Everyone knows that magnets tend to attract metals. Also, one magnet can attract another. But the interaction between them is not limited only by attraction, they can repel each other. The point is in the poles of a magnet - opposite poles are attracted, like poles are repelled. This property is the basis of all electric motors, and quite powerful.
There is also such a thing as levitation under the influence of a magnetic field, when an object placed above a magnet (having a pole similar to it) hangs in space. This effect has been put into practice in the so-called magnetic bearing.
What is a magnetic bearing
An electromagnetic type device in which a rotating shaft (rotor) is supported in a fixed part (stator) by magnetic flux is called a magnetic bearing. When the mechanism is in operation, it is influenced by physical forces seeking to shift the axis. To overcome them, the magnetic bearing was equipped with a control system that monitors the load and sends a signal to control the strength of the magnetic flux. Magnets, in turn, have a stronger or weaker effect on the rotor, keeping it in a central position.
Magnetic bearing is widely used in industry. These are mostly powerful turbomachines. Due to the absence of friction and, accordingly, the need to use lubricants, the reliability of machines is many times higher. Wear of the nodes is practically not observed. The quality of dynamic characteristics also increases and the efficiency increases.
Active magnetic bearings
A magnetic bearing, where a force field is created using electromagnets, is called active. Positional electromagnets are located in the bearing stator, the rotor is represented by a metal shaft. The entire system that provides shaft retention in the unit is called an active magnetic suspension (AMP). It has a complex structure and consists of two parts:
- bearing block;
- electronic control systems.
The main elements of the ILA
- The bearing is radial. A device that has electromagnets on the stator. They hold the rotor. There are special ferromagnet plates on the rotor. When the rotor is suspended at a midpoint, there is no contact with the stator. Inductive sensors track the slightest deviation of the rotor position in space from the nominal. The signals from them control the strength of the magnets at one point or another to restore equilibrium in the system. The radial clearance is 0.50-1.00 mm, axial - 0.60-1.80 mm.
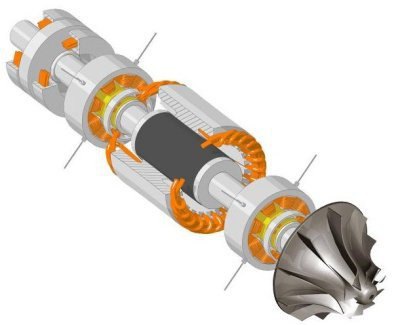
- The thrust magnetic bearing works in the same way as a radial bearing . A thrust disk is fixed on the rotor shaft, on both sides of which there are electromagnets mounted on the stator.
- Safety bearings are designed to hold the rotor when the device is in the off state or in emergency situations. In the process, auxiliary magnetic bearings are not involved. The gap between them and the rotor shaft is half that of a magnetic bearing. Safety elements are assembled on the basis of ball devices or sliding bearings.
- The control electronics include rotor shaft position sensors, transducers and amplifiers. The whole system works on the principle of adjusting the magnetic flux in each individual electromagnet module.
Passive magnetic bearings
Permanent magnet magnetic bearings are rotor shaft holding systems that do not use a control circuit that incorporates feedback. Levitation is carried out only due to the forces of high-energy permanent magnets.
The disadvantage of this suspension is the need to use a mechanical stop, which leads to the formation of friction and a decrease in the reliability of the system. The magnetic stop in the technical sense has not yet been implemented in this circuit. Therefore, in practice, a passive bearing is used infrequently. There is a patented model, for example, Nikolaev’s suspension, which has not yet been repeated.
Wheel bearing magnetic tape
The concept of "magnetic wheel bearing" refers to the ASB system, which is widely used in modern cars. The ASB bearing is characterized in that it has an integrated wheel speed sensor inside. This sensor is an active device embedded in the bearing gasket. It is built on the basis of a magnetic ring on which the poles of an element sensing a change in magnetic flux alternate.
When the bearing rotates, there is a constant change in the magnetic field created by the magnetic ring. The sensor records this change, generating a signal. Next, the signal enters the microprocessor. Thanks to it, systems such as ABS and ESP work. Already they are adjusting the operation of the car. ESP is responsible for electronic stabilization, ABS regulates the rotation of the wheels, the pressure level in the system is brake. It monitors the operation of the steering system, lateral acceleration, and also adjusts the operation of the transmission and engine.
The main advantage of the ASB bearing is the ability to control rotation speed even at very low speeds. At the same time, the overall dimensions of the hub are improved, the installation of the bearing is simplified.
How to make a magnetic bearing
The simplest magnetic bearing with your own hands is not difficult to do. It is not suitable for practical use, but it will clearly show the possibilities of magnetic force. To do this, you will need four neodymium magnets of the same diameter, two magnets of slightly smaller diameter, a shaft, such as a piece of plastic tube, and an emphasis, such as a glass half-liter jar. Smaller magnets with hot melt are attached to the ends of the tube in such a way as to form a coil. A plastic ball is glued on the outside in the middle of one of these magnets. The same poles should look out. Four magnets with the same poles up are laid out in pairs at a distance of the length of the length of the tube. The rotor is placed above the lying magnets and on the side where the plastic ball is glued, they support it with a plastic jar. Here is the magnetic bearing and ready.