What are lipids? Biochemistry pays particular attention to this class of organic compounds. Let us consider in more detail the features of their structure, as well as properties, functions, applications.
Theoretical aspects
Lipids (fats) are low molecular weight organic substances that are partially or completely insoluble in water. They can be extracted from the cells of plants, animals, microorganisms using non-polar organic solvents (benzene, ether, chloroform).
How are lipids secreted? The biochemistry of these compounds is based on the characteristics of their chemical composition and structure. They have fatty acids, alcohols, phosphoric acid, heterocyclic nitrogenous bases, carbohydrates. It is difficult to give a single definition of lipids, given how versatile their chemical structure is.
Biological importance
How is lipid metabolism? Biochemistry is characterized by numerous functions performed by these compounds: reserve, energy, structural, regulatory, protective. We analyze them in more detail:
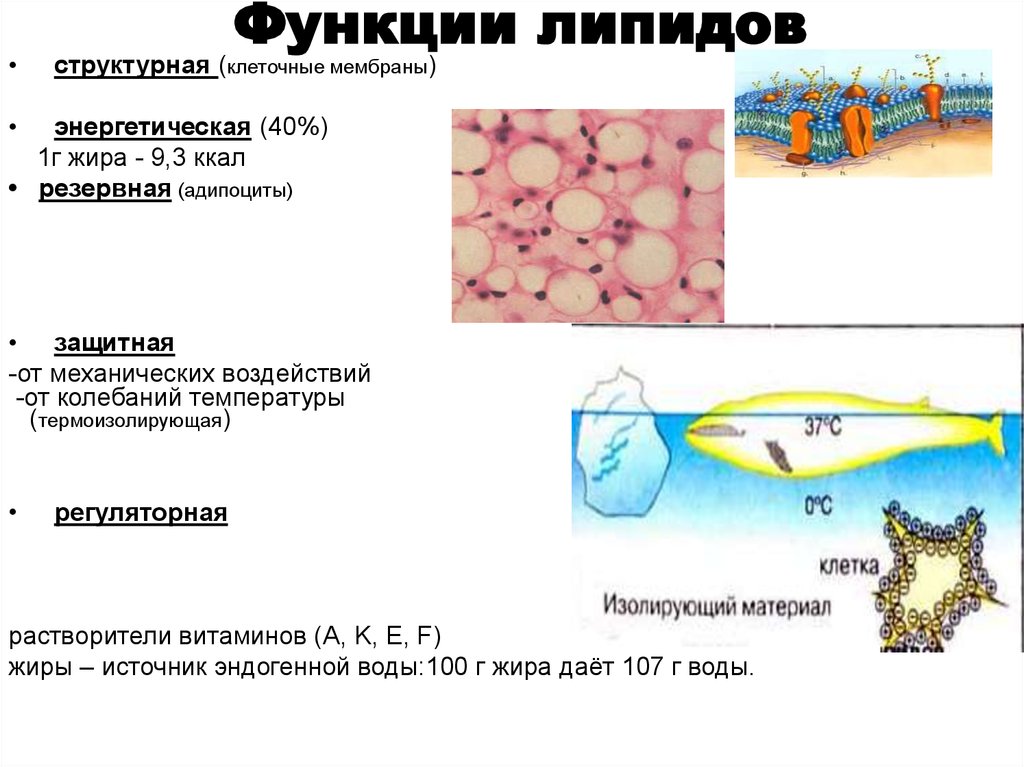
- Structural function. Lipids together with proteins are structural components of biological membranes of cells, that is, they affect their permeability, take an active part in the transmission of a nerve impulse, in the formation of intercellular interaction.
- Energy function. Lipids are called “cellular” energy-intensive fuels. The oxidation of one gram of fat is accompanied by the release of 39 kJ of energy, which exceeds the oxidation of carbohydrates by 2 times.
- Reserve function. It consists in the accumulation of additional energy in the cell. Reservation is carried out in fat cells - adipocytes. The body of an adult contains 6-10 kg of lipids.
- Protective function. Thermal insulating properties are characteristic of fats, due to which they protect the body from physical and mechanical damage. Thanks to the wax coating, plants are guaranteed protection against infections and water retention.
- Regulatory function. Lipids are considered precursors of vitamins, hormones (thromboxanes, prostaglandins, leukotrienes). This function also manifests itself depending on the activity of membranes on the properties and composition of lipids.
It is important to know
What is lipid metabolism? Human biochemistry depends on fat metabolism. In case of its violation, various pathological conditions arise: metabolic acidosis, obesity, atherosclerosis, gallstone disease. How does lipid oxidation occur? Blood biochemistry - what is it? To find answers to these questions, we turn to their classification.
Subdivision
Lipids include LDL, triglycerides, cholesterol, HDL. For the human body, only certain lipid compounds that are present in the blood in the maximum amount are important. The rest are not so important, since the concentration of these lipoproteins is minimal. What is lipid classification based on? Biochemistry involves the allocation of three groups:
- 1 group. LDL (low density lipoproteins), which are “bad” cholesterol, are dangerous for humans with an increase in their concentration in the blood. Such fats quickly accumulate on the walls of vascular structures, reducing lumen. This contributes to a number of cardiovascular diseases (atherosclerosis).
- 2 group. HDL (high density lipoproteins) are “good” cholesterol and help minimize the accumulation of “bad” fat in blood vessels. How does lipid digestion occur? Biochemistry involves their circulation through the human vascular systems, as a result of which LDL is accumulated on their walls.
- 3 group. Triglycerides, which are compounds of several fatty acids, as well as two protein molecules. They are derivatives of glycerol, a source of energy for the functioning of body cells, active participants in biological processes.
Lipid profile
It is unacceptable to change the concentration of triglycerides neither downward nor upward. Similar trends indicate the development of a pathological condition in the body.
Cholesterol esters and phospholipids are also distinguished in the classification of blood lipids. These indicators are needed for specialized research. A lipid profile is a set of blood tests that detect abnormalities in the metabolism of fats in a particular body. It can be considered a synonym for lipidograms. Such a study consists in detecting the concentration of fats in the blood. The profile includes a quantitative indicator of basic blood fats (“good” and “bad”), their comparison.
The purpose of the lipid profile
It allows you to identify pathologies of the cardiovascular system, to assess the risks of the formation of an individual predisposition to an increased amount of lipids in the blood. Analyze the results of the lipid profile should be a professional. For each individual person, the concept of "norm" varies, depending on many parameters: lifestyle, hereditary diseases.
Destination Option
Lipid tests are needed to diagnose atherosclerosis. A lipidogram is an optional examination. As part of the basic prevention of certain diseases, it is necessary to carry out it with a frequency of 1-2 times a year. Among the specific indications for such an analysis, experts consider the following problems:
If a person has at least one of the pathologies listed above, the frequency of lipid analysis is 1 time in 6 months. A lipid profile is considered the most important study to prevent the risks of disease complications, to monitor the possibility of their therapy.
How is the survey
It is necessary to take blood from the cubital vein for analysis in the morning (on an empty stomach). Prior to determining the lipid profile, proper preliminary preparation is necessary to prevent distortions in laboratory studies.
Among the basic preparatory measures are: blood donation in the morning, refusal from alcohol, smoking, excessive loads, stress (at least 24 hours). A lipid profile is carried out in this way. The diagnostician conducts a conversation with the patient. If there are no contraindications, a blood test from a vein or phalanx of the finger is performed. Next, the biomaterial is sent to the laboratory for research. As a result, a diagnostic sheet is drawn up, which describes in detail the lipid profile of the examined patient. The results are given to a person’s hands, or redirected to a specialist.
To summarize
Lipids are a group of organic substances that include fats and lipoids (fat-like compounds). Fats found in all cells are a natural barrier. They limit the permeability of cells, are included in the composition of hormones. They are hydrophobic substances that form an emulsion with water. Lipids are readily soluble in organic solvents (alcohols, acetone, benzene). Without fats, the full functioning of the human body is impossible. Violations of lipid metabolism negatively affect the condition, leading to serious diseases.