Electrical engineers know what electrical stations and substations are, what they are intended for and how they are designed. They know how to calculate their power and all the necessary parameters, such as the number of turns, the cross section of the wire and the dimensions of the magnetic circuit. This is taught to students in technical universities and technical schools. People with a humanitarian education realize that the structures, often standing apart in the form of houses with no windows (graffiti lovers like to paint them), are needed for energy supply of houses and enterprises, and they should not be penetrated, eerily emblems in the form of skulls and lightning speak eloquently. attached to dangerous objects. Perhaps many do not need to know more, but information is never superfluous.
A bit of physics
Electricity is a commodity that you have to pay for, and it’s a shame if it is spent in vain. And this, as with any production, is inevitable, the task is only to reduce wasted losses. The energy is equal to the power multiplied by time, so in further considerations you can operate on this concept, since time flows constantly, and it is impossible to turn it back, as the song says. Electrical power, in a rough approximation, excluding reactive loads, is equal to the product of voltage by current. If we consider it in more detail, the cosine phi, which determines the ratio of energy consumed with its useful component, called active, will fall into the formula. But this important indicator is not directly related to the question of why a substation is needed. Electric power, therefore, depends on the two main participants in Ohm and Joule-Lenz laws, voltage and current. Small current and high voltage can produce the same power as vice versa, high current and low voltage. It would seem, what's the difference? And she is, and very big.

To heat the air? Dismiss
So, if you use the active power formula, you get the following:
- P = U x I, where:
U is the voltage measured in Volts;
I is the current measured in amperes;
P is the power measured in watts or volt-amperes.
But there is another formula that describes the Joule-Lenz law already mentioned, according to which the thermal power released during the passage of current is equal to the square of its value times the resistance of the conductor. To heat the air surrounding the power line means wasting energy in vain. And to reduce these losses can theoretically in two ways. The first of these involves a decrease in resistance, i.e. a thickening of the wires. The larger the cross section, the lower the resistance, and vice versa. But you don’t feel like spending metal in vain either, it’s expensive, copper all the same. In addition, the double consumption of the material of the conductor will lead not only to a rise in price, but also to heavier, which, in turn, will lead to an increase in the complexity of installation of high-altitude lines. And the support will require more powerful. And losses will only be halved.
Decision
To reduce the heating of the wires during energy transfer, it is necessary to reduce the amount of transmitted current. This is completely clear, because halving it will lead to a reduction in losses by four. And if ten times? The dependence is quadratic, which means that losses will become a hundred times less! But the power should “swing” the same, which is needed by the aggregate of consumers waiting for it at the other end of the power transmission line, sometimes going hundreds of kilometers from the power plant. The conclusion suggests itself that it is necessary to increase the voltage as many times as the current is reduced. The transformer substation at the beginning of the transmission line is just for this. Wires come out of it under a very high voltage, measured in tens of kilovolts. Throughout the entire distance separating a thermal power plant, hydroelectric power station or nuclear power plant from the settlement where it is addressed, energy travels with a small (relatively) current. The consumer needs to get power with the specified standard parameters, which in our country correspond to 220 volts (or 380 V phase-to-phase). Now we need not a step-up substation, like at the entrance of a power line, but a step-down substation. Electrical energy is supplied to the switchgear so that the lights burn in the houses, and machine rotors spin in the factories.
What's in the booth?
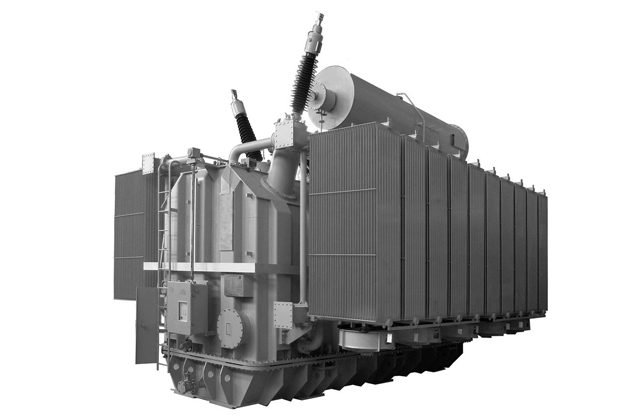
From the foregoing, it is clear that the most important part in the substation is a transformer, usually a three-phase one. There may be several. For example, a three-phase transformer can be replaced with three single-phase. Larger quantities may be due to high power consumption. The design of this device is different, but in any case, it has impressive dimensions. The more power is given to the consumer, the more serious the structure looks. The device of an electrical substation, however, is more complex, and includes not only a transformer. Here is equipment intended for switching and protecting an expensive unit, as well as more often for cooling it. The electrical part of the stations and substations also contains switchboards equipped with instrumentation.
Transformer
The main objective of this facility is to bring energy to the consumer. Before sending, you need to increase the voltage, and after receiving it, lower it to a standard level.
Despite the fact that the circuit of the electrical substation includes many elements, the main one is still a transformer. There is no fundamental difference between the device of this product in a conventional power supply unit of a household appliance and industrial designs of high power. The transformer consists of windings (primary and secondary) and a magnetic circuit made of a ferromagnet, that is, a material (metal) that enhances the magnetic field. The calculation of this device is a completely standard educational task for a student at a technical university. The main difference between the substation transformer and its less powerful analogues, which is striking, in addition to dimensions, is the presence of a cooling system, which is a combination of oil pipelines encircling heating windings. The design of electrical substations, however, is not an easy task, since many factors must be taken into account, starting from climatic conditions and ending with the nature of the load.
Traction power
Not only residential buildings and enterprises consume electricity. Everything is clear here, you need to apply 220 volts of alternating current relative to the neutral bus or 380 V between phases with a frequency of 50 hertz. But there is also urban electric transport. Trams and trolleybuses do not need a constant voltage, but a constant voltage. And different. The tram’s contact wire must have 750 volts (relative to the ground, i.e. rails), and the trolleybus needs zero and 600 volts DC on the other, the rubber treads of the wheels are insulators. So, we need a separate very powerful substation. Electric energy is converted on it, that is, rectified. Its power is very large, the current in the circuit is measured in thousands of amperes. Such a device is called draft.
Substation Protection
Both a transformer and a powerful rectifier device (in the case of traction power supplies) are expensive. If an emergency occurs, namely a short circuit, a current will appear in the secondary circuit (and therefore the primary). Hence, the cross section of the conductors is not calculated. An electrical transformer substation will start to heat due to resistive heat dissipation. If such a scenario is not foreseen, then as a result of a short circuit in any of the peripheral lines, the wire of the windings will melt or burn. To prevent this from happening, various methods are used. These are differential, gas and maximum current protection.
Differential compares the current values in the circuit and the secondary winding. Gas protection is triggered when insulation products, oil, etc., appear in the air. Current protection trips the transformer when the current exceeds the maximum value.
The transformer substation should automatically turn off also in the event of a lightning strike.
Types of substations
They are different in power, purpose and device. Those of them that serve only to increase or decrease the voltage are called transformer. If you also need to change other parameters (rectification or frequency stabilization), then the substation is called converting.
According to their architectural design, substations can be attached, built-in (adjacent to the main object), intra-workshop (located inside the production room), or can be a stand-alone auxiliary building. In some cases, when high power is not required (when organizing the power supply of small settlements), the mast construction of substations is used. Sometimes for the placement of a transformer, power transmission towers are used, on which all the necessary equipment is mounted (fuses, arresters, disconnectors, etc.).
Electric networks and substations are classified by voltage (up to 1000 kV or more, that is, high voltage) and power (for example, from 150 VA to 16 thousand kVA).
According to the schematic feature of the external connection, substations are nodal, dead-end, walk-through and branch.
Inside the camera
The space inside the substation, in which transformers, buses and equipment are located, ensuring the operation of the entire device, is called a camera. It can be fenced or enclosed. The difference between the ways of its alienation from the surrounding space is small. A closed chamber is a completely isolated room, and the fenced is located behind non-continuous (mesh or lattice) walls. They are made, as a rule, by industrial enterprises according to standard designs. Maintenance of energy supply systems is carried out by trained personnel who have access and the necessary qualifications, confirmed by an official document on permission to work on high-voltage lines. Operational monitoring of the substation is carried out by an on-duty electrician or power engineer located near the main switchboard, which can be located remotely from the substation.
Distribution
There is another important function that a power substation performs. Electric energy is distributed between consumers according to their standards, and in addition, the load of the three phases should be as uniform as possible. In order for this task to be successfully solved, switchgears exist. The switchgears operate at the same voltage and contain devices that switch and protect the lines from overload. The switchgear is connected to the transformer by fuses and interrupters (unipolar, one for each phase). Distribution devices at the location are divided into open (located in the open air) and closed (located indoors).
Security
All work carried out in an electrical substation is classified as particularly risky, therefore they require emergency measures to ensure occupational safety. Mainly repairs and maintenance are carried out with full or partial blackout. After the voltage is turned off (electricians say "removed"), subject to all the necessary tolerances, the busbars are grounded to prevent accidental switching on. The warning signs “People work” and “Do not turn it on!” Are also intended for this. The staff servicing the high-voltage substations is systematically trained, and the skills and knowledge gained are periodically monitored. Admission No. 4 gives the right to perform work on electrical installations over 1 kV.