The general structure of the hair is a rather interesting question, since not all people know about it. But the shape and color of the hair depends on it. The structural features of hair need to be known not only to specialists in this field, but also to other members of society. The article will answer all your questions and allow you to find out some amazing facts.
What is hair
Before you understand the structure of human hair, it is necessary to give the concept of this accessory component of the skin. The follicle is a root that combines with connective tissues, resulting in a single complex. Each person is born with a certain amount of hair follicles, which is simply impossible to change.
In the structure of the scalp there is a "hair nipple". It is in it that the blood vessels are located. It is one of the elements of connective tissue and plays an important role in the growth of hairs.
Any hair follicle is an independent and independent formation, which is characterized by an individual process of development and growth. The successive cycles, where the change of the lock occurs, differ from each other, because of which the period of updating our hair goes almost unnoticed.
What are they needed for
The structure of the skin and hair is interesting to people for the simple reason that these integuments perform important functions. The purpose of the skin is known to everyone, but not everyone knows about the second element.
As you know, hair covers the entire body, with the exception of the palms and soles of the feet. They protect the skin and the entire body from adverse environmental influences.
Varieties
A rather interesting question is the structure of hair and nails, because both of these elements are replaced throughout life. The second ones grow quite quickly and noticeably, which cannot be said about the first. Hair growth directly depends on various factors.
When the fetus is inside the womb, its body is completely covered with a light fluff. From the moment of birth to the age of two years, this cover begins to replace the hair, distributed throughout the trunk and limbs. Their density and color may vary.
In adults, hairs can be only three varieties:
- cannon - their length is not more than 1.5 mm, they cover the whole body;
- bristly - they are eyebrows and eyelashes;
- terminal (long) - grow on the head, beard, and also the genitals.
External structure
Finally, it's time to find out what the external structure of the hair is. Its chemical composition contains water, keratin protein, as well as residual traces of minerals and vitamins, which are directly involved in metabolic skin processes.
The hair itself is not whole, as many people think of it. In fact, it consists of a huge number of small horn plates. He has a root, which is located in the capsule - the so-called hair sac, defined under the skin.
Hair shaft
Considering the structure of the hair, along with the capsule, you should also learn about the shaft - this is just what is visible on the surface. It has a three-layer structure:
- Medulla. It is the core of the rod and is absent only in the cannon. It contains soft cells mixed with air bubbles, which later become keratinized. Just this layer is responsible for thermal conductivity. Moreover, any chemical participation is completely excluded.
- Cortex. This is the basis of the hair, which occupies about 80% of the total volume. This layer consists of a large number of keratin fibers intertwined with each other. They are often compared with a thread that consists of thin components. Such fibers are woven into spirals and make up the cortical stratum corneum.
- Cuticle. The outer layer is required to perform a protective function. It consists of several layers lying on top of each other according to the type of wood rings. If you look at it through a magnifying device, you can see something similar to a pine cone. Cuticle scales are proportional to hair growth, starting from the root itself. They consist of nitrogen, sulfur and amino acids. If the hairline is healthy, then the scales are quite tight, providing softness, but due to improper care, they puff, creating a not very aesthetic appearance.
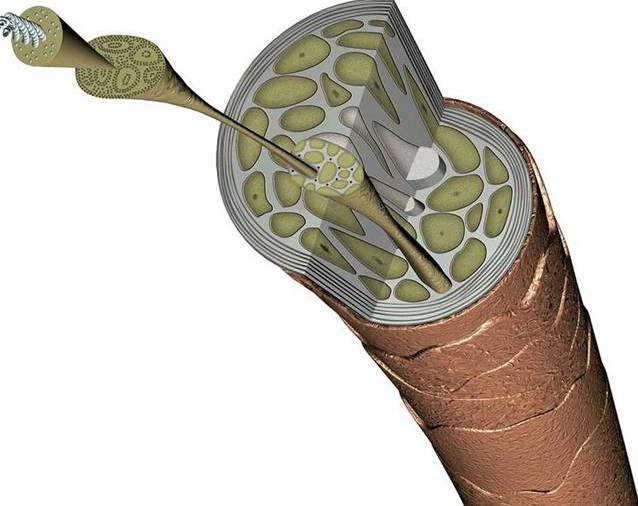
Internal structure
Oddly enough, the internal structure of the hair can not be called less complicated. An important role is played by the follicle, which is a bag of epithelial and connective skin. Inside it is the root, that is, the ducts of the sebaceous and sweat glands, and the bulb.
On top of the skin, the root is visible in the form of a small extension. On the bulb on top is a small papilla, which is responsible for the nutrition, development and growth of the hair.
As for the middle and outer layers, they consist of elastic fibers and collagen bundles. The so-called argentophilic are attached to the skin and are needed for the membrane surrounding the capsule. Just above the bulb is a thin layer that is designed to refract light. She is responsible for the brilliance, which directly depends on the natural processes of the appearance of fatty grease, consisting of an antiseptic created to fight foreign microorganisms. In the epithelial cell division process occurs, as well as their change, which determines the growth rate of hairs.
At the point of contact of the skin and hairline are smooth muscles, which in appearance are very similar to tape. They attach to the skin through a short tendon. When the muscle contracts, it presses on the gland, thereby contributing to the raising of the hair, where the secret gets. Every person has had such a process, because with a feeling of fear, the hairs always stand on end.
How do they grow
Having learned about the structure and functions of hair, you should understand how they grow. This process consists of only three stages:
- Anagen (2-5 years). Here in the follicle area, active growth occurs. At this time, prerequisites are created for accelerated cell division and an increase in hair length. When a person is healthy, about 85% of the hairline is of this age.
- Katagen (crescent - 20 days). During this period, the function of the follicle is already less active. He slowly tears away from the papilla, which he eats. At this stage, there is only 1% of the hair throughout the body.
- Telogen (3-4 months). At this time, cell division stops, and the hair with the bulb falls out. In the vacant place, another hair begins to grow, which gradually breaks through the skin and performs all the same functions as the previous one.
Types
Each person has their own type of integument, even regardless of the fact that they have a similar hair structure. Hairdressing is the knowledge of the subtleties when choosing a haircut and hairstyle, because this phenomenon is explained by the individual characteristics of the body, as well as various external factors. Today, the following types of hair are distinguished:
- Normal. It reflects light well, has elasticity and has no traces of cross-section. Externally, such hair looks like an image in a glossy magazine. Just combing is enough to keep their shape for a long time. In addition, they do not need to wash too often.
- Dry. The rather faded and brittle hairs look painful and resemble dried grass in appearance. To improve their condition, experts recommend using professional compositions suitable for just such a head of hair.
- Fatty. This type has a huge amount of secreted secretion. The reasons for this can be a genetic predisposition, as well as malnutrition. Oily hair quickly becomes dull and unkempt, and therefore needs to be washed frequently.
- Mixed. It is more inherent in owners of long hair. Closer to the roots, they are greasy, and to the tips are brittle. This is explained precisely by the length, since the released fat simply cannot be enough for even distribution to the very ends.
Color
People who know the structure of the hair of the head can explain why the hair has one color or another. For others, this information is unknown, so you need to understand it in more detail.
Under the skin, not far from the follicle, is the pigment responsible for the tone of the hairs. It is melanin. It consists of nitrogen, iron, and arsenic. Specialists divide this element into pheo- and eumelanin. In composition, they are quite similar to each other, but the only difference is the different shape and color sets. The first looks like an elongated granule, and the second resembles an oval.
Eumelanin is a brown dye. It consists of three whole shades - yellow, red and blue. As for pheomelanin, it is saturated yellow.
Both compounds are present in all hair. They are responsible for the color of hair. Since ancient times, people believed that in nature there are only three options - red, blond and black. But over time, when it became known about the predominance of one over the other, experts began to talk about many possible shades. For this reason, on the street you can meet a person with a unique hair color.
Gray hair appears, as you know, not only among the elderly, but also among some young people. This is due to the excessive amount of air capsules that come from the follicle. In this case, the hair is not able to stain naturally, so it becomes gray.
Some facts
In hairdressing, the structure of the hair and its features are important nuances, so every specialist should know them. You can learn this in specialized schools or in courses where only basic information is provided, but nothing is said about interesting facts noticed by scientists over a long period of time:
- women's hair is thinner than men's;
- growth rates are affected by length;
- the most difficult to color are red hair.
This knowledge will help hairdressers quickly and better understand their business and provide themselves with stable earnings.