Constructive activity - a type of activity related to modeling. With the help of this, a person not only learns the system around him, but can also imitate it. It is this orientation that distinguishes design from other types of occupations. Constructive activity leaves its mark on the development of the child during preschool years.
Basic concepts
Constructive activity - an individual’s activity aimed at a specific, previously known result that will meet predetermined requirements. Design develops the mental, moral, aesthetic, labor abilities of a person.
By modeling, younger students learn not only to distinguish objects by external signs, but also to perform various kinds of actions. In the process of constructive activity, the student apart from external perception disassembles the object into parts, images and details.
Children and adults
Design can cause some difficulties in the child. Here you can find some connection with the artistic and technical activities of adults and constructive activities in the preparatory group and school. They are inherent in directing the results of their efforts to achieve a specific goal. To achieve the design goals, an adult thinks out a certain plan in advance, selects the appropriate material, performance techniques, design, and the correct sequence of actions. A similar algorithm also exists in the constructive activities of the preparatory group and schoolchildren. Solved tasks are similar. The design results in children are often applicable to the game. Many pedagogical works say that various modeling actions performed by a child in childhood prepare him for adult activity, creating a culture. Thus, constructive activity in the older group and among schoolchildren by methods is close to more meaningful adult activity. And although the modeling methods of adults and children are similar, the results of the activities are radically different. The control of constructive activities in the preparatory group has an extremely positive effect on the overall development of children.
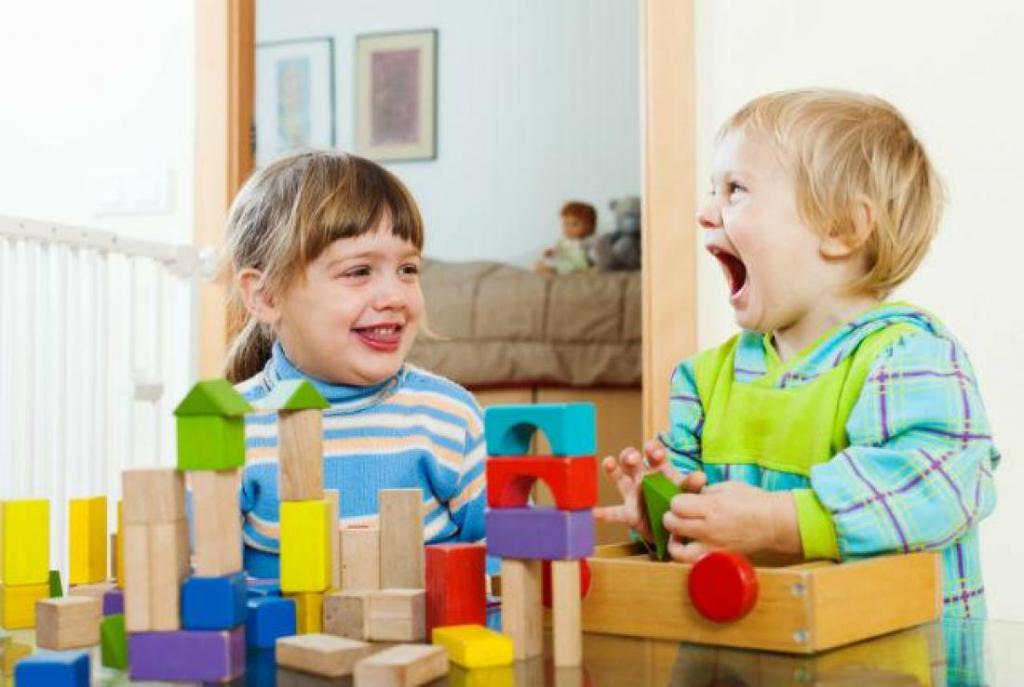

Technical and art modeling
Constructive activity in the senior group and the school period is divided into two types: technical and artistic design. They are interconnected and focused on modeling real-life objects, as well as reproducing various fairy-tale, musical and stage images. Both the artistic and technical parts of the object are modeled: the roof of the building, windows and doors, the deck of the ship, etc.
The technical type of constructive activity in the senior group and school includes the construction of:
- Models of objects from building materials.
- Objects from bulky modular blocks.
The aim of the artistic type of constructive activity is not so much to accurately convey the structure of transmitted images, but to express one’s attitude towards them, to convey character with the help of such a technique as “breaking” proportions, as well as changing color, texture and shape. Most often, the construction of the artistic type is made of paper or natural material.

If the goal of constructive activity of a technical type in adults often has a practical motive, then in children's modeling the goal is completely different. A group of children can build a model of the zoo. But when the time comes for completion, interest in this activity is noticeably lost. Most often, with the achievement of the goal, children of primary and school age lose any interest in the completed activity. In this case, the activity fascinates the child much more than the end result itself. But it is in artistic design that the basic meaning of constructive and technical activity is most fully reflected. Even if the craft is not interesting to children from the practical side, then during its creation, it makes it as suitable as possible for further use. The basic principles for reproducing a design product are exactly the same as in the design itself.
Features of Fine Modeling
It is worth saying that most often in graphic design and modeling activities in the older group, preschoolers achieve striking similarities with the object of modeling. If the final goal is intended for practical use, then the child pays much less attention to the process and design. In this case, the main thing for a preschooler and a schoolboy is the presence of the qualities necessary for the game in the final result. For example, during the game it was necessary to fly on an airplane, therefore, according to the child, the wings, the helm and the chair are important. The appearance of the model fades into the background: if the object meets the basic needs of games, then it is quite suitable. The situation is completely different if a child, for example, sets himself the task of showing the differences between the types of aircraft. In this case, the constructive-model activity in the senior group is honed with special zeal. We can conclude that the quality of the final result depends, rather, on the desire of the child, and not on his skills. The presence of technical and visual types of design, which have their own characteristics, requires careful selection and study of cases in which they can be applied.

Materials for modeling. Paper
Constructive activities in the senior subgroup of kindergarten are carried out mainly from paper, cardboard boxes, spools of thread and other materials. This type of activity requires more energy than regular games.
Children are given paper and cardboard squares, rectangles, circles, etc. The preliminary step before making the toy is to prepare patterns, work out details and decorations. It is necessary to thoroughly check all the cuts and only then proceed to the manufacture of toys. The child must be able to measure, use scissors and needles. This is a much more complex process than the usual constructive activity in the preparatory group, consisting of creating toys from ready-made forms. Various parts of boxes, coils and other materials used in this case are the so-called semi-finished product. If you teach children to see and make up a single whole from various details, then in this way you will develop tactical and strategic thinking in your child, and besides, he will learn how to create interesting toys from improvised materials.

If a child uses paper in the design, then he becomes familiar with concepts such as angle, side, plane. Preschoolers learn to bend, cut, bend, deform paper and thereby get completely new images from it. Modeling various geometric shapes and figures of animals, people, preschoolers learn to make compositions and various combinations of crafts. Preschoolers acquire the skill of making various crafts from matchboxes using various combinations and compounds. With the help of these processes, children acquire completely new skills and abilities.
The combination of theory and practice in modeling
A feature of the development of constructive activity in both senior and younger preschoolers can be called a combination of the practical and theoretical parts of construction. In the pedagogical works of L. S. Vygotsky it is said about the inevitability of the transition of the younger and older preschoolers from theory in modeling to action. Studies by Z. V. Lishtvan and V. G. Nechaeva, which examine the features of constructivism in children at various stages of development, showed that, under the strict guidance of teachers, the concept and its implementation begin to fully correspond to each other. In the constructive activities of children, one can see not only the final result, but also ways to create a model. It is noteworthy that the idea itself is formed in the process of construction. The higher the level, the more clearly the child imagines the end result. The verbal description and drawings of the upcoming object also testify to the quality level of the final idea. The main goal of constructive activity of children is the development of cognitive activity.
In numerous studies of Russian teachers such as D.V. Kutsakov, 3. V. Lishtvan, L.V. Panteleeva, which are devoted to designing in child care facilities, a huge role is given to paper crafts. As these wonderful teachers say, the manufacture of paper crafts positively affects the development of fine motor skills in the hands of preschoolers, as well as improving the eye and sensorimotor as a whole.
Nowadays, it is known for certain that constructive activity in kindergarten groups or elementary grades, especially the manufacture of paper and cardboard crafts, improves brain activity and positively affects the work of both hemispheres in preschoolers and primary schoolchildren, which increases their general level of intelligence and develops qualities such as mindfulness, receptivity, imagination, logical thinking. Thinking becomes more creative, its speed, flexibility, originality grows.
Cognitive activity and modeling
Children’s thinking about the methods of construction begins to take shape in the process of mental activity at various levels: at the level of perception - when trying to reproduce the actions of other people, at the stage of presentation and thinking - if you have to choose from the proposed options. When solving constructive problems, younger students can show various creative elements while searching for design methods. In the constructive activity of the idea, as well as in the construction according to the given conditions, the idea is created by the children themselves. If they model as planned, they will certainly get many opportunities to solve the problem in various ways. This is described in detail in the writings of V.F. Izotova, Z. V. Lishtvan and V. G. Nechaeva. A lot of older preschool children, on the basis of knowledge about spatial relationships, as well as experience in design, in the process of analyzing various designs, may well create an intelligible plan both in structure and in way of activity, and relate the practice to their original plan.
The preschoolers and primary schoolchildren are often fascinated and inspired by the surrounding world to constructive activities: a variety of flora and fauna, social phenomena, various fiction and educational literature, all kinds of activities, especially games. But, unfortunately, children perceive the world very superficially because of their age: they try to reproduce in their activities exclusively the external, understandable side of surrounding phenomena and objects.
Of great importance is the emotional coloring of the child’s activities, thanks to which he will use various materials, create original models with even greater pleasure. The connection of constructive activities in the middle group of kindergarten and elementary school with everyday life, with the various types of diverse activities included in it, makes design incredibly interesting, filled with various emotions and allows you to be not so much a form of activity as a way of self-expression. Do not ignore this increasingly manifest need in children.
Side effects of construction
During the educational activity, children from the middle and preparatory group of the kindergarten develop not only technical skills, but also the ability to analyze the reality surrounding them, the formation of general ideas about the various objects modeled by them begins, independent thinking, a craving for creativity, and artistic taste develop. The child is formed as a person.
In designing, two major stages can be distinguished: work on an idea and its implementation. Most often, working on an idea is a creative process, since it consists in thinking it over and miscalculating possible ways of implementation. Also, creative activity is to determine the final result, methods and sequence of its achievement.
Practice in the implementation of ideas can not be completely and completely performing - design activity, even among older students, combines both thought and practice.
If we talk about designing among preschoolers, then the interaction of practice and thought can be called one of its strengths. At the same time, practical activity does not have to be close to certain canons - you can also experiment, which is stated in the pedagogical works of L. A. Paramonova and G. V. Uradovskikh. The original idea, in turn, is regularly refined and changed as a result of the application of various practical methods, which positively affects the development of further creative design. Often, at the same time, children reason aloud, pronouncing their actions and approaching the final result.
Modeling Issues
Without proper training, the proper work of a teacher, and without working with frequently encountered problems, design classes will be incomplete. The most common design problems that need to be worked out include:
- The lack of a clear design, which can be explained by the vague structure of the image.
- Lack of a clear goal (when creating one object, it turns out to be completely different, which, despite the mismatch with the plan, completely suits the creator).
- The emphasis is not on design, but on execution (too little attention is paid to the design).
- Lack of a clear plan for the execution of actions.
- Wrong task.
If you do not work out these tasks, then, most likely, the result of children's design will not satisfy either the teacher or the child.
Where does the child get inspiration from?
Children are often inspired by the world around them: various objects around, social events, fiction, various activities, primarily games, as well as the one that they perform themselves. But most often, younger schoolchildren and preschoolers perceive the world quite superficially: they manage to capture only the external signs of phenomena that they are trying to reproduce in constructive activity. In order for a child to develop more fully and comprehensively, it is necessary to teach him to see the essence of phenomena and objects, and not just their shell.