Protein molecules have a complex structure and are composed of amino acids. The latter are the material for the assembly of proteins, which is why any living organism needs constant replenishment. The main source of amino acids is any food protein that must enter the digestive system of the body and break down to elementary components. At the same time, food proteins that enter the human blood are immunogenic substances whose presence inside the vessels is unacceptable. Any foreign protein that directly contacts the internal environment of the body causes harm to the latter and acts as an antigen.
Characterization of food proteins
In the case of normal eating behavior, which eliminates cannibalism, mainly substances that normally are absent in the body enter the human digestive system. This means that all food proteins that enter the human blood are foreign. Therefore, before they are absorbed, they must be split into elementary components - amino acids. This need is explained by the fact that any protein has some properties, the presence of which is explained by a specific chemical and spatial structure. Some of them are enzymes, and some are poisons.
Any protein retains its properties as long as it has the same spatial structure. And the most reliable and energetically correct way of its assimilation is just complete cleavage, which consists of the stage of denaturation and the gradual rupture of peptide bonds. Without splitting, all food proteins that enter the human blood are antigens. Moreover, the intravenous administration of food proteins threatens the rapid death of a person, while the introduction of amino acids or dipeptides into the blood can be used by athletes or depleted patients with protein starvation without harm to the body.
Contact of foreign proteins with the immune system
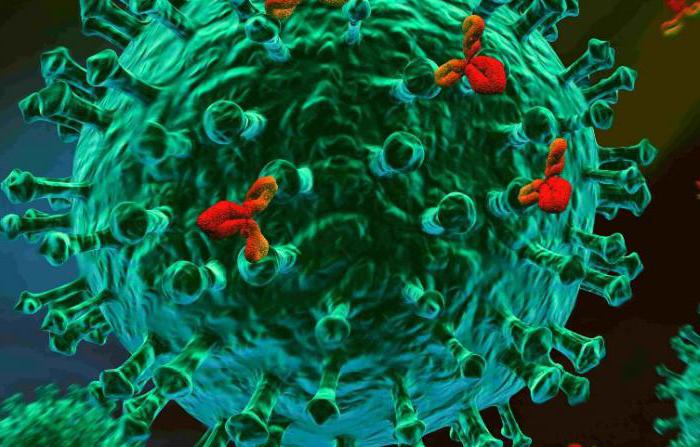
When studying immunology and microbiology as a test, designed to find out the level of ownership of the material, trainees may be asked provocative questions. For example, a question of a similar nature: food proteins that enter human blood are what? If this is computer testing, then the following answers may be offered: antibody, enzyme, antigen, hormone. The only correct option is the antigen, since any foreign protein in the internal environment of the body is attacked by the immune system and is perceived as a xenobiotic or poison. It also cannot be a vitamin.
Causes of the immune response
The body is able to use for its needs only those proteins whose primary structure is encoded in its genome. This means that even the ingestion of an enzyme that normally exists in humans will cause an immune system reaction. This will happen due to the inadmissibility of the presence of certain substances in some biological environments. For example, intracellular enzymes, normally present in the mitochondria or in the nucleus, are foreign when they enter the bloodstream. Therefore, they are perceived by the immune system as antigens and are eliminated by the macrophage system.
An exception is only those proteins that are fully consistent in structure with certain enzymes or hormones. For example, artificially synthesized insulin when introduced into the blood does not cause an immune response. This happens due to the fact that it has the same chain structure and electric charge as that of natural human insulin. However, insulin is not a dietary protein. Once in the blood of a person, it is a hormone. But all other dietary proteins when administered intravenously have significant harm.
For successful absorption, food proteins must be broken down in the digestive system. Then they can get into the blood already in the form of amino acids, having lost their structure. In this form, they can be used by cells for the biosynthesis of their non-immunogenic proteins, which will act as hormones, mediators or enzymes inside the cell or in the blood. The statement that food proteins that enter human blood are enzymes, antibodies, or hormones is false. They remain only antigens, and can not be anything else.
Why foreign proteins are not antibodies
To finally understand why a foreign protein cannot be an antibody, you need to correctly understand the course of immune processes. An antibody is a complex globulin protein that is synthesized by the plasmocytes of the human immune system. And an antigen is a molecule that triggers a reaction of the immune system. All dietary proteins that enter the human blood are antigens. Upon initial contact, they are absorbed by the macrophage, which recognizes the structure of the protein and transforms into an antigen-presenting cell. Based on the information obtained after antigen lysis, immunoglobulins are synthesized. The latter are antibodies.
Antibody synthesis
An antibody is a protein molecule synthesized in the human body in order to eliminate a specific antigen. It is synthesized in response to the appearance of antibodies in the internal environment of the body. The mechanism of their interaction can be expressed as follows: an antibody, in case of contact with an antigen, allows the macrophage to begin mass destruction of a foreign protein, bypassing the stage of antigen presentation on its membrane. Antibody synthesis is a way of transition from cellular immunity to humoral, and all food proteins that enter the human blood are antigens that must be eliminated.
The outcome of the introduction of dietary protein into the blood
The hypothetical result of intravenous administration of a foreign protein is difficult to predict, since it depends on the specific protein and its dose. In minimal doses, an immune response will develop, and the protein will be absorbed by macrophages, which will provide antigens to plasmocytes. The latter synthesize antibodies after about 2 weeks. In the case of repeated introduction of protein into the blood, a reaction will occur not of cellular, but of humoral immunity. At the same time, food proteins that enter the human blood are not antibodies.
The introduction of proteins in large quantities
In large quantities, edible proteins introduced directly into the blood will lead to death due to increasing renal failure or pulmonary embolism. The latter option is possible with the introduction of protein in the composition of oil solutions or in the form of solid particles. However, specific experiments designed to confirm such hypotheses were not conducted for ethical reasons.
Obviously, the body can not absorb proteins from the blood, and uses for its needs only the components of which they consisted. Then the question should be answered: in the case of direct intravenous administration, are the food proteins that enter the bloodstream of a person are antibodies, antigens, enzymes or vitamins? The answer is antigens. Some of them, without splitting, are poison at all. Getting directly into the bloodstream, they are not neutralized by the liver, and therefore can kill a person.