The human body contains about 650 muscles, which account for from a third to half of its total mass. The main muscle groups of the body not only allow you to sit, stand, walk, talk, chew, but also provide breathing, blood circulation, the movement of food along the gastrointestinal tract, eye function and perform many other functions.
Classification of major muscle groups
Each part of the body consists of a specific muscle group. Consider the main muscle groups and where they are located:
- The muscles of the head and neck allow a person to bite, chew and talk; pharynx - swallow; eyeball - see everything around 180 degrees.
- The large muscles of the neck stabilize, tilt and rotate the head.
- Many facial muscles provide facial expressions.
These include: the circular muscle of the mouth, the occipital-frontal and circular muscles of the eyes. Chewing include: temporal, buccal.
The most important functions of the muscles of the body are to maintain the vertical position of the body, perform various movements, and provide breathing.
- The sternocleidomastoid muscle goes from the temporal bone to the upper part of the sternum and clavicle.
- In the back there are such muscles: large round, rhomboid, infraspinatus, lateral, extensors of the spine.
- Responsible for the movement of the arm and shoulder: deltoid, brachial, coracoracorachis and trapezius muscles.
- The chest has the following composition: pectoralis major, dentate pectoralis, intercostal muscles.
- The muscles of the arms consist of biceps and triceps, forearm flexors, extensors of the wrist, brachioradialis muscle.
- The hips and buttocks are equipped with a huge number of muscles, among which are: quadriceps, large adductor thighs, tailor, long adductor thighs, and comb muscle. This category includes: biceps femoris, semi-tendon, semi-membranous, iliac-lumbar, gluteal muscles.
- The abdomen consists of straight and external oblique muscles.
- The tibia is equipped with the anterior tibial, gastrocnemius, and soleus muscles.
The main muscle groups are listed in the table below.
| Muscle groups | Kinds | Work in progress |
| Heads | Chewing | Move the jaw |
| Mimic | Reflect the mood and condition of a person |
| Neck | | Keep the head in balance, provide head and neck movement, swallowing and speech |
| Torso | Breast | They change the volume of the chest, provides movement of the hands, breathing |
| Abdominal muscles | Provide inclinations and turns of the spine, breathing, bowel movement, urine output, blood circulation through the veins |
| Dorsal | Flexion of the spine, neck, work of the upper limbs and chest |
| Limbs | Arm muscles | Responsible for flexion and extension of the arm |
| Leg muscles | Flex and extend the hip joint and lower leg |
Along the line of fibers
Since the main muscle groups have different functions during contraction, they are divided into:
- straight and parallel muscles, which are significantly shortened during contraction;
- oblique muscles do not contract much, but prevail in quantity, and with their help you can develop effort;
- the transverse muscles are like oblique and function the same way;
- circular muscles, or sphincters, are located around the openings of the body and constrict them with their contractions.
In shape
Each muscle depends directly on the lines of muscle fibers located relative to the tendon.
Distinguish them in shape:
Long are placed in the arms and legs of a person. For convenience, this category is called at the end of the word: biceps, triceps, quadriceps. These include those that are formed by a combination of muscles of various origins, such as pectoral or dorsal.
Short ones stand out in relatively small sizes.
Types of Muscle Tissue
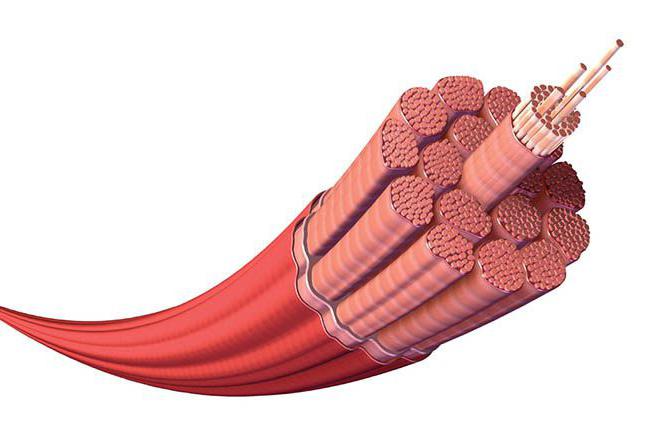
The main muscle groups of a person are formed by bundles of elongated cells - fibers capable of contracting and relaxing. Muscle fibers consist of many parallel threads - myofibrils, and they - of protein threads, myofilaments. The alternation of thin and thick myofilaments gives the fiber a characteristic transverse structure.
Among the main muscle groups, there are three types of muscle tissue:
- heart muscle;
- skeletal muscle;
- smooth muscles.
Myocardium
The heart muscle myocardium is the only muscle of the human heart. The heart is rhythmic, pumping blood non-stop - about 7200 liters daily. With its contraction, blood is pushed out in the arteries, and with relaxation it returns through the veins back to the heart. This muscle works automatically, without the influence of consciousness. It consists of many fibers - cardiomyocytes, which are connected into a single system.
The work of this muscle is controlled by a system of conducting muscle nodes. In one of the nodes is the center of rhythmic self-excitation - a pacemaker. It is he who sets the rhythm of contractions, which changes under the influence of nervous and hormonal signals from other components of the body. As soon as the body is subjected to a heavy load, the muscles need more oxygen. At the same time, the heart accelerates its rhythm, pumping more blood in a period of time.
Skeletal muscle
It represents the main muscle groups in the human body. These fibers have a characteristic structure and large sizes, therefore they are also called striated. The work of this muscle tissue can be controlled by consciousness, and the muscles themselves are arbitrary. The main groups of skeletal muscles are connected to the bones of the body and provide movement. Even when the person is in a fixed position, some muscles still work, maintaining the accepted posture.
Their role is very great for the body. Related to the skin, they provide facial expressions. Interestingly, with a smile, 17 different muscles work. In addition, with the help of skeletal muscles, joints, joints of bones are strengthened, internal organs are protected from external influences. Taking just one step forward, a person uses 54 different muscles.
Smooth muscle
With the help of its fibers all hollow organs are formed. These include blood vessels, the digestive tract, and the bladder. Such muscles contract and relax slowly, but for a long time they can maintain a state of tension. Their work, like that of the heart muscle, is not controlled by consciousness. Stable activity of smooth muscle fibers provides peristalsis - waves of contractions and relaxations that promote the movement of contents along all tubular organs. Smooth muscles are also present in other parts of the body. An example is the eye. Such musculature in the eye automatically changes the lens curvature and pupil diameter, controlling the sharpness and brightness of the perceived image.
Muscle work
The work of the main muscle groups and their functions are associated with the conversion of energy, part of which is dissipated in the form of heat, which makes it possible to maintain a body temperature of about 37 degrees. Muscles, being at rest, generate about 16% of heat. During physical activity, this percentage increases sharply. Therefore, with heavy movement, the body warms up even in extreme cold. When a person trembles from the cold, his muscles work harder, thereby increasing heat transfer.
Muscle structure
The main muscle groups are surrounded by elastic connective films, which are penetrated by nerves and blood vessels. This fibrous tissue extends beyond the muscle, forming tendons or plates that connect it to the bones. This material is much stronger than muscle. Skeletal muscle fibers are bundled. Cross-striped fiber is a huge cell, sometimes passing, for example, in the legs, along the entire muscle 30-40 cm long. It is filled with many parallel contractible threads, myofibrils. Each of them consists of alternating bundles of thick and thin protein filaments, the ends of which are slightly overlapping. When a muscle receives a nerve signal, it starts inside the chemical processes that cause thick fibers to slip relatively thin, penetrating into the gaps between them. As a result, the fibers contract, and ultimately the muscle. A muscle can only contract, that is, move the bone with which it is connected, only in one direction. Relaxing, she returns to her previous length due to external stretching. Therefore, the main muscle groups of a person are assembled into groups, forming opposite pairs that pull the same part of the body in opposite directions.
Where does muscle strength come from ?
Considering the work and structure of the main types and groups of muscles, you need to know their source of energy. Muscle tissue receives the main energy for its contraction by burning glucose in its fibers with the help of oxygen to form water and carbon dioxide. This is how cellular respiration occurs, while glucose enters the body with food, and oxygen from the air during respiration. With the help of blood, these substances enter the muscles. With intense work, muscles need much more energy and nutrition than at rest. As a result, breathing quickens, and the heart beats faster, delivering more blood to the muscles. However, if the load is too high, the lungs and heart cannot cope with their task. And although glucose stores in the body accumulate, without the right amount of oxygen, the muscles begin to receive energy, oxidizing glucose without its participation. Anaerobic respiration occurs. As a result, water and carbon dioxide are not formed, but lactic acid accumulates. With a high concentration of acid, the muscles tan, spasms and soreness appear in them. That is why extreme stress often leads to aches throughout the body. After overloads, the body needs rest to remove lactic acid and restore blood glucose and hemoglobin levels.
Interesting about muscles
The most massive muscle in the body is the gluteus maximus muscle. The smallest in the human body is the stirrup, which regulates the pressure on the inner ear of one of the auditory ossicles, the stapes.
The longest muscle is the tailor muscle, extending from the pelvis and tibia and flexing the leg in the hip and knee joints.
Chewing muscles, clenching teeth, can develop strength up to 91 kg, that is, they can hold such weight.