Climatic zones on our planet are distinguished depending on what type of climate is characteristic of their territory. What climatic zones exist, what air masses circulate above them, how the African tropical zone is characterized, read the article.
Air masses
This is the air of the troposphere in large volumes, with approximately the same properties. Air masses spread over vast areas, which are measured in thousands and millions of square kilometers. They extend upwards at a distance of several kilometers, right up to the border with the troposphere. Air masses move in a general direction, but inside them there are different wind forces. A mass of air forms above the surface, which is called the underlying. In contact with it, it acquires characteristic properties: temperature, humidity, degree of dust or transparency. When moving over a surface with other properties, the air mass undergoes heating or cooling, moistening or drying out, as a result of which it acquires the properties of another air mass, that is, it transforms.
Climatic zones
The climate in different parts of our planet is different. It is influenced by the inclination of the sun's rays to the surface of the Earth. This or that climatic zone is located in a certain climatic zone. What it is? Climatic zones are vast territories encircling the Earth with a strip that is continuous or intermittent. There are a total of thirteen climatic zones in the Northern and Southern Hemispheres. The border of each of them is determined by various factors. These include the amount of radiation coming from the sun, and the type of air mass that is dominant.
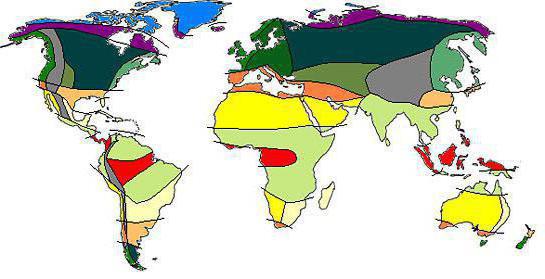
Each latitudinal strip has approximately the same climate. But there are significant differences in temperature, atmospheric pressure, prevailing winds, rainfall in different climatic zones. The movement of air masses is also changing. Even during the year, different types dominate in one territory. They stretch horizontally in the west-east direction and replace each other vertically, starting from the equator to the poles, climatic zones and types of climate. The tropical zone, for example, is classified as the main climatic zone, but there are also transitional ones, which will be discussed later in the article.
Classification of climate zones by type of air mass
Temperature and precipitation are distributed within the zones under the influence of a number of factors: the proximity of the oceans, topography, warm and cold currents. Therefore, in the climatic zones, regions are distinguished, each of which is characterized by its own climate. Depending on the type to which the air masses belong, and climatic zones are different:
- The main ones are characterized by the presence of a single type of air mass throughout the year. These include the equatorial, arctic, antarctic type of air masses, as well as two temperate and tropical ones.
- Transitional. They are characterized by the dominance of two types of air masses simultaneously. Such climatic zones and air masses characteristic of them are limited to the main zones. These include: subarctic, subantarctic, as well as two sub-equatorial and subtropical ones. Names are given by the type of air masses, and “sub” is a prefix to the word, which means that this belt is secondary and is located next to the main one.

Transitional the belts are characterized by a change in air masses depending on the seasons. For example, in winter, the same air masses prevail as in the main belt adjacent to the pole, and in the summer to the equator. Thus, the subequatorial tropical belt is characterized by the dominance of the equatorial air mass in the summer, and the tropical one in the winter.
Climate types
What is climate? This is a weather mode characteristic of a particular area and repeating over the years. Its manifestation is a regular change of weather that is observed in a given area. The climate is divided into types, which are understood as climatic indicators (their constant set), characteristic of a particular area for a long time. These include:
- Solar radiation (its quantity).
- Temperature fluctuation.
- The type of air mass that prevails in a given area.
- Mode of precipitation and their amount.
For the equatorial, arctic and antarctic climatic zones, only one type of climate is characteristic, since air masses are constant throughout the year. In tropical, temperate and variable zones, regions are also distinguished, the climate of each of which has its own type.
Tropical climate zone
It spreads throughout the Southern Hemisphere as a continuous strip. Over the oceans throughout the year dominated by constant baric maxima. They form the air masses of the tropical zone. It is torn over territories such as Indochina and Hindustan. The gap occurs because the air masses of the tropical zone do not dominate here throughout the year. In summer, the equatorial air penetrates into the Asian minimum, and in winter - the invasion of moderate air masses from its maximum.
Tropical climate
Its main characteristic is the dominance of the air masses of the tropical zone throughout the year. Moreover, their temperature is always high. In the warmest month, the thermometer shows +30 ° C and more. There are days when the temperature reaches +50 , and the Earth’s surface heats up to +80 . The tropical climate zone is characterized by increased pressure and also descending air flows, as a result of which water vapor condensation does not occur. For this reason, there is little rainfall, up to 250 mm per year, which leads to the formation of such deserts in Africa, the Arabian Peninsula and Australia, which are considered the greatest in the world, for example, Sahara, Kalahari.

But not everywhere, the climate of the tropical zone is arid. On the east coast, where trade winds blow from the ocean, precipitation falls in large quantities, 1,500 mm per year. These are the territories of the Antilles, the east coast of Africa and others. The climate is influenced by warm currents that wash the coast of the continents from the east. The western coasts are characterized by a climate called “garua”, or “drizzling fog”. It has an interesting feature: when precipitation is 0 mm, the indicators of relative humidity range from 85 to 90%. The climate of the western coasts is formed under the influence of constant baric maxima that hold above the oceans, and cold currents that run along the coasts of the continents.
Tropical belt of Africa
Air masses are characterized by properties such as dryness, dustiness, high temperature, lack of precipitation, the amount of which is less, the farther from the center of the African continent. Therefore, there are many deserts for the formation of which there are all conditions: the presence of dry air, location away from the ocean and pressure, which is always elevated.
The largest desert of our planet, located in Africa, is the Sahara. Here, for several years in a row, precipitation has not been falling, so it is very difficult for a person to survive in the desert. The air masses of the tropical zone are filled with dust, because the strong winds that blow here often create storms of sand and dust. The result of their "creation" are various forms of sand reliefs.
The climate of Africa is characterized by sudden changes in temperature. During the day, it reaches +40 ° C and more, and at night it drops to zero or lower. On the territory of the Libyan Desert, located in the African tropical zone, the temperature is +58 ° C.