other Aryan speaking variants were still unified. The unity of Celtic, Italian is not so obvious as Slavic, Lithuanian, Indo-Iranian. This is due to a more ancient origin.
In the study of Aryan languages, it was possible to determine a substantially less profound similarity between the Celtic and the Teutonic language than the Celts and Latin. Mostly similarities are characteristic of words related to the phenomena of civilization. At the same time, a minimum of total was revealed in morphology. It is assumed that this speaks of superiority in the field of politics, the proximity of geographical zones, while not indicating primitive unity.
Teutonic, Slavs and Lithuanians
The Aryan languages used by these peoples have a deep resemblance.It is relatively complete, since it covers both words reflecting civilizational phenomena and grammatical features. The Slavs, the Teutons finally divided, apparently, not so long ago. The languages of these peoples have similarities in the terminology that describes metallurgy, but weapons, maritime affairs are areas in which different words are used. If we compare the similarities of the Slavs, Lithuanians, Teutons, you can see deep mutual relations, and the most obvious version of the demonstration is the replacement of the original symbol "bx" by "m" in a number of cases at the end of the word. A similar variation is not characteristic of any other dialect of the same group.

At the same time, the similarity of Indo-Iranian, Slavic-Lithuanian belonging to the Aryan languages is spoken by 16 words known to linguists, philologists, in which “k” is replaced by “s”. Such a replacement is not characteristic of the Teutonic language. In Iranian word is “bhaga”, adopted to describe the supreme divine essence. It was also used by the Phrygians, Slavs. Nothing of the kind could be found in the languages of the Greeks, Latin. Accordingly, we can confidently talk about a single family of Slavic-Lithuanian, Iranian, Teutonic dialects. At the same time, they recognize that the Greek language strove for Italian, Iranian in its various aspects.