Drifter fishing is fishing that is carried out by drifters - fishing vessels. The vessel drifts with the current and the wind together with a very long network, the so-called drift order, or floating networks, making up a single system. The length of the networks can reach 50 km. These nets catch moving fish. The need for drift nets arose in connection with the need to catch some species of fish that are kept sparse. In this way, tuna is caught, salmon, mackerel and herring are harvested.
Network Features
Drifter (or smooth) nets are a net web that the fish do not regard as an obstacle, so it pulls the cells very tightly, tightly entangled in them without the ability to escape. Rectangular individual networks 10-12 m high and 30 meters long are connected to each other in a single drift order, the basis of which can be a leader rope, and buoys and floats support this system at a given depth. Drifter nets are used for commercial fishing from drifters.
Materials used
The tackiness of gear depends on many factors, including the material and thickness of the thread, the size of the cells, dyeing, planting the canvas on rebounds. If previously used vegetable threads, including cotton from twisted yarn, now the most commonly used and more durable fishing nets are nylon, as well as nylon, amylan and the like from artificial fibers.
Monofilament fishing nets (fishing lines), the so-called vein networks, demonstrate high efficiency. The main advantage of these gears is their transparency. Even in daylight, the catch in transparent water is very high, while well-painted nets of other materials can scare away fish. In addition, they have higher stiffness than twisted filaments, which keeps the cells straightened and prevents the networks from getting tangled and dirty. Although stiffness complicates the work with them a little and increases the volume, requiring more space on the deck.
Constructive types of networks
By their structure, fishing gear can be single-walled gill, double-walled or three-walled. The last two species are also called "prostitutes." The most effective are three-walled fishing nets, consisting of three net webs. Outside there are large-sized canvases, called rez (ryazh, rez), and in the middle there is a smaller part (del). All three canvases are planted on the same rebounds, but the particle has a large length and is located between the outer layers with significant slack. Passing through the cut, the fish gets entangled in a piece, falling into a net bag. Double-walled consist of two canvases with different mesh sizes and are effective when it is known exactly which side the fish is coming from.
For drifter fishing, kapron fishing nets from monofilament or from nylon monofilament are most often used. Rebounds are also taken nylon. The most effective three-wall smooth networks.
Drift order construction types
Networks can be interconnected in different ways. Three main types can be distinguished: simple, with an upper or lower leader. Small simple orders can be used in the coastal zone, but in the open sea a more reliable construction is necessary, therefore orders with leaders are used to ensure the integrity of the order and increase reliability.
Simple order
For a small drift order, sometimes several separate networks are connected sequentially between each other by the lower and upper ears. So get a simple drifter order. It is used in lakes and marine coastal areas by small vessels. Most often it includes only 15-20 networks, but when they take more, they generally do not exceed 1-1.5 km.
Buoys are attached to buoy leads, which keep order afloat. The desired horizon is set by adjusting the length of the leads. From below, the network is heavier, placing the load in the lower selection. On both sides of the order there are also burns. In front of them they fasten with a stopping end - a rope that goes directly to the ship, and behind the rods they are connected to the beacon end - a rope fixed on the lighthouse. This lighthouse (a lantern or pennant mounted on a buoy with a weight) shows where the order ends.
To organize such an order is easy, but for long networks, and even more so for use on the high seas, it is not suitable. The tension of the networks during the drift is very high, therefore, with such an organization, the order may tear off the vessel or it will be destroyed.
Leader's appointment
To significantly reduce the risk of breakage, the so-called leader is used - a thick rope, to which order is attached along the entire length. Fishing involves combining together up to 100-150 nets. The tension during drift falls on a reliable leader, and not on the network itself. Separate networks are attached not only to each other, but also to the leader, which also strengthens the design.
The leader himself can be divided into three parts: the leader himself, the locking (parking) end for connecting to the vessel, and the beacon end for attaching the beacon. It turns out that the leader is attached to the ship, which holds the network. The parking end is made as strong as possible. Its length can reach 200-500 m, which depends not only on the depth to which the order plunges, but also on the state of the sea and wind strength.
When sampling networks, traction is carried out by the leader. This allows you to mechanize the production process. In addition, automatic machines are used to control the leader’s tension, if necessary, bleed him to reduce excess tension.
Leader Features
Depending on the fishing technique and the type of vessel itself, the required length of leads is set to make it convenient to select drift nets: the leader is selected through the Malgoger, and the net must reach a certain place on board, the leads should just provide the required distance. On small vessels it is only 1.5-2 meters, and on large vessels it can reach 10 m.
Due to the fact that the leader's tension decreases with distance from the ship to the lighthouse, the leader is often made composite, reducing the thickness of the rope. Additionally, this reduces the cost of the order and reduces the weight of the order. But to prevent sagging near the end of the network due to lower tension, sometimes floating anchors are added to the lighthouse or the distance between the buoys is changed.
Order with the lower leader
To organize the order with the lower leader, the individual drift nets are connected into a single whole also for the upper and lower ears, but at the same time, the leader goes under the nets throughout the order. It is connected to the networks with leader lines using quick-disconnect nodes. Buoys are kept afloat, which are attached with streamers at the junction of networks or to the upper selection. The depth of the nets depends on the length of the leads. Additional cargo at the bottom is not required, since the leader himself serves as a load, stretching the network.
Apply this order for shallow depths, immersing the network at 30-40 m. It is convenient to operate. For marking and sampling the order you have to work only with leader streamers, without the hassle of sinkers.
Top Leader Order
If necessary, fishing at great depths often use the order with the top leader. In this case, it passes over the networks. Buoy leads are attached to him, sometimes reaching a length of more than one hundred meters. Between themselves, buoys are connected by a wire-conductor for the convenience of sampling. The leader leads are connected to the upper selection or to the nets of the nets. On the lower rebounds, you have to add a load in the form of cast-iron sinkers.
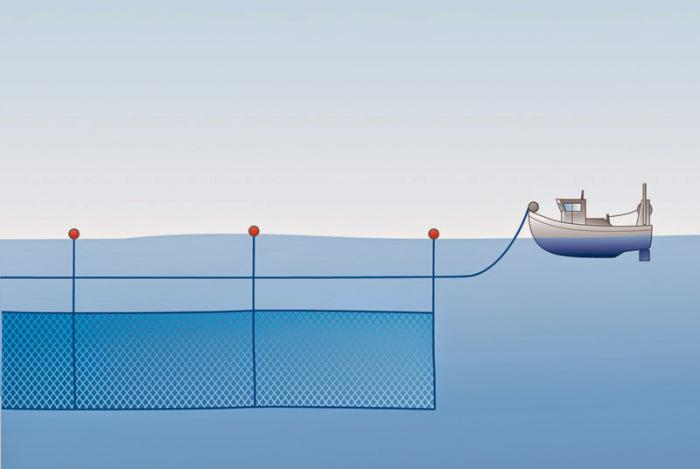
It is more difficult to work with this order than using the lower leader, since it is necessary to organize the loading, and the buoy conductor requires additional attention. However, such drift fishing is a necessity when fishing at great depths. In this case, the lower leader can wrap nets over himself when sampling or even pulling, so he does not apply. In addition, the damping of buoys can also be added to the advantages of the top leader, so the networks will be more calm. The downside is the risk of detachment of the buoy itself at large waves.
In fact, different-depth orders are sometimes used to determine where a particular fish is located. To do this, often create combined types of orders.
Harm from drifting networks
In some regions fishing with drift nets is prohibited. So, do not use it in the North Pacific Ocean in order to preserve the stocks of some species of fish. Large-scale drift fishing is prohibited by the UN General Assembly in the open waters of the oceans. Scientific fishing is allowed by such networks, but this feature is often abused. There is no complete prohibition of drift fishing, but shortened terms and some restrictions on this type of fishing have already been established .
Drift nets often include marine mammals and seabirds, which are killed in doing so. The numbers are just awesome. So, only in the Far East in the Russian economic zone, over 100 thousand birds and 2.5 thousand mammals die annually because of this. And the populations of salmon themselves are declining.
Another serious threat is the attitude of the fishermen themselves. This is often the way salmon is hunted - the most valuable salmon, while the rest of the fish, including young salmon, other salmon breeds, pink salmon and chum salmon are simply thrown overboard. This sorting destroys aimlessly huge amount of fish, which is a violation of fishing rules.