The Soviet aircraft LA-7 was created in OKB-21 (the city of Gorky, today - Nizhny Novgorod). The development was led by S. A. Lavochkin, one of the best Soviet designers. This aircraft was considered one of the most effective means of combat aircraft during the Second World War. He combined the most important functions for gaining superiority in the air - maneuverability and armament.
General information
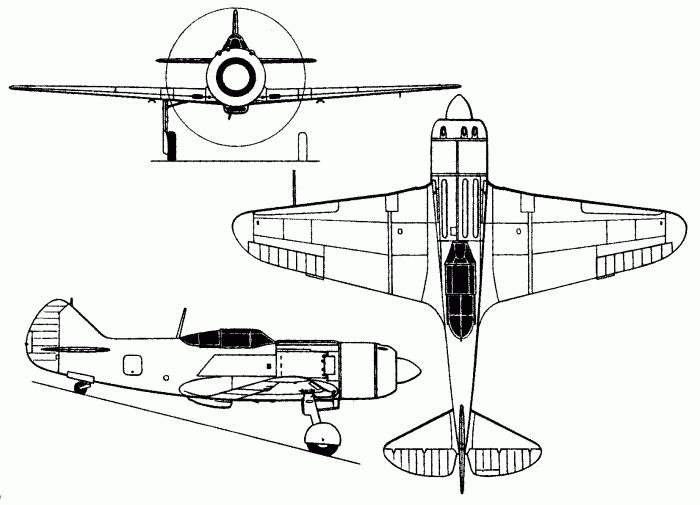
LA-7 is an aircraft that can be classified as a monoplane (an apparatus with one pair of wings). He has one engine located in the bow, and the only landing place - for the pilot. Its predecessor is the LA-5 fighter, also developed in the 21st Design Bureau. The first prototype aircraft (code LA-120) took off in November 1943.
In early 1944, he successfully passed flight tests and entered the military service. By the time the war ended, more than 5,700 LA-7 fighters had left the assembly line. According to the recognition of many Soviet pilots, this aircraft was the best: its maneuverability, speed, reliability and firepower were highly appreciated. At the helm of such a high-class fighter, confidence was gained in victory over any ace of the Third Reich.
Appearance story
LA-7 was the result of the technological evolution of a series of several aircraft. The very first fighters LaGG-2 (developed in 1939) and LaGG-3 (1940th) appeared. Designers M. Gudkov and V. Gorbunov also participated in their creation. The second fighter was able to fly at a speed of 600 km / h - much faster than German aircraft of its class. But it was heavy: 600 kg more than the Yak-1. LaGG-3 maneuverability and rate of climb left much to be desired.
In 1942, the LA-5 appeared with a lighter engine, which proved to be excellent in the Battle of Stalingrad. The new aircraft was superior to the Messerschmitt, it had as many as two 20-mm caliber guns, and they turned out to be more effective than the “German” with one gun, supplemented by two machine guns.
In 1943, by the time of the battle near Kursk, the country's aviation received a new generation of fighters - the LA-5FN with a boosted engine, lower weight and easier control. Even the latest German Fokke-Wulf-190 could not compete with this Soviet aircraft. And finally, at the end of 1943, a new model took off - the LA-7. On it, in comparison with the previous fighter, a third gun appeared, and also the aircraft could reach a speed of 680 km / h.
Design genius
The person who led the creation of the LA-7 is Semyon Alekseevich Lavochkin. He is a gold medalist, in the years 1918-1920 he served in the ranks of the Red Army and the border troops. Then I studied at the Moscow Higher Technical School (today it is Bauman Moscow State Technical University), where I received the profession of an aeromechanical engineer. The theme of his thesis was related to the development of a bomber.
Semyon Alekseevich began working in the aircraft design industry in the late 1920s, first working on the design of aircraft for the USSR fleet, and then moving on to work on fighters. In the second half of the 30s, when the world was already restless, the Soviet government decided to pay special attention to the development of the Red Army Air Force. First, Lavochkin together with S.N. Lyushin created the aircraft LL-1, armed with dynamo-reactive cannons. Later, a prototype I-301 appeared, containing outstanding design drawings. LA-7 owes its appearance to the design endeavors of Semen Alekseevich of those years.
Specifications
The speed and rate of climb of the LA-7 aircraft, in principle, remained comparable to those of the LA-5FN. The maximum speed of the fighter was 680 km / h (when flying at an altitude of 6 thousand meters), the maximum rate at the ground is 597 km / h. The flight range of the LA-7 was 635 km, the ceiling height was 10 km 750 m.
Fighter climb - 1098 meters per minute. The length of the car is 8.60 m, the height is 2.54 m. The empty weight is 2605 kg, the curb weight is 3265 kg. The wing area of the fighter is 17.5 square meters. m. Maximum take-off weight - 3400 kg. The wing span of the aircraft is 9.80 m. The LA-7 engine is one of three types: ASH-82FN, ASH-83 or 71. The fighter has a thrust of 1850 horsepower (which is equivalent to 1380 kilowatts). One of the fundamental differences between the LA-7 and previous aircraft is its lightweight design (thanks to metal spars).
Armament
The combat equipment of the LA-7 aircraft included, as a rule, two 20-mm ShVAK guns or three guns of the same caliber of the B-20 type. They knew how to prevent shells from falling into the propeller blades, thanks to the installed hydromechanical synchronizer. The ammunition for the ShVAK gun was usually 200 rounds per gun. Also, the ammunition was supplemented with shells of armor-piercing incendiary type (capable of penetrating armor up to 22 mm from a distance of 100 m), as well as shells of fragmentation incendiary type. Bombs could be placed under the wings of the aircraft (up to 100 kg on each wing). Most often these were shells of the types FAB-50 and 100, ZAB-50, 100 (the index indicates the mass of the bomb - 50 or 100 kg).
disadvantages
Military experts noted that the aircraft LA-7 from time to time refused to work hydraulics. The fighter engine was not quite stable. Due to the fact that the engine’s air intakes were in the plane of the wings, they tended to become clogged with dust during take-off and landing. Therefore, the engine could refuse to work. This property was overlooked by specialists at state tests: acceptance took place in the winter, when there was no dust.
It is recognized that the engine on the LA-5FN failed much less frequently than on the LA-7. The aircraft oil cooler was located under the fuselage, and because of this it was very hot in the cockpit (about 40 degrees in winter and 55 in summer). Pilots had a hard time, given the fact that exhaust fumes from the engine got into the cockpit, and condensation often fell on the glass.
Comparison with analogues: theory and practice
The aircraft LA-7, the photo of which is found in most Soviet aviation textbooks, is often perceived as a fighter, far superior to its German counterparts - FW-190 and Messerschmitt-109. However, the pilots themselves said that fighting with German aircraft was very difficult. For example, according to the recognition of some Soviet aces, “Germans” could do a dive much better than this machine. Therefore, to win the match, if the enemy performed a similar aerobatics, as a rule, only the most experienced pilots of the Soviet Air Force could.

But, which is especially important, in such cases, the LA-7 gave an advantage, thanks to a sharp set of speed. Having managed to quickly get closer to the German, it was possible to attack the enemy. At the same time, the indicators of the bend radius (horizontal maneuverability) of the LA-7 made it possible to speak of superiority over German aircraft. This was due to the lower load of the Soviet fighter on the wing: about 190 kg / sq. (when the "German" - more than 200 kg / sq.). Therefore, the LA-7 made a turn 3-4 seconds faster than, for example, the Focke-Wulf.
Combat experience
LA-7 is a plane on which I.N. Kozhedub is a legendary pilot, a hero of the Soviet Union three times. He began the combat journey at the helm of LA-5, on which he shot down several dozen aircraft. Reseeding on LA-7, Kozhedub destroyed 17 German fighters, triumphantly completing his combat sorties during the battles near Berlin.
Active combat use of the aircraft began in June 1944. This fighter was held in high esteem by the guards regiments of the Soviet Air Force. About the legendary LA-7 spoke positively A.I. Pokryshkin - ace, hero of the Soviet Union three times. Performing combat sorties on this plane, he shot down 17 German fighters, including the Messerschmitt-262 jet. The great Soviet pilot considered the LA-7 a model of excellent maneuverability, speed, and armament: all this was ideally combined with the ace's favorite "formula": "speed, maneuver, and fire."
Hero plane
LA-7 historians of the Great Patriotic War are traditionally associated with the name of Ivan Nikitovich Kozhedub, who won 64 victories (not a single ace of the countries of the anti-Hitler coalition had any more). The pilot opened the account of battles in March 1943 on a LA-5 combat aircraft. Subsequently, Kozhedub made 146 sorties on a fighter of this type and shot down 20 “Germans”. In May 1944, the pilot moved to LA-5FN, which was raised with the money, interestingly, of a collective farmer from the Stalingrad region. On this plane, he destroyed 7 units of enemy aircraft. In August, the Kozhedub regiment was transferred to the new for the Soviet Air Force fighter aircraft LA-7. On this type of aircraft, Ivan Nikitich fought until the end of World War II.
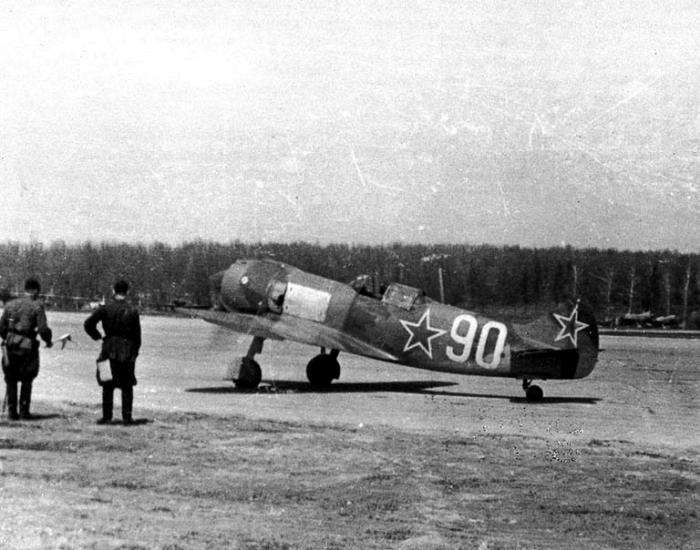

During one of the combat missions of the LA-7, Kozhedub was hit, his engine stalled. Deciding not to surrender to the enemy, the Soviet ace directed the plane at one of the objects on earth. But when the fighter began to dive down, the engine suddenly started working, and Kozhedub, taking the LA-7 out of the peak, returned to the airfield. Throughout the war, Ivan Nikitich flew out on a combat mission 330 times, participated in 120 air battles in which he destroyed 64 enemy aircraft. Awarded with three Golden Star medals.