The TU-95 aircraft is a long-range bomber in service with the Russian Federation. It is a strategic turboprop missile carrier. Today it is one of the fastest bombers in the world. In the American codification is designated as "Bear". This is the last Russian turboprop aircraft adopted in serial production. Currently has many modifications.
Design History
The TU-95 bomber-bomber in its original form was designed by Andrey Tupolev back in 1949. Developments were based on the 85th model of the aircraft. In 1950, the political situation around the USSR required immediate strategic strengthening. This is what caused the creation of a new advanced missile carrier with increased speed and maneuverability. The aim of the development was to achieve maximum range in the shortest possible time.
In the summer of 1951, the project was headed by N. Bazenkov, but very soon it was replaced by S. Jäger. It is the latter that is considered to be the father of the Bear. Already at the initial stage in the drawings, the TU-95 bomber surprised with its size and power. For a more detailed presentation of the project, a wooden model was even assembled.
In October 1951, the TU-95 was finally approved for production. Prototype development was carried out for several months. And only in September 1952 the plane was brought to the Zhukovsky airfield. Factory tests were not long in coming. Testing was successful, so a month later it was decided to conduct the first take-off on a sample of a bomber. The tests lasted about a year. As a result, the flight on an experimental simulator revealed several serious problems. Testing did not pass the third engine. Its gearbox collapsed in a fire two months after the start of the test. Thus, the engineers faced the task of correcting the mistakes made so that in real flight such excesses could be eliminated. At the end of 1953, due to similar problems, 11 crew members, including the commander, died.
First flight
A new prototype bomber arrived at the airport in February 1955. Then the test pilot was appointed M. Nyukhtikov. It was he who made the first flight on a new prototype. The tests were completed only after a year. During this time, the strategic bomber TU-95 made about 70 flights.
In 1956, aircraft began to arrive at the Uzin airfield for future use. Modernization of the bomber started in the late 1950s. The production and partial assembly of the TU-95 was carried out by the Kuibyshev aircraft plant. It was there that the variations of a missile carrier with nuclear warheads first appeared. Gradually, the 95th model was rebuilt for all kinds of military needs: reconnaissance, bombing of long-range targets, passenger traffic, an air laboratory, etc.
Currently, mass production of TU-95 is frozen. However, the project is still supported by the Air Force and the Russian authorities.
Design features
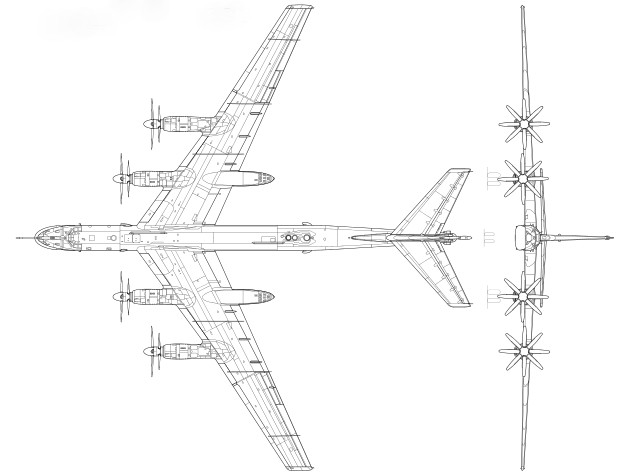
The missile carrier has an autonomous DC supply system for heating the wings, keel, stabilizer and propellers. The engines themselves consist of biaxial groups of AV-60K blades. The cargo compartment is located in the middle of the fuselage, next to the launcher, to which 6 cruise missiles are attached. It is possible to attach additional products to the suspension.
The Russian bomber TU-95 is an air vehicle with a triple landing gear. Each rear wheel has its own brake system. During take-off, the supports are retracted into the fuselage and wing gondolas. The front pair of wheels is equipped with a hydraulic system, and the rear ones are equipped with electric mechanisms with a total power of up to 5200 watts. Emergency opening of the chassis is only possible with a winch.
In pressurized cabins there is a crew. In an emergency case, the ejection seats are disconnected from the aircraft through a special hatch, which is located above the front landing gear. Conveyor belts are used as hand hooks . Ejection from the rear of the bomber is provided through a dropable hatch.
It is worth noting that the missile carrier is equipped with special life rafts in case of emergency landing on water.
Engine specifications
The TU-95 turboprop bomber is one of the three most powerful large-sized aircraft in the world. This result is achieved thanks to the NK-12 engine, which has a highly efficient turbine and a 14-speed compressor. An air bypass system is used to adjust the performance. At the same time, the efficiency of the NK-12 turbine reaches almost 35%. This figure is a record among turboprop bombers.
For easy adjustment of the fuel supply, the engine is designed in a single unit. Power NK-12 is about 15 thousand liters. from. In this case, the thrust is estimated at 12 thousand kgf. With a full fuel compartment, the aircraft can fly up to 2500 hours (about 105 days). Engine weight is 3.5 tons. The length of the NK-12 is a 5-meter unit.
The disadvantage of the engine is its high noise. Today it is the loudest aircraft in the world. Even locator submarine installations are capable of detecting it. On the other hand, a nuclear strike is not a critical issue.
Of the other characteristics of the missile carrier, it is worth highlighting 5.6-meter screws. Also noteworthy is the blade anti-icing system. It is an electrothermal installation. Fuel to the engine comes from the fuselage and caisson tanks. Thanks to the use of economical theater and an improved propeller system, the TU-95 bomber is considered to be the “toughest” strategic air target in terms of flight range.
Missile carrier characteristics
The aircraft can accommodate up to 9 crew members. Due to the specific application, the bomber is up to 46.2 meters in length. At the same time, the span of one wing is about 50 m. The dimensions of the strategic missile carrier are really amazing. The area of only one wing occupies up to 290 square meters. m
The mass of TU-95 is estimated at 83.1 tons. However, with a full tank, the weight increases to 120 thousand kg. And with a maximum load, the mass exceeds 170 tons. The rated power of the propulsion system is about 40 thousand kW.
Thanks to the NK-12, the bomber is capable of speeds up to 890 km / h. In this case, the movement on autopilot is limited to 750 km / h. In practice, the range of the missile carrier is about 12 thousand km. The lift ceiling ranges up to 11.8 km. For takeoff, the aircraft will need a strip of 2.3 thousand meters.
Armament bomber
The aircraft is able to lift up to 12 tons of ammunition. Aircraft bombs are located in the fuselage compartment. Allowed the placement and free-falling nuclear missiles with a total mass of 9 tons.
The TU-95 bomber nominally has purely defensive weapons. It consists of 23 mm cannons. On most modifications paired AM-23s are installed in the lower, upper and aft parts of the aircraft. In rare cases, the GSH-23 aircraft gun takes place.
In the case of the AM-23 installation, the missile carrier is equipped with a special automatic gas removal system. The gun is attached to the spring shock absorber and guide boxes of the housing. The shutter in both cases is wedge inclined. A special pneumatic charging unit is used to accumulate energy and mitigate the impact from the rear gun.
Interestingly, the length of the AM-23 is almost 1.5 meters. The weight of such a gun is 43 kg. The rate of fire is up to 20 rounds per second.
Operation problems
The development of the missile carrier began with noticeable difficulties. One of the main disadvantages was the cabin. Initially, the TU-95 bomber was poorly adapted to long-haul flights. Because of the uncomfortable seats, the crew often had a backache and numb legs. The toilet was a regular portable tank with a toilet seat. In addition, the cabin was very dry and hot, the air was saturated with oil dust. As a result, the crew refused to do long flights in such an unprepared aircraft.
Repeatedly there were problems with the oil system of engines. In winter, the mineral mixture thickened, which directly affected the revolutions of the screws. At the initial stages, to start the engines, turbines had to be preheated in advance. The situation has changed with the release of large-scale production of special motor oil.
First use
The TU-95 bomber was first seen at an airfield in the Kiev region at the end of 1955. As it turned out, several originals and modifications joined the ranks of 409 TBAP at once. The following year, another regiment of the division was formed, in which there was also a place for four TU-95. For a long time, the missile carriers were armed only with the Ukrainian Air Force of the USSR. However, since the late 1960s. TU-95 and its modifications were filled with military hangars in the territory of present-day Russia.
The purpose of the formation of regiments around the bombers was targeted attacks on NATO strategic forces in southern Asia, as well as on China. Aircraft were always on alert. Soon, the American authorities noticed such a dangerous accumulation of military power at their bases and began to engage in diplomatic relations. As a result, the USSR had to disperse most of the missile carriers throughout its territory.
Since the 1960s TU-95 is now and then noticed over the Arctic, Indian Ocean, the Atlantic zone and Britain. Repeatedly, the countries reacted aggressively to such actions, shooting down missile carriers. However, no formal recordings were made of such cases.
Recent application
In the spring of 2007, Russian missile carriers repeatedly observed from the air the military exercises of the British army. Similar incidents occurred in Clyde Bay and the Hebrides. However, every time in a matter of minutes, British fighters flew into the sky and, under the threat of a blow, escorted the TU-95 beyond its borders.
From 2007 to 2008, missile carriers were spotted over NATO military bases and aircraft carriers. During this period, one Tu-95 bomber crashed. No official clarification of the causes of the accident has been reported.
Today, the Bears continue their worldwide intelligence activities.
Aircraft crash
According to statistics, every 2 years there is one major accident of the TU-95 bomber. In total, 31 missile carriers crashed during operation. The death toll is 208 people.
The most recent accident of the TU-95 bomber occurred in July 2015. The crash happened with the modification of the aircraft. The main cause of the crash, experts call the outdated physical condition of the unit.
The accident of the TU-95 MS bomber claimed the lives of two crew members. The crash occurred near Khabarovsk. As it turned out, all the engines at once refused a rocket carrier in flight.
In service
TU-95 were on the balance sheet of the USSR Air Force until the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991. At that time, most were in the arsenal of Ukraine - about 25 missile carriers. All of them were part of a special heavy aviation regiment in Uzin. In 1998, the base ceased to exist. The result was the decommissioning of aircraft and their subsequent destruction. Some of the bombers were converted to commercial cargo.
In 2000, Ukraine transferred to the Russian Federation the remaining TU-95 to pay off part of its public debt. The total amount paid was about $ 285 million. In 2002, 5 TU-95 were modified to multi-functional heavy aircraft.
At the moment, about 30 missile carriers are in service with Russia. Another 60 units are in storage.
Major modifications
The most common variation of the original is the TU-95 MS. These are aircraft carrying X-55 type cruise missiles. To date, they remain the most among others from the 95th model.
The next most popular modification is TU-95 A. It is a strategic nuclear missile carrier. Equipped with special compartments for storing radiation warheads. It is also worth noting educational modifications with the letters "U" and "KU".
Comparison with foreign analogues
The closest technical specifications to the TU-95 are the American B-36J and B-25H bombers. There is no fundamental difference in nominal weight and dimensions. However, the Russian missile carrier develops a much higher average speed: 830 km / h against 700 km / h. Also, the TU-95 has a much larger combat radius and range. On the other hand, the American counterparts have a practical ceiling that is almost 20% higher and a cargo compartment (7-8 tons) more capacious. The thrust of the engines is approximately equal.