A biosystem is a complex network of biologically relevant organizations, from global to subatomic. This conceptual illustration reflects multiple nesting systems in nature - populations of organisms, organs and tissues. On a micro- and nanoscopic scale, examples of biological systems are cells, organelles, macromolecular complexes, and regulatory pathways.
The organism as a biosystem
In biology, an organism is any adjacent living system along with animals, plants, fungi, protists or bacteria. All known types of creatures on Earth are able to some extent respond to stimuli, multiply, grow, develop and self-regulate (homeostasis).
An organism as a biosystem consists of one or several cells. Most unicellular organisms have a microscopic scale and, therefore, belong to microorganisms. Humans are multicellular organisms consisting of many trillions of cells grouped into specialized tissues and organs.
The many and diverse biological systems
Estimates of the number of modern Earth species range from 10 to 14 million, of which only about 1.2 million have been officially documented.
The term “organism” is directly related to the term “organization”. The following definition can be given: it is an assembly of molecules that function as a more or less stable whole that exhibits the properties of life. An organism as a biosystem is any living structure, such as a plant, animal, fungus or bacteria, that is capable of growing and multiplying. Viruses and possible anthropogenic inorganic life forms are excluded from this category, since they depend on the biochemical mechanism of the host cell.
The human body as a biosystem
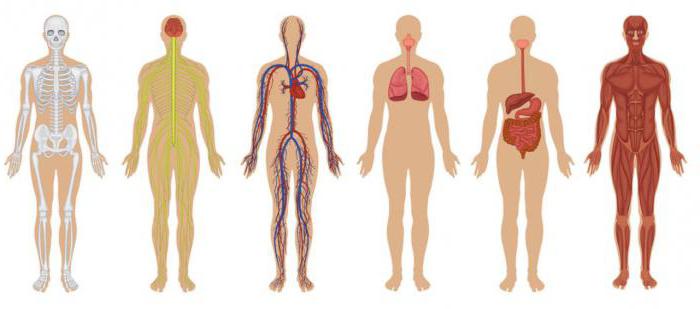
The human body can also be called a biosystem. This is the totality of all organs. Our bodies are made up of a number of biological systems that perform the specific functions necessary for everyday life.
- The circulatory system works by moving blood, nutrients, oxygen, carbon dioxide and hormones through organs and tissues. It consists of the heart, blood, blood vessels, arteries and veins.
- The digestive system consists of a number of connected organs, which together allow the body to absorb and digest food, as well as remove waste. It includes the mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, colon, rectum, and anus. The liver and pancreas also play an important role in the digestive system because they produce digestive juices.
- The endocrine system consists of eight major glands that secrete hormones into the blood. These hormones, in turn, travel through different tissues and regulate various body functions.
- The immune system protects the body from bacteria, viruses and other harmful pathogens. It includes lymph nodes, spleen, bone marrow, lymphocytes and white blood cells.
- The lymphatic system includes the lymph nodes, ducts and blood vessels, and also plays a role as the body's defenses. Its main task is to form and move lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells that help the body fight the infection. The lymphatic system also removes excess lymphatic fluid from the body tissues and returns it to the blood.
- The nervous system controls both voluntary (e.g., conscious movement) and involuntary actions (e.g., breathing), and sends signals to various parts of the body. The central nervous system includes the brain and spinal cord. The peripheral nervous system consists of nerves that connect each part of the body to the central nervous system.
- The muscular system of the body consists of about 650 muscles that help in movement, blood circulation and perform a number of other physical functions.
- The reproductive system allows people to multiply. The male reproductive system includes the penis and testes, which produce sperm. The female reproductive system consists of the vagina, uterus and ovaries. During conception, the sperm merge with the egg, which creates a fertilized egg that grows in the uterus.
- Our bodies are supported by a skeletal system of 206 bones that are connected by tendons, ligaments and cartilage. The skeleton not only helps us move, but also participates in the production of blood cells and the storage of calcium. Teeth are also part of the skeletal system, but they are not considered bones.
- The respiratory system allows you to take vital oxygen and remove carbon dioxide in a process that we call breathing. It consists mainly of the trachea, diaphragm and lungs.
- The urinary system helps eliminate an unnecessary product called urea from the body. It consists of two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, two sphincter muscles and an urethra. Urine produced by the kidneys moves down the ureters to the bladder and leaves the body through the urethra.
- Skin is the largest organ of the human body. It protects us from the outside world, bacteria, viruses and other pathogens, and also helps regulate body temperature and eliminate waste through sweat. In addition to the skin, the integumentary system includes hair and nails.
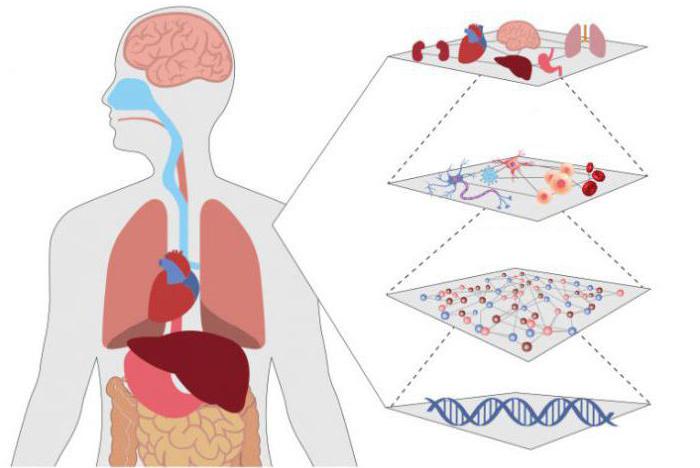
Vital organs
People have five vital organs that are necessary for survival. These are the brain, heart, kidneys, liver and lungs.
- The human brain is the center of control of the body, receiving and transmitting signals to other organs through the nervous system and through secreted hormones. He is responsible for our thoughts, feelings, memory and general perception of the world.
- The human heart is responsible for pumping blood throughout our body.
- The work of the kidneys is to remove waste and extra fluid from the blood.
- The liver has many functions, including detoxification of harmful chemicals, drug breakdown, blood filtration, bile secretion and the production of blood coagulation proteins.
- The lungs are responsible for removing oxygen from the air we breathe and transferring it to our blood, where it can be sent to our cells. The lungs also remove carbon dioxide, which we exhale.
Funny facts
- The human body contains about 100 trillion cells.
- The average adult takes more than 20,000 breaths per day.
- Each day, the kidneys process about 200 quarts (50 gallons) of blood to filter out about 2 quarts of waste and water.
- Adults excrete about a quarter and a half (1.42 liters) of urine every day.
- The human brain contains about 100 billion nerve cells.
- Water makes up more than 50 percent of an adult’s body weight.
Why is the body called a biosystem?
A living organism is a certain organization of living matter. It is a biosystem, which, like any other system, includes interconnected elements, such as molecules, cells, tissues, organs. Everything in this world consists of something; a certain hierarchy is also characteristic of a living organism. This means that cells are composed of molecules, cells are tissues, tissues are organs, organs are organs, and organs are organs. The properties of biosystems also include emergence, which means the appearance of qualitatively new characteristics that are present when elements are combined and are absent at previous levels.
A cell as a biosystem
One single cell can also be called a complete biosystem. This is an elementary unit that has its own structure and its own metabolism. It is able to exist independently, reproduce its own kind and develop according to its own laws. In biology, there is a whole section devoted to its study, which is called cytology or cell biology.
A cell is an elementary living system that includes individual components that have specific features and fulfill their functional duties.
A complex system
A biosystem consists of living matter of the same type: from macromolecules and cells to population communities and ecosystems. The following levels of organization exist in it:
- gene level;
- cell level;
- organs and organ systems;
- organisms and systems of organisms;
- populations and population systems;
- communities and ecosystems.
The biological components of various levels of organization in a certain order interact with inanimate nature, energy and other abiotic components and substances. Depending on the scale, different systems are subjects of study of different disciplines. Genetics deals with genes, cells are examined by cytology. Physiology takes over the organs. Organisms are studied by ichthyology, microbiology, ornithology, anthropology and so on.