The human body is in constant interaction with abiotic and biotic environmental factors, which affects it and changes it. The origin of man has been of interest to science for a long time, and theories of its origin are different. It is also that a person came from a small cell, which gradually, forming colonies of cells of its own kind, became multicellular and, in the course of a long course of evolution, turned into a humanoid monkey, and which, thanks to work, became a man.
The concept of levels of organization of the human body
In the process of training in a secondary school at biology classes, the study of a living organism begins with the study of a plant cell and its components. Already in high school, in class, students are asked the question: "What are the levels of organization of the human body." What it is?
The term "levels of organization of the human body" is understood to mean its hierarchical structure from a small cell to an organismal level. But this level is not the limit, and it is completed by the supraorganismal order, which includes the population-species and biosphere levels.
Highlighting the levels of organization of the human body, their hierarchy should be emphasized:
- Molecular genetic level.
- Cell level.
- Fabric level.
- Organ level
- Organizational level.
Molecular genetic level
The study of molecular mechanisms allows us to characterize it with such components as:
- carriers of genetic information - DNA, RNA.
- biopolymers are proteins, fats and carbohydrates.
At this level, genes and their mutations are distinguished as a structural element, which determine variability at the organismic and cellular levels.
The molecular genetic level of organization of the human body is represented by genetic material, which is encoded in a chain of DNA and RNA. Genetic information reflects such important components of the organization of human life as morbidity, metabolic processes, type of constitution, gender component and individual characteristics of a person.
The molecular level of organization of the human body is represented by metabolic processes, which consist of assimilation and dissimilation, regulation of metabolism, glycolysis, crossing-over and mitosis, meiosis.
Property and structure of a DNA molecule
The main properties of genes are:
- invariant reduplication;
- ability to local structural changes;
- transmission of hereditary information at the intracellular level.
The DNA molecule consists of purine and pyrimidine bases, which are connected by the principle of hydrogen bonds with each other and for their connection and rupture requires enzymatic DNA polymerase. Invariant reduction occurs according to the matrix principle, which ensures their connection at the residue of the nitrogenous bases of guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine. This process occurs in 100 seconds, and during this time 40 thousand pairs of nucleotides have time to collect.
Cell level organization
Studying the cellular structure of the human body will help to understand and characterize the cellular level of organization of the human body. The cell is a structural component and consists of elements of the periodic system of D. I. Mendeleev, of which the most predominant are hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen and carbon. The remaining elements are represented by a group of macroelements and microelements.
Cell structure
The cell was discovered by R. Hooke in the XVII century. The main structural elements of the cell are the cytoplasmic membrane, cytoplasm, cell organelles and the nucleus. The cytoplasmic membrane consists of phospholipids and proteins as structural components to provide cells with pores and channels for the metabolism between cells and the entry and removal of substances from them.
Cell nucleus
The nucleus of the cell consists of the nuclear membrane, nuclear juice, chromatin and nucleoli. The nuclear shell performs a shaping and transport function. Nuclear juice contains proteins that are involved in the synthesis of nucleic acids.
Kernel functions :
- storage of genetic information;
- reproduction and transmission of genetic information ;
- regulation of cell activity in its life-supporting processes.
Cell cytoplasm
The cytoplasm consists of general purpose and specialized organelles. General purpose organelles are divided into membrane and non-membrane.
The main function of the cytoplasm is the constancy of the internal environment.
Membrane organelles:
- Endoplasmic reticulum. Its main tasks are the synthesis of biopolymers, intracellular transport of substances, is a depot of Ca + ions.
- Golgi apparatus. It synthesizes polysaccharides, glycoproteins, participates in the synthesis of the protein after it leaves the endoplasmic reticulum, carries out transport and fermentation of secretion in the cell.
- Peroxisomes and lysosomes. Absorbed substances are digested and macromolecules are broken down, neutralize toxic substances.
- Vacuoles. Storage of substances, metabolic products.
- Mitochondria. Energy and respiratory processes inside the cell.
Non-membrane organelles:
- Ribosomes. Proteins are synthesized with the participation of RNA, which transfers genetic information from the nucleus about the structure and synthesis of the protein.
- Cell center. Participates in cell division.
- Microtubules and microfilaments. Carry out a supportive function and contractile.
- Cilia.
Specialized organelles are the acrosome of sperm, microvilli of the small intestine, microtubule, and microcilia.
Now to the question: “Describe the cellular level of the organization of the human body”, you can safely list the components and their role in the organization of the cell structure.
Fabric level
In the human body, it is impossible to distinguish the level of organization in which any tissue consisting of specialized cells would not be present. Tissues are composed of cells and intercellular substance and, according to their specialization, they are divided into:
- Epithelial. Distinguish single-layered and multi-layered epithelium. It performs many functions, such as integumentary, secretory and others. Epithelial tissue lines the inner surface of the hollow internal organs and forms glandular organs.
- Muscle. It is divided into two groups, among which smooth and striated muscle tissue. It forms the muscular framework of the human body, is located in the walls of hollow organs and glands, blood vessels.
- Connective. It serves as the basis for the construction of the skeleton, as well as lymph, adipose tissue and blood.
- Nervous. It integrates the external and internal environment, regulates metabolic processes and higher nervous activity.
The levels of organization of the human body pass smoothly into each other and form an integral organ or system of organs that line many tissues. For example, the gastrointestinal tract, which has a tubular structure and consists of a serous, muscle and mucous layer. In addition, it has the blood vessels that feed it and the neuromuscular apparatus, which is controlled by the nervous system, as well as many enzyme and humoral control systems.
Organ level
All levels of organization of the human body, listed above, are components of the organs. Organs perform specific functions to ensure in the body the constancy of the internal environment, metabolism and form a system of subsystems subordinate to it, which perform a specific function of the body. For example, the respiratory system consists of the lungs, respiratory tract, respiratory center.
The levels of organization of the human body as a whole are an integrated and fully self-supporting organ system that forms the body.
Organism as a whole
The combination of systems and organs form the body in which the integration of the systems, metabolism, growth and reproduction, plasticity, irritability are carried out.
There are four types of integration: mechanical, humoral, nervous and chemical.
Mechanical integration is carried out by intercellular substance, connective tissue, and auxiliary organs. Humoral - blood and lymph. Nervous is the highest level of integration. Chemical - hormones of the endocrine glands.
The levels of organization of the human body is a hierarchical complication in the structure of his body. The body as a whole has a physique - an external integrated form. Build - this is the external form of the human body , which has various gender and age characteristics, structure and position of internal organs.
There are asthenic, normosthenic and hypersthenic types of body structure, which are differentiated by growth, skeleton, muscle, the presence or absence of subcutaneous fat. Also, in accordance with the type of physique, organ systems have a different structure and position, size and shape.
The concept of ontogenesis
The individual development of an organism is determined not only by genetic material, but also by external environmental factors. Levels of organization of the human body, the concept of ontogenesis, or the individual development of the body in the process of its development, uses different genetic materials involved in the functioning of the cell in the process of its development. The work of genes is affected by the external environment: through environmental factors, there is an update, the emergence of new genetic programs, mutations.
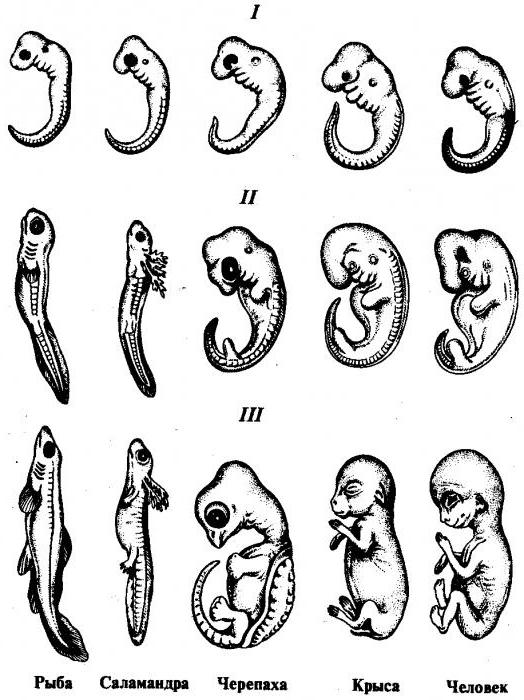
For example, hemoglobin changes three times during the entire development of the human body. Proteins synthesizing hemoglobin go through several stages from embryonic hemoglobin, which passes into the hemoglobin of the fetus. In the process of maturation of the body, hemoglobin passes into the form of an adult. These ontogenetic characteristics of the level of development of the human body briefly and clearly emphasize that the genetic regulation of the body plays an important role in the development of the organism from the cell to the systems and the organism as a whole.
A study of the organization of biological systems allows you to answer the question: "What are the levels of organization of the human body?" The human body is regulated not only by neuro-humoral mechanisms, but also by genetic ones, which are located in every cell of the human body.
The levels of organization of the human body can be briefly described as a complex subordinate system, having the structure of the same structure and complexity, as the whole system of living organisms. This pattern is an evolutionarily fixed feature of living organisms.