Often in the midst of ordinary people in colloquial interchangeability of two terms occurs - “wire” and “cable”. These words are used as synonyms for each other. But this is not entirely true. Since these two concepts in a professional environment mean similar, but different products that are used to move electric current from a source, such as an outlet, to a device in which under the influence of electricity some process is performed, for example, heating an iron or conditioning a room.
What is wire and cable? Key Features
The word "wire" refers to a metal core, or a core made of several thin wires, (in another way, a conductive core), shrouded in single-layer insulation. A conductor is also inserted in the middle of the cable - one or more. The presence of one core will indicate that the cable is single-core. Accordingly, a cable with several cores is called multi-core. The main difference between the cable and the wire is the multilayer protective sheath.
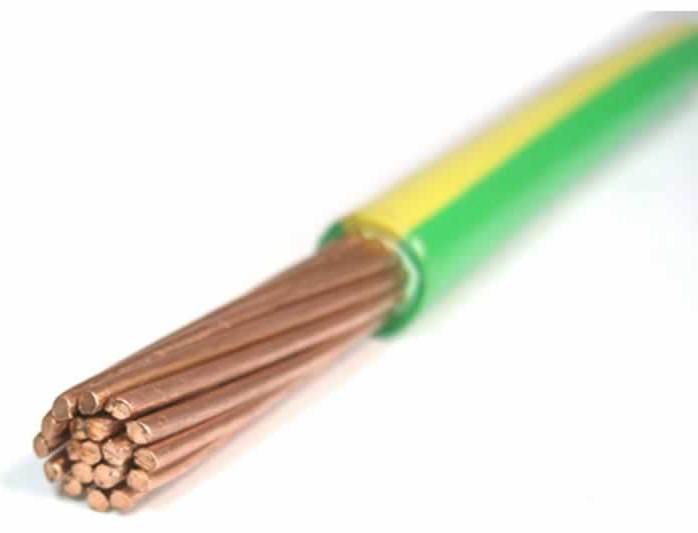
To protect cables and wires from moisture, acids, gases, wind, and the sun, materials from non-combustible rubber, aluminum, corrugated steel, plastic, and lead of a grade of at least C-3 are used. The lead content in the shell should be at least 99.9%. For protection from aluminum, metal of a grade not lower than A1 with a content of at least 99.97% is used. The rubber layers of the containment should be oil and petrol resistant and not subject to burning. High-strength polyvinyl chloride plastic - not combustible and vibration-resistant. The production standards determine the thickness of the protective layers, which depends primarily on the purpose, then on the structural features and cable diameter. Cables can be laid in the ground, in sewers, in water. The protective layer of the cable may be leakproof.
Inside the coaxial single-core cable is a copper, aluminum or steel wire, which is the central conductor. In some constructions, a dielectric can encircle it in the form of a fluoroplastic tape in some cases, a protective screen made of foil or bundles of thin metal wires is braided around it, then, as an option, a corrugated tube is put on. The extreme insulating layer is most often made from undergoing additional processing in order to protect from thickened polyethylene external negative factors (e.g. ultraviolet radiation).
Single core shielded and twisted pair. The scope of use of such products
Currently, coaxial single-core shielded cable is used in measuring and sound recording equipment, for example, in oscilloscopes and microphones. In the recent past, it was mainly used for laying local computer networks. But since when using a coaxial cable it was found that poor noise immunity is associated with it, they began to look for other options for network connections.
When arranging ordered cable computer systems, a twisted-pair single-core cable is now used. Its use is in direct contact of the equipment with the network. It is also used for laying in walls and ducts with subsequent connection to outlets, because the copper wire of the core of a twisted-pair single-core cable has a large cross-section and cracks when bent, and should be fixed. Stranded twisted pair is durable in twisting and bending; it is used as a dynamic switching cable connecting network devices.
Core thickness (section) and cable features
The cross-section of a single-core cable or the thickness of the core depends on the strength of the current that flows through it, the voltage in the network and other factors. A cable is just like a water hose, which in its internal diameter can pass one or another amount of water. If the water pressure is increased, then the hose may explode, because through it such an amount of liquid will flow that it is not designed. A single-core shielded cable, like any other, of course, will not burst, like a hose, with an increase in amperage, but it will burn out.
To facilitate the work of electricians, now, according to formulas known from the school curriculum, tables have been calculated to determine the required cross section of the cable core. It can be seen from them that with increasing values of voltage, power and current strength, the numbers of the section of conductive wires increase. For example, a copper single-core cable with rubber insulation with a permissible continuous current of 40 A will have a cross section of 2.5 mm². If the wire with a permissible current of 50 A, then there will be 4 mm².
UTP cable. Key Features
In everyday life, for the transmission of information, for communication lines and various low-voltage networks, a single-core UTP cable is the most popular product. The design of these types of cables is different. For networks of short length and with little interference, products without protective shielding are used. In places where there is interference, cables that do not include a protective shield cannot be used.
The external insulation of twisted pair made of polyvinyl chloride is painted differently. The colors determine the functionality: gray ones are designed for indoor use, black color indicates an additional layer that protects from external influences, orange color indicates that the shell is made of non-combustible plastic.
Marking, abbreviation
Cable labeling describes the characteristics of unshielded twisted pairs. The abbreviation UTP 5e means a UTP cable of 4 pairs single-core, which provides a good speed of distribution of data and information. Therefore, it is widely used for 1 Gb Ethernet. UTP 5 is both single-core and multi-core. But the UTP 3 cable is used in telephone networks. Because it is he who can withstand only low speed.
The main features of power cables. What is it and why are they used?
Single-core power cables are used to transport energy by industrial frequency currents indoors and outdoors. From switchboards operated by industrial or utility enterprises, three-phase current is transmitted to consumers through such products by stationary laying. In addition, multicore power cables are used when connecting various mobile units and equipment. All SCs differ in materials, sizes, designs, depending on the type and field of application. The basic structure of the cable includes a conductive rod, insulation and sheath. A paper impregnated with a special composition can be used to insulate the power cable. Mineral and synthetic oils and rosin are commonly used. Some sections of cable lines are treated with mixtures with the addition of synthetic ceresin.
Shells are formed from lead and aluminum. To increase the basic and protective indicators, shielding, belt insulation, placeholders, and booking are used. Materials for cores are usually copper or aluminum.
For example, for laying fixed joints in shields, a single-core VVG cable 1 x 6 with one monolithic copper rod and a cross-section of 6 mm² is used. The service life of such a cable reaches 30 years. Cables are used strictly in the geographical areas for which they are designed. On the marking of the VVG cable 1 x 6 it is indicated: UHL1. These signs are deciphered as follows: it is possible to use in temperate and cold macroclimatic regions with operation in open areas with a likely strong wind.
The marking data of wires and cables are not only informative, but also have a warning value: they help reduce injuries to workers associated with electricity.
Advantages of single core
Finally, I would like to consider the advantages of single-core cables. One of their main advantages is the lower resistance of 1 km of wire. The second advantage is ease of installation. This feature applies in particular to contact compounds. Another advantage is this low price.
The advantages of stranded
The main advantage of these cables is their flexibility. This is especially true for wires with a cross section of 10, 16 and more mm². Of course, such wires are practically not used in everyday life. But, in principle, they may be needed. Another advantage - thanks to the availability of brass lugs on the market, you can easily mount the cables without any additional tools and devices. Stranded with screw terminals are used. Also, after special pressing, they can be used for WAGO terminals.
Little conclusion
Now you know what cables are, why they are used. We also examined the distinctive features of single-core and multi-core cables. In addition, we described in detail where they are used. Therefore, choosing between these two types, remember that each of them has its own scope. For example, if hidden wiring is mounted in the wall, then it will obviously be cheaper for you to stay on a single-core cable. When mounting a temporary electrical installation, it will be much more practical to use a multicore product.