The problem of copying large files to ordinary flash drives and removable memory cards occupies the minds of many ordinary users. And very often they blame it on removable drives, although the problem here is completely different. Next, it is proposed to understand how to drop a large file on a USB flash drive and as much as possible. But first, let's look at the problem itself and find out what causes the occurrence of such situations.
Why can’t I drop a large file on a USB flash drive?
Apparently, it makes little sense to talk about which files in most cases are of such size that it can be simply impossible to transfer them to a regular flash drive. As a rule, most often the copying problem arises with files of modern video formats, which, depending on the quality of the material, can be quite impressive in size. Think of at least the amount of data stored on the same Blu-ray discs. And ordinary DVD movies with high quality and length of space can take up no less. The same can be said about some installation distributions, which may contain specialized databases in the form of a single or several large files. Very often this refers to virtual synthesizer libraries, which are now widely used in musical computer sequencers and studios.
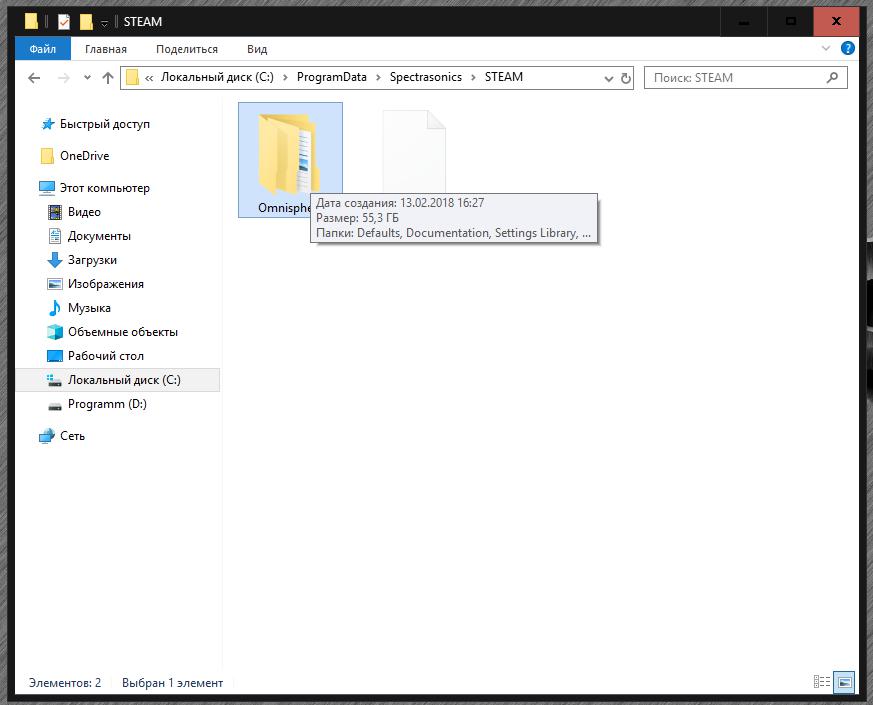
For example, the instrument file of the popular Omnisphere 2 synthesizer takes up more than 50 GB. And transferring such an object to removable media is not only long, but also impossible (and not at all because of the limitation of the volume of the flash drive itself). The main problem is that for all flash drives, the FAT32 file system is used by default, which has its own limitations due to the fact that it does not know how to work with file volumes of more than 4 GB. The actual file size, of course, is determined, but it is impossible to take actions to move or copy such objects in it.
Using formatting in NTFS
How to throw a large file on a USB flash drive if it has the above structure? Apparently, many have already realized that it needs to be transformed. To perform such actions, the easiest way is to use the most common drive formatting with NTFS as the final file system.
In this case, it is completely optional to use full formatting, but you can limit yourself to a quick or so-called clearing of the table of contents. In any Windows-system, access to this tool can be done directly through the PCM context menu on the selected medium.
Note: similar to the standard process, formatting can be performed from the command line or using the same tools to copy the file to an external device. Due to the fact that such procedures look more complicated for ordinary users, they will not be considered. The final effect is still the same.
Additional formatting utilities
Speaking about how to drop a large file onto a USB flash drive, it is worth mentioning some third-party programs that allow you to quickly and easily format any type and any medium.
In most of these programs, both the interface and features are very similar to Windows tools. But some of them (in particular, the HDD Low Level Format Tool) are advisable to apply when problems with flash drives or memory cards are observed due to a change in format, failure of the controllers or other damage of a non-physical nature.
How to write a large file to a USB flash drive without formatting?
But let's assume that the user has a removable drive with information recorded on it, to which you need to transfer a file with a size of more than 4 GB. How to copy a large file to a USB flash drive in such a situation, because you don’t want to format it with the destruction of already recorded files? In this case, you can use the FAT32 to NTFS conversion tool, which means only converting one file system to another without the need to format the drive. Unfortunately for many inexperienced users, this only works in the command console (cmd).
The conversion itself is performed by executing the convert N: / fs: ntfs / nosecurity / x command, where N is the removable media letter displayed in Explorer.
Note: if a volume label is set for the removable disk, you must enter it in order to complete the operation. But the easiest way is to remove it first through the properties section in the "Explorer", and only then start the conversion.
Partition the source object
Finally, let's see how to drop a large file onto a USB flash drive with FAT32 without any formatting or converting the file system to another standard. Since you cannot jump above 4 GB, you need to split the file into parts that will be smaller than this size, and then copy them to the media. But what to use to perform such actions? The most common archiving programs (WinZIP, 7-Zip, WinRAR, etc.) are best suited.
In any such application, you just need to add the file you are looking for and specify the sizes of the parts that will be created during compression. To simplify your work, just from the special list with predefined parameters you can choose just the size corresponding to the maximum in the FAT32 structure. It goes without saying that if you copy a movie this way, it will be impossible to play it on home devices or software players without extracting the contents of the archive.
Note: you can also simply split the source file into parts without compression in the Total Commander file manager.
Brief Summary
That’s briefly and everything that concerns the main solutions related to the problem of how to drop a large file onto a USB flash drive. If you sum up a peculiar result in terms of choosing the best way to copy, it seems the best option is either formatting or converting the file structure to NTFS. The use of archiver programs is advisable only if the compression concerns not multimedia formats that need to be played from a removable device, but ordinary files and folders that need, for example, to be transferred to another computer.