In 2015, the Kazan Helicopter Plant plans to start serial production of the Mi-38 helicopter. Photos of the new machine and its life-size models were presented back in 1989 during the international aerospace exhibition in Le Bourget. Design work began two years earlier, but only in the early nineties the company began to assemble the first prototype. However, the difficulties did not end there. It took more than a decade for a specific practical embodiment to loom in front of this machine. The fact is that the Mi-38 helicopter was conceived as a change to the veteran Mi-8, a well-deserved and beloved aviator in many countries (primarily Russian). The task is responsible, but there is hope that the beginner will not let us down.
Replacing the Mi-8 is a difficult task
Mi-8 has become one of the massive rotary-wing aircraft in the history of world aviation. His first prototype, another single-engine, took to the air in the year of Gagarin’s flight. Worked on the design for a long time and carefully. The helicopter turned out to be almost perfectly in line with the requirements for cargo-passenger class cars. It can be used for a variety of purposes, both civilian and military. Twelve thousand Mi-8 units of several tens of modifications were built. The range of application is wide, from agricultural to airborne assault purposes. The operators became more than fifty countries in different climatic zones of the planet - from the Arctic to the equator and further to the Antarctic. Among the countries that purchased this helicopter are the USA, Canada, South Korea, and Finland.

Mi-8s are manufactured and purchased to this day. The machine is very reliable, unpretentious and easy to maintain. Managing it is easy and enjoyable. To surpass this masterpiece is an ambitious task. Mi-38 helicopter should be even better, and much more. Fuel efficiency, not so important in the early sixties, today is becoming one of the main aviation parameters. Compared to the Mi-8, it should double, or better, three times.
External comparison of the Mi-8 and Mi-38
At first glance, there are many similarities in the general principles by which the Mi-8 and Mi-38 helicopters are built. The photo of the machine shows a certain continuity shown in the arrangement of the main components and assemblies. The fuselage is made according to a semi-monocoque scheme, with a flat floor and a rounded aerodynamic ceiling. The chassis is non-removable, tricycle, five-blade main rotor. The cockpit at the bottom is opaque, unlike the Mi-8. The shape of the bow is pointed, at the top above it there are no protruding protruding fairings of the turbine air intakes. The four-blade tail rotor. Volumetric fuel tanks located at the Mi-8 along the sides at the bottom of the fuselage are hidden inside the Mi-38. Technical characteristics, however, in these two compared machines are significantly different.
Technical indicators
Firstly, the practical range has grown. With a full fuel reserve of 3,796 liters, the Mi-38 helicopter can fly 800 km (for the Mi-8, depending on the modification, this figure ranges from 425 to 590 km). The cargo compartment has become more voluminous, its dimensions are 8630 mm (length), 2400 mm (width) and 1850 mm (height). Carrying capacity reached 6 tons. The speed also increased: on the Mi-8 it averaged 225 km / h, which is 65 km / h lower than on the Mi-38. The technical characteristics of the new machine differ favorably in terms of the ceiling, in 2012 it set a world record of 8600 m, but the following year it turned out that the Mi-8MSB veteran helicopter, if equipped with a new type of TV3-117VMA- engine SBM1V, also capable of something. He climbed to a new record height of 9150 meters. Climbing, however, remained "unbroken": in 6 minutes, only Mi-38 can gain three thousand meters. The characteristics of this machine, therefore, promise it a long and successful career in Aeroflot, and in the Air Force, and abroad.

Technological innovations of materials
Gone are the days when aircraft around the world were made only from duralumin. The Mi-38 helicopter is made with widespread use of plastic and composite materials. The blades of both screws have a multilayer structure, made by a winding method, which ensured their high elasticity and almost unlimited term of use (at least during the entire period of operation of the machine). The polymeric material is also used in the manufacture of rotor and tail rotor bushings (so-called elastomeric bearings are installed), as a result of which lubrication of these units is not required. In the manufacture of non-force elements of the fuselage (hoods, cockpit, dashboards, outer surface of the ramp and beam fairings), three-layer sandwich panels were used. Combined cladding consists of an outer metal and an inner polymer-honeycomb layer.
Power point
Ideally, the power required for efficient operation of the machine is 5000 liters. from. It is developed by two engines. There were two options for picking the power plant Mi-38. 2 Pratt & Whitney Canada turboshaft engines develop the necessary effort, providing the required economic performance. A booster system with triple redundancy controls their work. Such a scheme was dictated by the high export potential of the new machine. In 1990, it was assumed that it would be produced by a specially created JV Euromil, whose shareholders will become the plant named after him. Milya, Kazan Helicopter Plant, the company Eurocopter and NPO them. V.Ya. Klimova. Hopes, however, did not materialize, after 13 years the European group left the board of the joint venture, although it continues to cooperate with him on mutually beneficial terms. Most likely, the production models will be equipped with Klimovskaya TV7-117V engines, which are no worse than their overseas counterparts, although they have slightly lower power (2 x 2350 = 4700 hp), but they can quite successfully lift the Mi-38. The helicopter, whose characteristics will suffer slightly from this, will remain independent of imports.
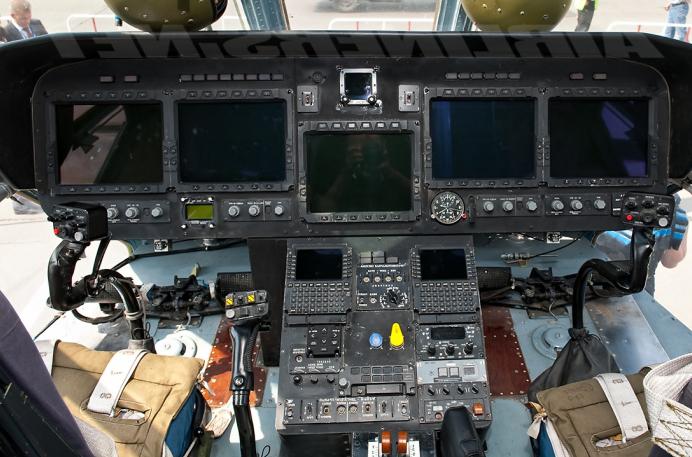

Devices
The modern avionics complex IBKO-38 was developed and manufactured by Transas Aviation, and the technology of a "transparent cockpit" was implemented in it. This means that thanks to the instruments, the crew will be able to have a circular view, visually assessing the situation around the aircraft and under it. The pilots' workstations are equipped with five liquid crystal displays, the computer complex digitally controls the modes of engines and all onboard equipment. The autopilot also operates on the basis of a computer. Navigation is equipped with a Doppler speedometer. The radar is located in the bow, in addition to the spatial position of the machine, the weather and weather conditions are also evaluated. There is also a separate camera that allows you to control the position of the load on the external sling. Mass and centering characteristics are evaluated automatically.
Security questions
To successfully pass international certification, any aircraft manufacturer must ensure that a number of conditions of the ICAO international organization are met. In total, four prototypes have been produced to date. The last Mi-38 (OP-4) differs from the previous one in the presence of a fuel system that can withstand strong impacts on the ground. Thus, a high level of fire safety is achieved. The chassis, which extinguish the momentum from a collision with the ground at high descent speeds, are also a measure of increasing the survivability of the crew and passengers in the event of an emergency, but they were structurally provided already in the development of previous copies (OP-2 and OP-3) of the Mi-38 helicopter.
2014 was the date of completion of all test activities and the end of preliminary design work. After the start of mass production, the improvement of the design will undoubtedly be continued, including in the aspect of improving operational safety.
Handling options
Already in the development of the base model, specialists of the Design Bureau Miles understood that since they were creating a multi-purpose machine, it should be adapted to solve the widest possible range of tasks. To do this, you need to consider the possibility of a fairly simple construction of profile modifications based on the main scheme. First you need a passenger car (in this version, it accommodates 32 people). The needs of the armed forces should not be forgotten either, the Ministry of Defense is a profitable and reliable customer. The national economy will also need to replace the Mi-8, therefore, cargo modification is also needed. Emergency Situations come in handy ambulance. And then - time will tell.
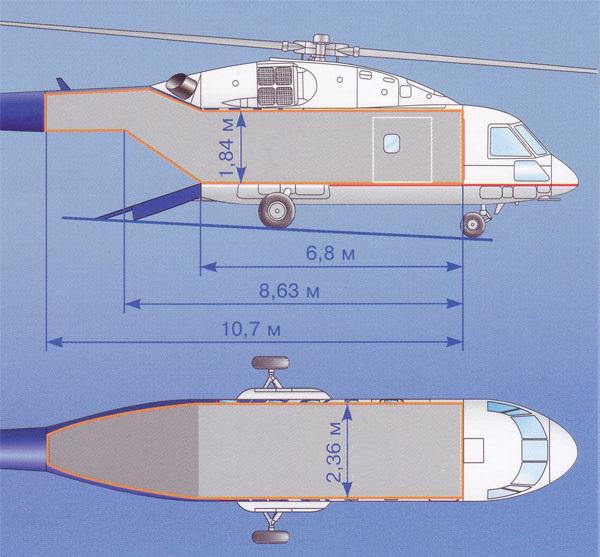
In all cases, the machine needs simple, reliable and convenient means of loading and rigging. All this is equipped with a Mi-38 helicopter. The photo of the cargo compartment is striking in the well-thought-out arrangement of all nodes designed to solve this problem. The cargo ramp has a width of 1800 mm, it is equipped with a lifting mechanism with remote hydraulic control. A universal high-capacity winch (300 kg) is mounted in the opening of the side cargo door, and movements inside the cabin are facilitated by removable roller tracks.
Soon!
It seems that the wait for the start of regular operation of the Mi-38 helicopter is not long. The first production model has already been laid on the stocks of the Kazan Helicopter Plant, followed by others. Several years will pass, and the characteristic silhouette of this car will become familiar to everyone. Will there be as many Mi-38s as 8s? Will they become as famous around the world? Time will tell.