The time when water from a well or a well could be safely used was long gone. Even the springs of distant districts from megacities are unsafe for health. This is explained by the serious environmental situation associated with the pollution of water resources around the world. The difficulty lies in the fact that water can penetrate almost everywhere, no matter how the harmful production wastes are mothballed, not to mention the cases of direct releases to the water area. Therefore, the use of purifiers and water softeners is vital today.
General information on installations and purpose
Water softening is necessary if its increased hardness is observed. These are those cases when the excess of calcium and magnesium salts in the liquid is obvious and is manifested by the appearance of plaque on heating elements: spirals of kettles, boilers, washing machines. The reason for water hardness is its contact with different rock formations of the soil, in particular, with Cretaceous and Dolomite.
To solve the problem, softening plants were developed - a set of equipment and reagents that remove excess salts from water. It is wrong to assume that water softeners completely remove hard elements from it - this is unacceptable, in particular, and because of the daily need of the human body in some of them. Therefore, a quality installation leaves a certain percentage of salts permitted by sanitary standards for water.
Installation of continuous action is more technically complicated than conventional periodic softener. It is applicable in cases where water supply is required constantly, for example, a water softener for a boiler house, food industry, non-ferrous metallurgy, petrochemicals, and heat and power enterprises.
Operating principle
The chemical process that takes place in a continuous water softener is based on the replacement of magnesium and calcium ions, dissolved by water, with sodium ions, at the moment the liquid passes through the resin ion exchange layer. When the resource of the latter is depleted (depletion has occurred), and it can no longer soften water, the resin layer is saturated with a solution of sodium chloride.
All continuous water softeners are divided into two categories that differ in principle of operation. These are the so-called twin and duplex systems.
- Twin equipment contains two cylinders, a common water flow control unit and a single salt tank. Cylinders operate in a priority mode, and each of them provides the performance that the consumer needs in full. While one cylinder performs softening, the second is in regeneration mode, that is, the structure of the reagent is restored, and then goes to the standby state when the filtration cycle of the working cylinder ends. Further, everything changes places and the cycle repeats.
- The duplex system works differently. Here, the filtration mode starts immediately with two cylinders, each of which has its own salt tank. The entire process is controlled by a three-way valve. Both cylinders provide full productivity, one - only half. Therefore, when the filtering cycle of one of the softeners ends, and it switches to the regeneration mode, the system performance drops sharply by half. After recovery of the ion exchange resin, two balloons are again softened with water. Next, the cycle repeats, but with a different softener.
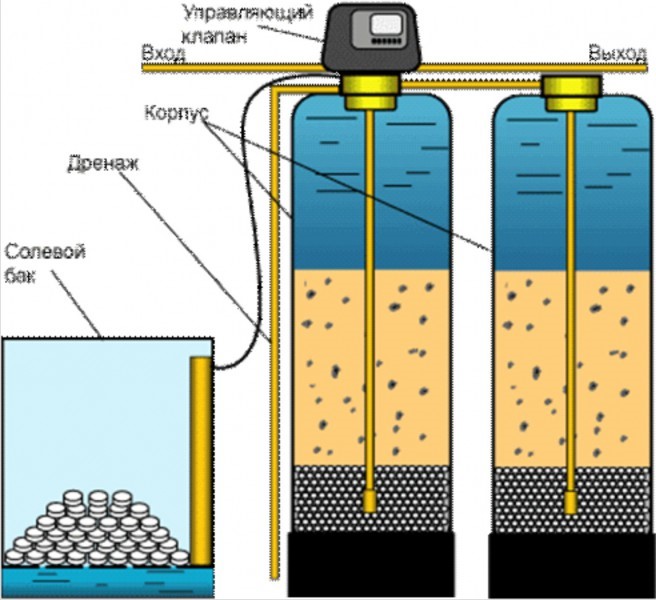
Equipment
Continuous water softeners of different models have a typical design with the following basic elements:
- Filter containers in the form of cylinders with ion-exchange resin. Untreated hard water is supplied there, softened comes out.
- Salt containers - are used to regenerate (restore) the ion-exchange resin after the end of the filtration cycle.
- Controller - controlling the process of switching the fluid flow. This is, in fact, a computer with a built-in counter of the volume of passed water, sending signals to the multi-way valve.
- Drainage distribution system.
- The filter element is based on a cationic-sodium strong acid resin in gel form.
- Saline reagent for carrying out regeneration (sodium chloride) tableted or granular.
- Stiff filters for suspended particles, which are placed before the installation of water softening.
- Shut-off and distribution valves for connecting the unit to water pipes.
Rules for connecting to water supply
- The water softener should be placed on a hard, level surface of the room with acceptable humidity and temperature.
- The place where the unit is connected to the system should be at the water supply inlet immediately after the accumulator and pressure tank, if any. Nearby should be the input of the sewer pipe.
- Connecting the equipment to the common system should not be carried out directly, but through the bypass line where the shut-off valve is installed, in order to be able to supply the initial state water to the consumer when the equipment breaks.
- All irrigation taps are inserted before the installation of water softeners, taps for taking samples - before and after the equipment.
- The water pressure of the system at any time of the day should not exceed the level of 6 atmospheres. To ensure this condition, it is recommended to equip the line with a reducer mounted on the inlet in front of the equipment.
- The pressure of the water supply should be no less than declared to ensure flushing of the system in fast mode.
- The overflow pipe should approach the sewage system through a separate line that is not connected to the outlet of the wastewater from the flushing system.
- Sewage into the sewer should be organized through a hydrobarrier in order to exclude the possibility of gas from the sewer into the room and the softener.
- It is recommended to connect the electrical circuit of the treatment equipment to the network through a stabilizing device.
Water softener installation: instruction
In order for the equipment to work correctly and function properly, it is necessary to observe some operating rules:
- In the salt tank, use only granular, tableted or edible table salt without iodine.
- Maintain a saline layer that must not fall below water level.
- Do not forget to replenish salt in the tank at least once a month.
- Periodically loosen the salt mass in order to avoid caking of the material.
- To clean reagent cylinders from sedimentary masses with a frequency of at least one to two times a year.
- Monitor the accuracy of the electronic scoreboard regarding time and date.
- Monitor the quality of water after cleaning and softening, and in case of deterioration, adjust the regeneration settings.
Specifications
The parameters by which to choose a deferrization and water softening installation are displayed in the characteristics of a specific installation model. In a generalized form, they look as follows:
- The claimed plant capacity in cubic meters per unit time.
- Possible weakening of pressure at nominal and peak performance.
- The volume of filter tanks in liters.
- The required dosage of salt per unit regeneration in kilograms.
- The duration of the regeneration process in minutes.
- Power consumption by the system.
Water requirements
Different water quality requires the use of different cleaners and softeners. Equipment in each case is selected individually. But basically, widely used plants are used to convert water, which must meet the following requirements:
- total hardness indicator - not higher than 20.0 mmol / liter;
- the general indicator of the presence of salts is not higher than 1000.0 mg / liter;
- color index - not higher than 30.0 degrees;
- lack of sulfides and hydrogen sulfides;
- active chlorine in a free state - not higher than 1.0 mg / liter;
- permanganate oxidizability - not higher than 6.0 mg O / liter;
- lack of oil products;
- amount of suspended solids - not higher than 5 mg / liter;
- the total iron indicator is not higher than 0.5 mg / liter;
- working temperature - not lower than 5 ° and not higher than 35 ° .
Conclusion
Automatic water softeners are designed in such a way that their operation is understandable to the consumer, but still purchasing such equipment, it is advisable to stipulate the conditions for the maintenance of the system with qualified specialists.