The quality of many goods in furniture, automotive, construction industry and other industrial sectors directly depends on the solid and high-quality fastening of individual structural parts to each other. The countersunk head fixing bolt is one of the universal devices that reliably connect various elements into a single product.
Bolt appearance
In ancient Russia, the tips for crossbow arrows, having a different shape , were called bolts. Later, it was called any elongated product of a cylindrical shape. And only with the development of construction technologies, the screw connection of parts replaced all other meanings of the word.
Today, threaded bolts are used in various fields of both daily life and industrial production.
Countersunk Bolt Description
This fastener received its name for the peculiar shape of the head. A flat rod with threaded screw threads is crowned with a flat cone-shaped hat with a slot - a turn-key recess or a screwdriver.
The countersunk head bolt enters the entire hole of the item being fastened. The head is buried in the material without protruding on its surface. A variety of sizes of countersunk head bolts, ease of use, bond strength and ability to withstand heavy loads significantly expand their scope.
Classification of bolt fasteners
Pitch and thread depth, screw length, head diameter and many other characteristics are determined by GOST. Countersunk bolts are divided according to purpose into several groups:
- Attachments of agricultural machinery are fixed with a forest head bolt.
- Furniture fasteners are used in the construction and furniture industries.
- Road fasten the elements of metal road fences and special structures.
- Engineering are used to connect parts in automobile, machine and instrument making.
The corresponding grade of carbon unalloyed or alloyed steel and production technology determine the strength of fasteners, expressed in nominal temporary resistance and yield strength. By mechanical
strength , countersunk head bolts are divided into 11 classes. Strength marking is applied to the cap and looks like two numbers with a dot between them (for example, 3.6 or 12.9). Unified marking simplifies the use of similar bolt fasteners in various industrial sectors. When calculating the load on the fastener, the
yield strength is primarily taken into account
, since when it is exceeded, irreversible deformations occur and the use of such a bolt with countersunk head is prohibited.
Steel and alloys
Mostly low-carbon steel with a content of not more than 0.4% carbon is used for the production of bolts. Subsequent heat treatment to prevent decarburization of fasteners, the process of cold or hot disembarkation and the application of a protective coating make it possible to obtain products of various strength classes.
In addition to carbon steel, bolts are made from other alloys:
- Alloyed steel grades are obtained by adding nitrogen, chromium, nickel, vanadium, copper and other additives that enhance the strength and corrosion resistance of products. Depending on the required physical or mechanical properties, the amount of alloying additives changes.
- Cold- resistant steel can withstand temperatures up to -75 0 C.
- Stainless steel is resistant to corrosion in the atmosphere or aggressive environment due to the high content of chromium in its composition.
- Heat-resistant (scale-resistant, heat-resistant) steel is not destroyed in gas environments at temperatures above +550 0 C. Nickel, chromium, molybdenum, titanium and silicon are used as additives.
- Heat-resistant alloys withstand high temperatures for a long time, without deforming and not collapsing. Alloying alloys of heat-resistant steels are chromium and silicon.
Less commonly, non-ferrous metals are used to make countersunk bolts: titanium, brass, copper, aluminum and polymers. High strength carbon alloys have a low level of corrosion resistance. If necessary, obtain fasteners of high strength and resistant to aggressive environments, the finished product is covered with a protective metal, inorganic, enamel or plastic coating by electrolytic or galvanic methods.
How to tighten countersunk bolts
To use a bolted connection, it is necessary to prepare the technological holes. Since the distinguishing feature of the bolt is the absence of a pointed tip, it will not screw into the material. With through fastening of parts, a hole is drilled without a thread as close as possible to the size of the bolt. The fastening is tightened with a nut. The fixing of the bolt in the material is ensured by an internal thread. The vertical hole is drilled 0.1-0.2 mm less than the diameter of the bolt and shorter by 1 mm. A thread is cut with a hand tap and the bolt is screwed in. The countersunk head is fully tightened flush with the surface of the product.
On the flat surface of the head of the slot, the slot may be in the form of a cross, a straight slot, or a hexagonal recess. A flat or Phillips screwdriver or Allen key is used, depending on the shape of the tightening hole.
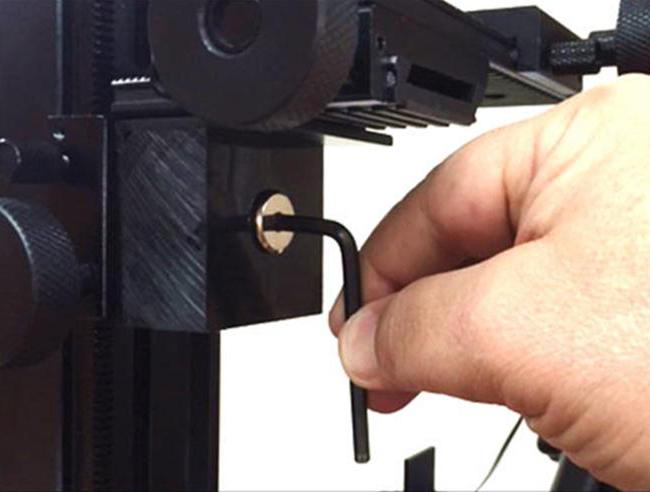
Hex Slot
The most widely used in all industrial fields hexagon socket head bolts. Fast and convenient installation with an electric or pneumatic tool provides increased strength for threaded fastening of parts. Conveyor assembly of high-strength mechanisms, components and assemblies is carried out with countersunk head bolts under the hexagon.
The special L-shaped hex keys are compact and easy to use. The exact dimensions and high strength of the hexagons make it possible to reliably tighten the bolts and, if necessary, to easily dismantle the connected parts.
The benefits of bolted connections
- Reliability of fastening is provided by a metric carving and a universal profile. The correctly selected strength class of the countersunk bolt and its high-quality tightening provide reliable protection of the product from self-loosening and guarantee the endurance of high loads.
- Made of appropriate steel grades, the bolts withstand axial and lateral loads.
- Using countersunk bolts, installation of any structures is faster and easier.
- The cost of assembly work is significantly lower than the cost, for example, for welding. Many building structures or automotive parts today are bolted to a countersunk head, since such work requires significantly less time and physical effort.

In the engineering and automotive industries, a countersunk head bolt with a mustache on the back of the cap is used to prevent unwinding. The triangular protrusion provides a stronger fixation of the bolt in the material. Most often, a bolt with a mustache is used when through the connection of parts and acts as a stopper when tightening the nut.
Scopes of hidden bolted connections
Countersunk bolts are widely used in all industrial fields and in everyday life. Accurate and durable connection of complex assemblies in instrumentation, vibration-resistant fastening of car parts and aircraft, reliable screeding of steel frames of buildings under construction, furniture assembly, decoration of buildings and many other types of joints are provided with countersunk bolts. Concealed fasteners made of durable and resistant to aggressive environments steel alloys not only provide reliable connections, they attract with their convenience and aesthetic appearance.
The flush head, recessed into the material, does not interfere with the moving parts of various mechanisms. Furniture or decorative elements of the interior, assembled with secret fasteners, without protruding bolt heads, have a very attractive appearance.