Many foreigners say that the Russian language is very difficult to learn. It is especially difficult with words that are not written as they are heard, or similar in sound to a radically different word. We are talking about homophones, to which we will devote this article.
A homophone is ...
Let’s figure out what it is. The list will help us:
- A couple or more words that sound the same, but are written differently and have completely different meanings.
- Phonetic (sound) ambiguity.
- Phonetic homonyms (from the Greek. - "the same sounds").
Homophones in Russian are formed thanks to the following sources:
- Change the vowel sound in an unstressed position.
- Stunning consonants when the latter are placed at the end of a word or before another consonant.
To make it easier for you to understand what we are talking about, we’ll give specific examples of homophones.
Homophones: examples of words and phrases
We will get acquainted with various types of this phonetic phenomenon. Examples of homophonic words:
- Stunning consonants: meadow-onion, rod-pond, cat-code, threshold-vice, opened-boiled, case-fall, cry-cry.
- Merging with the second consonant: score.
- Vowel reduction: give-betray, ghost-cast.
- Coincidence of the sound of the verb in the infinitive and the 3rd person of the present or simple future tense: it is necessary to decide - it will be decided today, we will build it - the village is being built.
You can also find examples of homophones-phrases - both the coincidence in the sound of one word and the whole phrase, and the coincidence of two phrases. Sometimes the only difference is the location of the space. For instance:
- pine - from sleep;
- not mine - dumb;
- skid - behind the nose;
- I carry different things - awkward things;
- in place - together;
- manure - for carriage;
- for business - hurt;
- from the hatch - and the cruel one.
In context, it looks like this:
- This warrior could stand up for his entire clan. In a public place you need to shut your mouth when yawning.
- He was always drawn to the sea, Paul said that it was his element. At this sad hour, I am writing you poems.
- What does it have to do with what I once told you? I already navigate in this area, and without the help of a navigator.
- It was decided to continue the movement, avoiding even the slightest delay. From line to line, Valya re-read her mother's letter again.
- I was again drawn to green meadows, noisy waterfalls, uncharted forests, brown rocks. Whatever he says, it seems that his speech is intertwined with a pun.
- Every day I go the same way, but I carry different things. She simply could not keep within her head these truly absurd things.
Origin of the concept
Homophone is a borrowed word. It came from the ancient Greek ὁμόφωνος, which means "speaking the same language", "consonant", "consonant". According to another version, the concept was formed from a combination of two ancient Greek words: ὁμός - "equal", "equal" and φωνή - "sound", "voice".
Similar concepts
Do not confuse homophones with related terms:
- Homonyms are completely identical both in sound and in writing morphemes, words and other units of the language; their cardinal difference is in meaning. Example: broadcasting broadcasting and broadcasting - organic matter.
- Homographs - such words are the same in spelling, but completely different in pronunciation. A castle with an emphasis on the first syllable and a castle with an emphasis on the second.
- Homoforms are the so-called graphic homonyms. Different words that coincide in spelling only in a specific grammatical form. For example, I fly - the verbs "fly" and "heal", I pay - the infinitives "cry" and "pay".
- Omomorphs are various morphemes (parts of a word - prefixes, roots, suffixes, endings) that coincide both in spelling and pronunciation, but have different meanings. A striking example is "a". It may be the ending of a noun in the plural (city), the ending of a noun in the genitive case (I’m at home today), the end of the past tense verb (accepted).
- Paronyms are words that have a similar sound and morphemic composition, but different meanings. Destination addressee, blood-bloody, subscription-subscription.
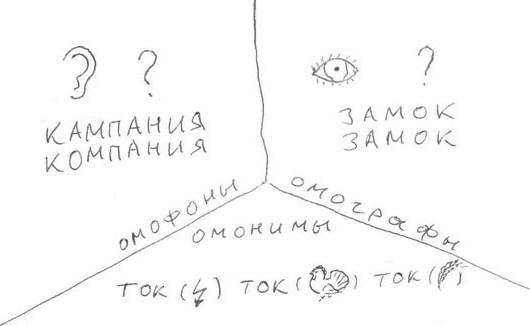
Homonyms are divided into:
- Full - words that match all forms. Note that homographs from this type of homonyms are distinguished by the fact that they can different parts of speech.
- Partial - not all absolutely word forms coincide.
- Grammatical - one, several forms coincides.
Homophones in other languages
Examples of homophonic words can be found not only in the Russian dialect:
- French is distinguished by the fact that it is extremely rich in homophones. The reason for this is that the vast majority of the final letters in it are not readable. Such a homophonic chain can line up: ver - verre - vers - vert.
- English learners also often had to be in a quandary due to frequent meetings with homophones. This is due to the fact that equally vowel and consonant sounds in this adverb are indicated in letters by completely different letters. For example: knew - new, bear - bare, whole - hole.
So, homophones are words that we pronounce the same way, but here we write in different ways, and the meaning in each of them is radically different. It is difficult for native speakers to get confused in this kind of phonetic ambiguities, but for Russian learners, homophones can become a serious problem.