Every mother sooner or later asks a question: if there is a rash on the child’s body, what should I do? Sometimes rashes are a reaction to physiological changes in the children's body that are not dangerous, but there are also pathological causes of the rash that require immediate action to eliminate them.
Some parents simply ignore this, especially if the rash on the child’s body is without fever, and some begin to give various medications without consulting a doctor. In both the first and second cases, a mistake is made, because in some diseases it is very important to identify the cause of the rash as soon as possible and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
What a rash might look like
The rash of the child does not always appear throughout the body, very often it happens in a limited area. It is formed both symmetrically and asymmetrically, acquiring all kinds of forms:
- Spots - a limited area of the skin of a different color (it is white, red, pink, etc.). As a rule, spots do not protrude above the surface of the skin.
- Bubbles and vesicles are small or large formations with fluid inside.
- Papules - formations above the surface of the skin without a cavity inside. You can feel it well.
- Pustule - a cavity with pus inside.
- A plaque is a formation that has a large area and is elevated above the skin.
- Tubercles are formations that do not have a cavity and are well felt on palpation.
The color of the rash can also be different - from pale pink to crimson. A photo of a red rash on a child’s body is presented below.
Each type of rash can talk about completely different reasons, so determining the location of the rash and its type is very important for making a diagnosis.
Causes
If a rash appears on the child’s body, the causes of this condition are very diverse, but still they can be divided into main categories:
- Infectious diseases, which, in turn, are divided into diseases caused by a viral pathogen (mononucleosis, chickenpox, rubella, measles) and bacteria (scarlet fever).
- Autoimmune processes in the body.
- Allergic reactions, when a rash occurs on the child’s body after contact with an allergen, which can act as food, household cleaning products, flowering plants, animal hair and many others. Contact dermatitis belongs to this category.
- Inflammatory skin processes.
- Insect bites.
- Diseases of a parasitic nature.
- Hormonal changes in the body of the child.
- Poor body hygiene.
Symptoms of a rash are quite multifaceted. It depends on what reason contributed to it. Next, we will analyze which pathologies can cause a rash, and what signs they are accompanied by.
Noncommunicable diseases. Acne Newborn
In about 20-30% of infants, the so-called acne of the newborn appears, characterized by the appearance of a rash on the body of a child without fever. The main location is the face and scalp, neck. The rash in this case has the form of papules and pustules. It occurs due to the fact that maternal hormones affect the work of children's sebaceous glands. It does not require special care, with the exception of hydration and thorough hygiene. It usually takes place during the first 6 months of the baby’s life.
Prickly heat
A rash that occurs in newborn babies during the warmer months or when wrapped heavily in clothing. The reason is the difficulty in perspiration and increased humidity when wrapping. Often occurs in places of diaper rash. With such a rash, inflammation is rarely possible, but it causes discomfort, as it can be very itchy. Passes with proper care pretty quickly.
Atopic dermatitis
This is a disease that a large number of mothers encounter during the first days of a baby's life. Dermatitis has a genetic predisposition and an allergic nature. It is characterized by the appearance of red itchy spots and dry skin. Rashes can cover both a small area - with a mild form, and spread over a large area of the body. In some cases, with the extensive presence of a rash in the child, traces of combing appear throughout the body, as an intolerable itching occurs. As a result of this, a secondary infection sometimes joins dermatitis.
Since dermatitis has several stages of development, there are also many options for a rash with this disease. These can be spots, papules, vesicles, plaques, crusts. Sometimes with untimely treatment, scars and age spots remain on the skin after rashes.
Teething rash
Sometimes the baby during teething is disturbed by a rash located in the mouth. It is a small pimple that appears due to increased salivation, and then the friction of this area. Such a rash does not leave any consequences after itself and, as a rule, passes independently. To make the healing process faster, you can gently wipe the mouth area from the saliva and prevent the child from licking dirty hands, as there will be a chance of infection.
Allergic rash in children
If parents notice a rash on the body of a child without fever, this is most likely an allergic reaction. Nowadays, people are surrounded by a huge number of all kinds of allergens. Children are most susceptible to them, so at the first manifestations you need to identify the cause and get rid of the irritant. An allergic reaction can be of the following types:
- Food. When a child eats a product that is an allergen to him. It appears in about 24 hours. The rash in this case occurs on the face, stomach, arms and legs of the child.
- Household. In this case, the allergen can be obtained from washing powder, chlorinated pool water, new shampoo and many other household products.
An allergic rash looks like red spots on the child’s body, but sometimes plaques and scratches appear, since skin rash is very worried about such rashes. One type of rash in this case is urticaria - pink or red blisters that itch very badly. When combing, they increase in size and can merge with each other, forming large areas of damage. Symptoms, in addition to the rash, may include irritability, moodiness, runny nose and cough.
In newborns, an allergen can enter the body with mom's milk. A nursing woman needs to review her diet as soon as possible. And there are also cases when an allergy provokes the nutrition of a future mother during pregnancy. Sometimes a rash occurs in the child throughout the body. But after getting rid of the allergen, rashes pass very quickly. A photo of an allergic rash on a child’s body is presented above.
Insect bites
A rash on the body of a child after insect bites is a very common occurrence, especially in the summer. Many parents are frightened by red spots, which can be large and appear over the skin. But they, as a rule, have no extraneous symptoms and consequences except for itching. But the exception is the allergic effects on saliva and poison of some insects. In this case, it is very important to give an antihistamine at the first signs of an allergy. Another dangerous phenomenon with a bite is an infectious disease, of which some insects are carriers.
Infectious rash in children
The appearance of a rash in a child throughout the body very often occurs due to infectious diseases. Some of them are common precisely in childhood, because after the child is ill, he develops one hundred percent immunity. Very rarely there are cases of reinfection. If the rashes appeared due to infection, the symptoms will be temperature and a small rash on the child's body, chills, cough, runny nose, lack of appetite, and general malaise are also added here.
In childhood, the most common diseases accompanied by a rash are as follows:
- Chicken pox (chickenpox). This disease is very contagious, easily transmitted by airborne droplets. The incubation period lasts 2-3 weeks. General malaise, accompanied by a moderate increase in temperature, sometimes a slight abdominal pain, occurs 1-2 days before the rash begins. Then a small rash appears on the child’s body, which is randomly located without affecting only the feet and hands. At first it looks like a red speck, which quickly turns into a papule, and that, in turn, into a vesicle with an infectious liquid inside. At the place of its breakthrough, a crust forms naturally or mechanically (during combing). Rashes are accompanied by itching, but they can not be combed, since the infection can be spread even more. Chickenpox is characterized by the fact that during the illness there are several rashes that are completely covered with a crust. Then they completely disappear, leaving small scars that disappear after a while. This happens on the tenth day after the rash begins. During the disease it is not recommended to visit public places. After recovery, the child develops lifelong immunity to chickenpox. Re-infection occurs only because of reduced immunity and under stress.
- Measles. A highly contagious infectious disease transmitted by airborne droplets. Nowadays, measles is rare, mainly in the form of short outbreaks in certain regions. The latent form of the disease lasts about 2-4 weeks, then within about four days the first signs of the disease begin to appear, which are very easy to confuse with a cold or digestive disorder: cough, runny nose, loose stools, fever, which can rise up to 40 degrees. After this period, rashes that have a cycle begin. First, white spots appear on the inside, which look like semolina. These spots are a very important symptom of measles. Then the rashes appear on the face and neck, descend on the chest, shoulders, stomach and back, and after the rash appears on the child’s body on the legs and arms. On the fourth day, the primary symptoms begin to recede, and the rash is on the decline. In place of spots, the skin becomes brown, then it begins to peel off and after 7-14 days it is cleansed. During measles, the rashes may itch a little, sometimes small bruises appear. Sometimes individual spots can merge into a continuous surface. It is worth noting that some manifestations of measles may occur within 10 days after the introduction of a live measles vaccine.
- Rubella is a contagious viral disease transmitted by airborne droplets. The incubation period can last up to three weeks. At the end of this period, a slight increase in temperature, general malaise, joint pain, and cervical lymph nodes can become inflamed. Then a small rash appears on the child’s body. It starts on the forehead and cheeks, spreads throughout the body. The favorite places that characterize rubella are the areas around the joints, knees, elbows and buttocks. A rash with this disease does not affect the feet and palms of the child. After about four days, the rashes stop, and after a week there is no trace of them.
- Roseola is a contagious disease that every baby can face. The first signs will be fever, sore throat and enlarged lymph nodes. Then a small rash appears on the child’s body, similar to rashes with rubella.
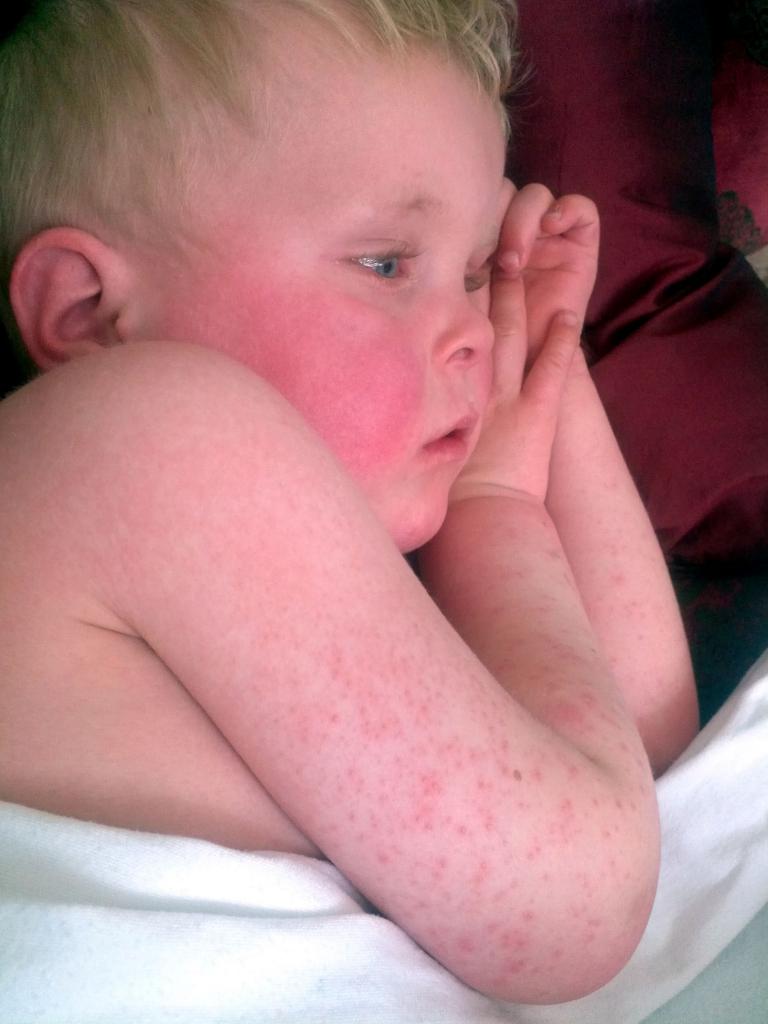
- Scarlet fever is an infectious disease caused by streptococcus. It is transmitted by airborne droplets, there is no vaccination against this disease. The latent phase lasts about a week. Then there is an increased temperature (up to 38-40 degrees), lymph nodes increase and symptoms of angina appear. The tongue is covered with white coating. Cleansing, it becomes a bright crimson color with pronounced papillae. After 1-2 days, a rash begins, which first affects the face, then the neck and everything else. Most rashes in the groin, in the elbow bends, on the inside of the arms and legs, in the area of the bends. At first, the rash has a bright color, but as the spots decrease, they begin to fade. A striking sign of scarlet fever is a pale nasolabial triangle against a background of bright red cheeks. This is due to the fact that the rash does not affect this area, and the skin in this place does not redden. After 4-7 days, the rashes pass, but leave a peeling after themselves. Angina has to be treated for some more time.
- Infectious mononucleosis is an infection that belongs to herpes viruses and is not too contagious. The characteristic signs of mononucleosis are inflammation of the lymph nodes, enlargement of the spleen and liver, body aches, tonsils, coated with plaque, fever. A rash with this disease is very rare. If rashes do appear, they look like a small pink rash that does not itch and passes without a trace for several days.
- Meningococcal infection. This is a very dangerous disease that requires immediate therapeutic action, since procrastination is fraught with the death of the patient. Meningococcus is a bacterium that lives in the nasopharynx in 5-10% of people and does not cause anxiety. Due to viral infections or a decrease in immunity, an active phase of bacterial growth can begin, leading to dangerous consequences. Transmitted by air. When it enters the blood, it makes its way to the brain, causing meningitis. In this case, a rash is not observed. The main symptoms are fever, drowsiness, vomiting, loose stools, hardness of the occipital muscles, confusion, the child cannot reach his chest with his chin. Symptoms develop very quickly. Meningococcus can also cause sepsis. It is very dangerous! The temperature can rise to 41 degrees and be accompanied by indomitable vomiting. Within a few hours, a rash appears that has an uneven star-shaped shape and a bright crimson or bluish color, itching is not present. Individual rashes can merge into one large dark purple spot. On the feet and palms, such a fusion forms “socks” and “gloves”. In such cases, the skin in these places may die. Sometimes meningitis and sepsis occur simultaneously. Meningococcal infection is deadly! At the first symptoms, you must immediately go to the infectious diseases hospital. With this disease every second is precious. Before the ambulance arrives, you need to lay the child on the floor, raising his legs, in case of loss of consciousness - lay on one side, do not give drink and eat.
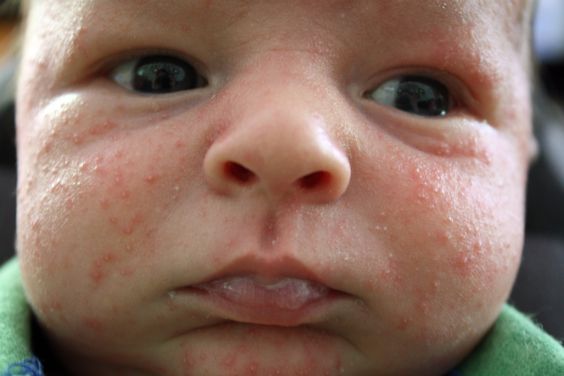
- Scabies. This disease is caused by a scabies mite. The rash is localized between the fingers, in the inguinal region, on the wrists, legs, pope and wherever thin skin is. Rashes are accompanied by severe itching, which occurs during the passage of the tick under the skin of the child. Scabies is very contagious.
The difference between an infectious rash and a non-infectious rash
An infectious rash is necessarily accompanied by additional symptoms, while a non-infectious rash occurs almost without third-party manifestations. So, a rash on the body of a child with a temperature will always talk about the infectious nature of the disease. Rashes without external symptoms do not pose a serious danger. A photo of the rash on the child’s body (without a temperature, the disease is not so dangerous) is not a very pleasant sight.
Itching without rash
Sometimes parents are concerned about a situation in which the child itches, but it is not possible to notice external causes. Itching of the body in a child without a rash can be for several reasons, but the final conclusion can be made only after taking a doctor and passing certain tests:
- The most likely cause of itching is allergy. In this case, in the absence of a rash, other additional symptoms may appear - cough, runny nose.
- Another reason may be poor hygiene.
- It happens that the cause of the itch is the psychological aspect, when stress and excitement are present in the child's life. In this case, there is a likelihood of developing neurodermatitis, in which the child is worried about severe itching without other additional signs.
- Skin parasites in which itching appears, but there is no rash.
- An important reason may be a violation in the functioning of internal organs and systems. The conclusion can be made by a doctor.
Rash treatment
A rash is not an independent disease, but a symptom. Therefore, first of all, you need to find the cause of the rashes. It is not recommended to self-medicate even in situations where parents are sure that they know the reason. In any case, you should consult a doctor. Therapy will depend on the diagnosis and condition of the sick child:
- When confirming an allergic reaction, it is necessary to exclude contact with the allergen and take antihistamines.
- With chickenpox, treatment will be aimed at relieving symptoms - antipyretic drugs and antihistamines are prescribed to help relieve itching. Rashes can be cauterized with brilliant green. Bathing a child is allowed, but only gently pouring water.
- With measles and rubella, treatment is also aimed at relieving symptoms - an antipyretic agent at high temperature, a cough and runny nose medicine, and heavy drinking.
- , , .
- – , . , .
- Meningococcal infection is the most dangerous bacterial infection in which there is a high risk of death. At the slightest symptom, an ambulance should be called immediately. The treatment is only inpatient; it is impossible to relieve symptoms at home. For treatment, antibiotics, anticonvulsant therapy, cardiovascular agents, the introduction of saline solutions, and others will be used.
Prevention of infectious diseases is vaccination. It is strictly forbidden to strip off rashes, squeeze them out and comb them.
Dangerous symptoms
There are some symptoms that accompany the rash, and in which you need to, without delay, call an ambulance:
- The rash covers the entire body area.
- There is an intolerable itch.
- There is a fever.
- Accompanied by edema, vomiting, loss of consciousness and nausea.
- The most dangerous sign is if the rash has the appearance of stellate hemorrhage.
Conclusion
In most cases, the rash does not pose a serious threat. But it is worth remembering about the serious diseases that it can accompany. Therefore, if there is a rash on the child’s body with fever and other symptoms, you should contact your doctor as soon as possible.