Modern biology is striking in the uniqueness and scale of its discoveries. Today, this science studies most of the processes that are hidden from our eyes. This is remarkable molecular biology - one of the promising areas that helps to unravel the complex secrets of living matter.
What is reverse transcription?
Reverse transcription (abbreviated as RT) is a specific process characteristic of most RNA viruses. Its main feature is the synthesis of a double-stranded DNA molecule based on messenger RNA.
OT is not characteristic of bacteria or eukaryotic organisms. The main enzyme, revertase, plays a key role in the synthesis of double-stranded DNA.
Discovery story
The idea that a ribonucleic acid molecule could become a matrix for DNA synthesis was considered absurd until the 1970s. Then Baltimore and Temin, working separately from each other, almost simultaneously discovered a new enzyme. They called it RNA-dependent-DNA polymerase, or reverse transcriptase.
The discovery of this enzyme unconditionally confirmed the existence of organisms capable of reverse transcription. In 1975, both scientists received the Nobel Prize. After some time, Engelhardt proposed an alternative name for reverse transcriptase - revertase.
Why OT contradicts the central dogma of molecular biology
Central dogma is a schematic diagram of sequential protein synthesis in any living cell. Such a scheme is built of three components: DNA, RNA and protein.
According to the central dogma, RNA can be synthesized exclusively on a DNA matrix, and only then RNA is involved in the construction of the primary protein structure.
This dogma was officially accepted in the scientific community before the discovery of reverse transcription occurred. It is not surprising that the idea of reverse synthesis of DNA from RNA has long been rejected by scientists. Only in 1970, together with the discovery of revertase, did this point come to an end, which was reflected in the concept of protein synthesis.
Bird Retrovirus Revertase
The reverse transcription process is not complete without the participation of RNA-dependent DNA polymerase. The revertase of a bird retrovirus has been studied to date.
Only about 40 molecules of this protein can be found in one virion of this family of viruses. The protein consists of two subunits, which are in equal amounts and perform the three most important functions of revertase:
1) Synthesis of a DNA molecule both on a single-stranded / double-stranded RNA matrix and on the basis of deoxyribonucleic acids.
2) Activation of RNase H, the main role of which is to cleave the RNA molecule in the RNA-DNA complex.
3) Destruction of sections of DNA molecules for insertion into the eukaryotic genome.
OT mechanism
The stages of reverse transcription may vary depending on the virus family, i.e. from the type of their nucleic acids.
Consider first those viruses that use revertase. Here the OT process is divided into 3 stages:
1) Synthesis of the “-” RNA chain on the matrix “+” of the RNA chain.
2) The destruction of the "+" RNA chain in the RNA-DNA complex using the enzyme RNase N.
3) Synthesis of a double-stranded DNA molecule on the “-” matrix of the RNA chain.
This method of reproduction of virions is characteristic of some oncogenic viruses and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV).
It is worth noting that for the synthesis of any nucleic acid on an RNA matrix, a seed or primer is needed. A primer is a short nucleotide sequence that is complementary to the 3'-end of an RNA molecule (template) and plays an important role in the initiation of synthesis.
When finished double-stranded DNA molecules of viral origin are inserted into the eukaryotic genome, the usual mechanism for the synthesis of virion proteins is triggered. As a result, the cell “captured” by the virus becomes a factory for the production of virions, where the necessary molecules of proteins and RNA are formed in large quantities.
Another method of reverse transcription is based on the action of RNA synthetase. This protein is active in paramyxoviruses, rhabdoviruses, picornoviruses. In this case, the third stage of RT is absent - the formation of double-stranded DNA, but instead the “+" RNA chain is synthesized on the matrix of the viral “-” RNA chain and vice versa.
The repetition of such cycles leads both to replication of the viral genome and to the formation of mRNA capable of protein synthesis under conditions of an infected eukaryotic cell.
The biological significance of reverse transcription
The RT process is of paramount importance in the life cycle of many viruses (primarily retroviruses such as HIV). RNA of the virion that attacked the eukaryotic cell becomes the matrix for the synthesis of the first DNA strand, on which it is not difficult to complete the second strand.
The resulting double-stranded DNA of the virus is inserted into the eukaryotic genome, which leads to the activation of the synthesis of virion proteins and the appearance of a large number of copies of it inside the infected cell. This is the main mission of revertase and RT in general for the virus.
In eukaryotes, reverse transcription can also occur in the context of retrotransposons - mobile genetic elements that can independently transport from one part of the genome to another. Such elements, according to scientists, have caused the evolution of living organisms.
Retrotransposon is a region of eukaryotic DNA that encodes several proteins. One of them, revertase, is directly involved in the delocalization of such a retrotrasporozone.
Use of OT in science
From the moment that it was possible to isolate revertase in its pure form, the process of reverse transcription was adopted by biological scientists. The study of the mechanism of RT and now helps to read the sequence of the most important human proteins.
The fact is that the genome of eukaryotes, including us, contains uninformative regions called introns. When a nucleotide sequence is read with such DNA and a single-stranded RNA is formed, the latter loses introns and encodes exclusively a protein. If DNA is synthesized using a revertase on an RNA matrix, it can then be sequenced easily and the nucleotide order will be recognized.
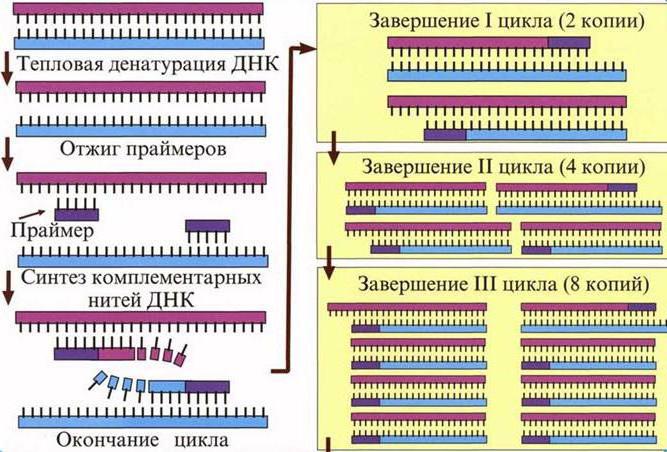
The nucleic acid that was formed by reverse transcriptase is called cDNA. It is often used in the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) to artificially increase the number of copies of the resulting cDNA copy. This method is used not only in science, but also in medicine: laboratory assistants determine the similarity of such DNA to the genomes of various bacteria or viruses from a common library. The synthesis of vectors and their introduction into bacteria is one of the promising areas of biology. If using RT to form the DNA of humans and other organisms without introns, such molecules are easily introduced into the bacterial genome. So the latter become factories for the production of substances necessary for man (for example, enzymes).