In this article, the reader will find information about the structure of the human throat, about its constituent elements and functions. In addition, we consider what the nasopharynx, oropharynx and larynx are. Let's get acquainted with the features of the anatomical structure of these structures.
What is the throat and larynx?
The throat is one of the most important organs of the human body, related to the upper respiratory tract. Its structure promotes the movement of air through the respiratory system, and food allows it to enter the digestive tract. In addition, the area includes a huge number of nerve tissues, blood vessels and pharyngeal muscles that are important for human life. In the structure of the throat, the main parts are represented by the pharynx and larynx.
With their continuation, they form the trachea. The structure of the throat and larynx is arranged in such a way that the first of these structures is responsible for the movement of air into the lungs, and food to the stomach, and the second structure takes responsibility for the vocal cords.
Device principle
The throat is a very complex organ responsible for breathing, speaking, and promoting food.
In short, its structure is based, as we said earlier, on the pharynx (pharynx) and larynx (larynx). Since this organ is a conducting channel, it is very important that all its muscles work smoothly and correctly. Inconsistency in their activities will lead to the fact that food can get into the respiratory system and create a dangerous situation, even bring to death.
The structure of the throat in a child is the same as in adults. But children have narrower cavities and tubes. As a result of this, every disease in which swelling of these tissues occurs can be extremely dangerous. It is desirable for a person to know the structure of such an organ, since this can be useful in case of care for him and during treatment. In the pharynx, the nasopharynx and oropharynx are secreted.
Pharynx
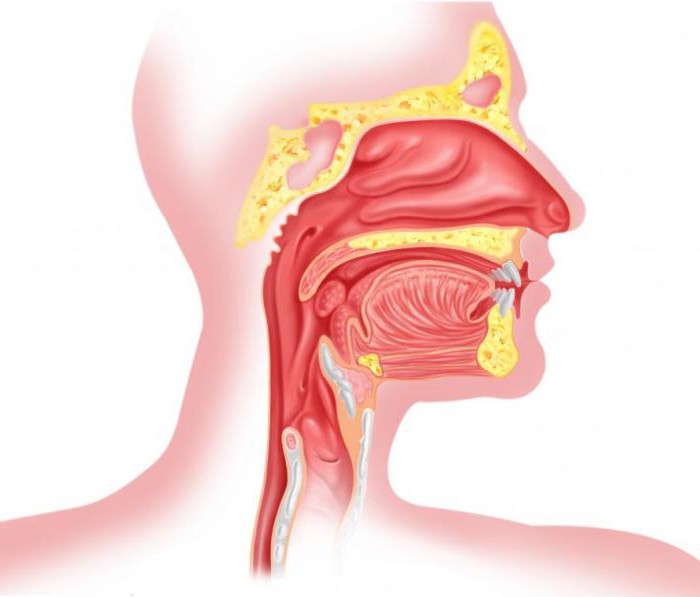
The pharynx (pharynx) is a cone-shaped structure, turned upside down. It is located behind the oral cavity and lowers to the neck. The cone is wider at the top. It is located near the base of the skull, which gives it more strength. The lower part combines with the larynx. The tissue layer covering the pharynx from the outside is represented by the continuation of the oral tissue layer lying on the outside. It has many glands that produce mucus, which is involved in the hydration of the throat when eating and talking.
Nasopharyngeal Compound
In the structure of the throat and larynx, the structures forming them, for example, the nasopharynx and oropharynx, mentioned above, are isolated. Consider one of them.
The nasopharynx is the part of the pharynx that occupies an upper position. From below it is limited by a soft sky, which in the process of swallowing starts to move up. Thus, it covers the nasopharynx. This is necessary to protect it from ingestion of food particles in the respiratory tract. In the upper wall of the nasopharynx there are adenoids - tissue clusters located behind its wall. This organ also has a tunnel connecting the throat to the middle ear. Such a formation is called the Eustachian tube.
The oropharynx is ...
Another element in the structure of the throat and larynx of a person is the oropharynx.
This fragment is located behind the oral cavity. Its main function is to conduct air flow from the mouth to the respiratory system. This part is more mobile in comparison with the nasopharynx. Due to this, when a muscle tissue of the oral cavity is reduced, a person can speak.
We already know that certain constituent elements are distinguished in the structure of the throat, but they will also include other, even smaller components. Among them, one can distinguish a language that helps to promote food into the esophagus by reducing muscle systems. And there are tonsils that are very often involved in sore throats.
Acquaintance with the larynx
In the structure of the throat there is another important composite fragment - the larynx.
This organ occupies space at the level of the 4th, 5th and 6th vertebra of the cervical spine. The hyoid bone is located above the larynx , and a group of hyoid muscles is formed in front. The lateral areas abuts against the thyroid gland. The area located behind carries a laryngeal fragment of the pharynx.
Cartilages form the skeleton of this area, connecting with each other through ligaments, muscle groups and joints. Among them stand out paired and unpaired.
Paired cartilage:
- scyphoid pair;
- horn-shaped pair;
- wedge-shaped pair.
Unpaired cartilage:
- cricoid;
- epiglottis;
- thyroid.
In the muscular system of the larynx, three main groups of muscle formations are distinguished. Among them there are tissues responsible for reducing the lumen of the glottis, tissues designed to expand the vocal cords, and tissues that strain the vocal cords.
General information about the structure of the larynx
The larynx has an entrance, in front of which is the epiglottis, and on the sides are scooped palatine folds, represented by a number of wedge-shaped tubercles. Behind the body are the arytenoid cartilages represented by horn-shaped tubercles. These fragments are located on the mucous membrane, along its lateral parts. The laryngeal cavity includes the vestibule, the sub-vocal region and the interventricular section.
The first part originates in the epiglottis and extends to the folds. Here, thanks to the mucous membrane, special folds are formed, between which lies a gap called the vestibule.
The sub-vocal region is the lower part of the larynx passing below into the trachea.
The interventricular section is a narrow section between the upper folds of the vestibule and the lower vocal cords.
A number of membranes are secreted in the larynx:
- mucous membranes;
- fibrocartilage;
- connective tissue.
The main functions of the larynx are attributed to protective, voice-forming and respiratory. Each of them has a special meaning.
The respiratory and protective functions form a close relationship with each other. This is due to the fact that there is a delivery of air flow to the lung organs, and at the same time the direction of flow is regulated. Regulation of the air path is ensured by the activity of the glottis, capable of compression and expansion. In addition, the protective function is performed by the glands located in the ciliated epithelium.
Although the structure of the ear, throat and nose is different, the interconnection of these organs in the human body is extremely large. They combine with each other and are located in approximately the same areas. The activity of each component affects the operation of the other. Their role is an irritating reaction followed by a cough when food enters the respiratory tract and organs. Using this mechanism, the larynx removes food into the oral cavity. This body is also involved in the formation of voice. The parameters of its height and sonority are determined by the anatomical structure of the larynx. For example, a hoarse voice appears due to insufficient moistening of the ligaments.