Any designer knows what a raster is. This is important for preparing images for publication, changing them, creating layouts. For the average network user, the difference between the formats is not so great. However, these are the basics of working with graphics that everyone who wants to be able to process photos should know.
Definition of a raster, its advantages and disadvantages
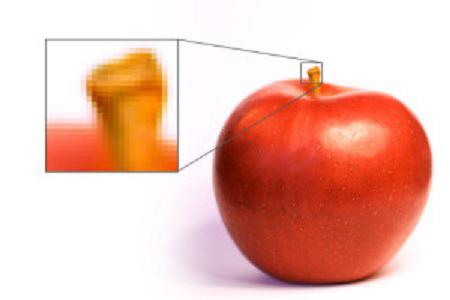
What is a raster? This is an image made up of a matrix of pixels colored with a specific color. They are easy to notice, greatly increasing the picture. The file with raster graphics stores a code containing the number of points and their color. Photos, scanned pictures, illustrations in magazines and on a computer screen are raster. A grid of pixels (dots) can transmit an image of any complexity, shadows, gradients, blur, halftone, 3D effects and even animation. Photorealism is the main advantage of this type of graphics.
The disadvantages of the raster include the following:
- Inability to scale. By enlarging the image (that is, by expanding the grid of pixels) or by reducing it (by stretching so that some of the dots disappear), you can significantly degrade the quality of the image.
- The bitmap is limited to a rectangle. That is, when the drawings are superimposed on each other, the lower one will “hide” under the white background of the upper one.
- The more complex the image, the more the file with it weighs.
Raster Characteristics
Raster images vary in size, resolution, color modules and number of shades. The grid characteristics themselves are also excellent. The following types of rasters by matrix type are known: regular and stochastic.
- Size (weight) - the total number of pixels in the image, calculated in KB (MB, GB). The larger and more complex the drawing, the more it weighs.
- Resolution - the number of pixels per inch (ppi) of Internet pictures, photos or dots per inch (dpi) of printed illustrations. The larger this parameter, the better and sharper the picture. The standard resolution of Internet images is 72 ppi, and print layouts are 300 ppi.
- The color module determines the basic shades. It can be widespread RGB, when red, green and blue are present in one or another quantity in each pixel and, when mixed, form the desired color. For the preparation of layouts, CMYK is often used - a module consisting of cyan, magenta, yellow and black. LAB is "light", red-green and blue-yellow; Grayscale - shades of gray.
- The color of the picture depends on how many bits are encoded in each pixel. In monochrome images, each dot weighs 1 bit. If the pixel has 4 bits, the picture consists of 16 colors. 8 bits per pixel give 256 colors, 16 bits - 65 thousand colors, 24 bits - 16 million colors.
- The following types of rasters are distinguished depending on the matrix of pixels: regular has a mesh structure (with dimming of points or a grid), stochastic does not have a clear organization, that is, the pixels are randomly arranged.

Difference of a raster image from a vector
In addition to the raster, there is a vector format - a way to create a picture in which the minimum image elements are simple geometric shapes: rectangles, ovals, circles, straight and curved lines. The vector graphic file contains mathematical formulas - shape parameters (diameter, length, width, fill, color, contour), their location on the canvas (X and Y coordinates) and position relative to each other. Vector drawing is easy to scale and edit - you just need to change the characteristics of the desired object. When you enlarge or reduce the image, its quality does not change. The image in the vector is not limited to a rectangular background - they can be superimposed on each other. In this case, the source file weighs significantly less than the raster.
With so many advantages, what can a raster contrast a vector with? Pictures in this format can hardly be called realistic - they have a slightly cartoony display due to the fact that they use pure colors and gradients. Modern graphic editors - Corel Draw, Adobe Illustrator - can work with complex effects: shadows, color mixing, blurring, but they are still far from the capabilities of processing raster images. In the vector prepare layouts for printing.
Raster Graphics Formats
Raster images can be saved in different formats, and conversion is simple - you need to open the file with any graphics editor, select the "Save As" menu item and the desired extension.
GIF is the simplest display format. It supports transparency and animation effects, weighs a little, but its color is low - 256 colors. In GIF it is convenient to store graphs, charts.
PNG uses lossless compression and supports transparency much more color than GIF.
TIFF is used to convert from a raster to a vector, since this format does not combine the layers in the picture.
JPEG is the most popular format used for photographs, scanned images, Internet images.
How to convert from a raster to a vector format
Designers need to convert a bitmap image to vector when making a layout, or if you need to enlarge a picture, change it without losing quality. Translation into a vector is a non-trivial task, since many photo effects cannot be reproduced. With automatic tracing, the picture quality is greatly reduced: colors may be distorted, details of the picture may be lost. This automatically creates objects from groups of pixels of similar colors, located along the contour of the raster image. If the picture is complex, there can be a lot of created objects, and editing them is not easy. Auto-tracking is available in Corel Drew or Illustrator.
A good quality picture can only be obtained by manual tracing. At the same time, the designer traces the figure along the contour, and the shadows or volume are created by superimposing figures of different sizes and shades on top of each other. The easiest way to do this is on a graphics tablet with a stylus tracing lines. Hand-made vector images are expensive and highly valued.
... and vice versa
Rasterization is the opposite of tracing, when a vector image needs to be converted to a raster, for example, to complement it with complex photo effects. Moreover, all the good properties of the vector disappear, that is, the resulting image cannot be scaled without loss of quality. Therefore, it is advisable to save the original file so that, if necessary, enlarge or change the picture.
Before converting to a raster (Convert to Bitmaps), you must set the following parameters:
- Color - the number of colors in the picture.
- Dithered - when this item is activated, colors will be formed by mixing.
- Redolution - permission.
- Anti-aliasing - lines and kinks of the original drawing will be smoothed.
- Trandparent Backgrounf - a parameter that makes the background transparent.
- Size - size.
So, for proper work with drawings, you need to know what a raster and vector are. A raster image is formed from a variety of pixels - the smallest graphic elements. The raster is colorful, reproduces many photo effects, even animation. However, such images are difficult to scale and resize. A vector, on the contrary, is easy to redo by changing any object in the picture; when scaling, its quality remains the same. However, shadows, blurring, complex gradients and color mixing are difficult to convey. The bitmap can be approximately displayed in vector format and vice versa.