Euglena algae are tiny, unicellular lower organisms that have a body shape that resembles a spindle or oval. Due to the fact that they are on the border of the plant and animal world, they were given the name border guards. The thallus is represented mainly by the monad, i.e., flagellum, palmeloid and amoebic forms are much less common. The color of algae is not very diverse, they are green, colorless and in rare cases red.
Spread
Euglena algae are found throughout the earth. They are present in any fresh water reservoir with stagnant water. However, they are practically absent in the seas and oceans. In fluid reservoirs, as well as in plankton of the central part of large ones, a small amount is found.
The most favorite place is shallow, fresh, standing water bodies, while being well warmed up and enriched with organic substances, located in the forest-steppe and forest zones:
- ponds;
- forest puddles;
- ditches.
In summer, you can often see the following picture - in a puddle or pond, the water turns green or they even say “it blooms”. The reason for this phenomenon is the massive development of algae. In a droplet of such water under a microscope, one can see spindle-shaped cells of green color. Changing their shape and bending, they move pretty quickly in different directions. They are called euglens - this is the central genus. The whole department has the same name.
general information
The Euglena Algae Division has over 900 species and 40 genera. Among them there are both saprophytes and parasites. And also one class of Euglenophysia, which combines several orders that differ in some details of the structure of the flagellar apparatus. All of them are flagellar unicellular organisms that live in fresh water. The movement is carried out as a result of metabolic changes in body shape and using a flagellum. Chlorophyll and other pigments are found in chloroplasts. By simple longitudinal, in two parts, cell splitting in both mobile and stationary state, reproduction occurs. These algae are characterized by several types of nutrition:
- consumption of dead organic substrates - saprotrophic;
- ingestion of organic matter - holozoic;
- photosynthesis - autotrophic;
- mixotrophic, i.e. mixed.
Representatives of euglenae algae include euglena, trachelomonas.
Euglena
Among the representatives of the order of the Euglenalians, the genus Euglen is distinguished. These are motile cells with a ribbon-like, spindle-shaped, cylindrical, ovoid or spirally twisted shape. In this case, one edge (front) is smoothed, and the other (rear) is pointed. The cell is covered with a soft shell - a pellicle. A distinctive feature is the presence of an external flagellum, with the help of which it moves. It is located at the front end of the cell in the flagellum (pharynx), to which the red eye (stigma) is adjacent.
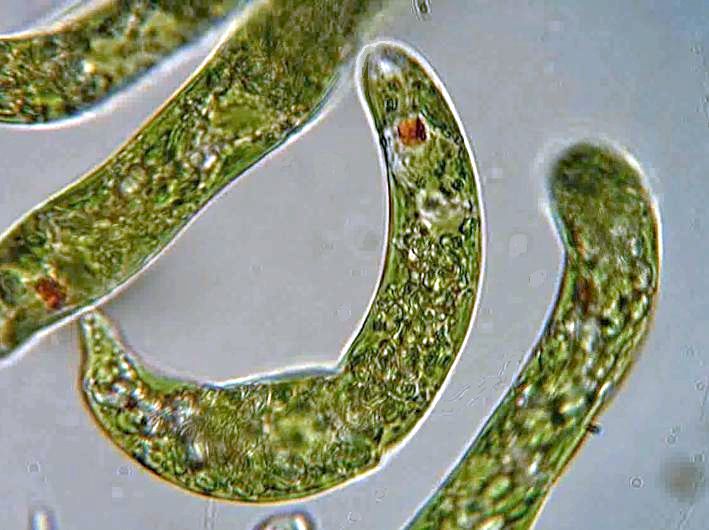
At the base of the flagellum there are contractile vacuoles, they throw the contents into the throat. The body of algae is able to perform functions such as respiration, digestion and excretion. Despite the fact that all euglens contain chlorophyll, they have a mixed type of nutrition. Asexual reproduction by binary longitudinal division. Algae can transform into a cyst under adverse conditions. Some species change their body shape. In nature, there are quite a few of them, they provoke the "bloom" of water, giving it a red tint. This color is associated with the presence of a significant amount of carotene pigment in the cells.
Fakus
This is a genus of unicellular algae, of which about one hundred and forty species are known. The cells have a flat-squeezed body ending at the posterior end with a curved narrow or straight process. The colorless shell is dense, on it there are rows of spines and granules. Pigment carriers (chromatophores) are small, numerous, wall, disc-shaped, without a cellular organelle. The nucleus is located in the back of the cell.
Algae is widespread in the coastal parts of lakes, rivers, as well as small stagnant water bodies that are contaminated with organic substances.
Trachelomonas
This genus includes about two hundred species of organisms that freely swim and own a flagellum and a solid house. The structure of the latter is considered a characteristic feature of the species. A differently shaped house is usually of a brown color. Its walls come with granules, spikes, papillae. The rear end is rounded or tapering.
Two or more pigments are present. There are species without chlorophyll, i.e. colorless. The cell divides during reproduction inside the house. One individual goes out through the existing hole and creates its own house.
The structure of euglenae algae
These are unicellular energetically moving organisms with one or two flagella. The body shape is oval, elongated or spindle-shaped. Outside the cell is covered by the so-called pellicle, consisting of a cytoplasmic membrane. If it is soft and elastic, then these types of algae are able to change the shape of the body. Others have a hard shell impregnated with iron salts.
The green color of euglegen algae provides chlorophyll, which is also present in higher plants. In addition to this pigment, algae has xanthophylls and carotenes located in chloroplasts. The main reserve substance is the reserve polysaccharide paramylum, which performs an energy function. A depression is observed at the anterior end; it is considered the outlet end for the contractile vacuole system. In the latter, as a result of metabolic processes, liquid with dissolved substances accumulates.
Features
Brief description of euglenae algae:
- Body shape - oval, spindle-shaped, needle-shaped. The front end is rounded, the rear end is elongated and pointed.
- Flagellum apparatus - from one to seven visible flagella. There are several forms in which it is absent. Most often found with two flagella of different lengths.
- The photosensitive apparatus is the paraflagellar body (flagellum thickening) and the eye.
- One big core.
- Contractile vacuole - located at the front end of the cell.
- Mitochondria - can merge and form a network. Euglena algae living under anaerobic conditions, they are absent.
- The cell wall is a pellicle, which is 80 percent protein. In addition, it contains carbohydrates and lipids.
- Chloroplast - different species have their own form: disk-like, star-shaped, lamellar, etc. Several chloroplasts are present in the cell.
- The replacement product is paramilon.
- Lysine biosynthesis - carried out, as in real animals and fungi.
- Life cycle - multiply by dividing cells into two parts.
Value and Ecology
The physiological properties are associated with the practical importance of euglenae algae. Thanks to the nutrition of organic substances, they are actively involved in the self-cleaning of water bodies that are contaminated with living substances. Among these algae, there are several species that are excellent indicators of the degree of pollution of the reservoir. They are capable of forming on their surface unstable films of multi-colored colors - red-brick, green, brown, yellow-green.
Due to the fact that algae have various ways of nutrition, they are actively used in the form of models in medicine, cytology, biochemistry, physiology. Among them there are parasites that live in the intestines of amphibians, nematodes, on the gills of fish, oligochaetes.