Anatomical formations, which will be discussed in this paper, are part of two systems of the human body: respiratory and digestive. Outwardly resembling wells or cells, they have a completely different histological structure and perform dissimilar functions. In the process of embryogenesis develop from two germ layers - endoderm and mesoderm. These are human alveoli. They contain airy tissue of the lungs and depressions in the bones of the upper and lower jaw. Let's get acquainted with these structures in more detail.
External structure of structural units of lung tissue
The human lungs are paired organs that occupy almost the entire cavity of the chest and ensure that oxygen enters the cells of the body and removes excess carbon dioxide and water. Permanent gas exchange is possible due to the unique structure of the lung tissue, consisting of a huge number of microscopic sack-shaped formations. The protrusion of the walls of the parenchyma of the respiratory system, resembling a honeycomb - this is what the alveolus is. It is connected with neighboring structures by an interalveolar septum, consisting of two epithelial layers containing cells of a flat shape. Between them are collagen and reticular tissue fibers , intercellular substance and capillaries. All of the above structures are called interstitium. It should be noted that the network of blood vessels in the lungs is the largest and most branched in the human body. This is explained by the fact that with their help in the alveoli of the lungs, carbon dioxide is transported from venous blood to the alveolar cavity and oxygen is transferred from it to the blood.
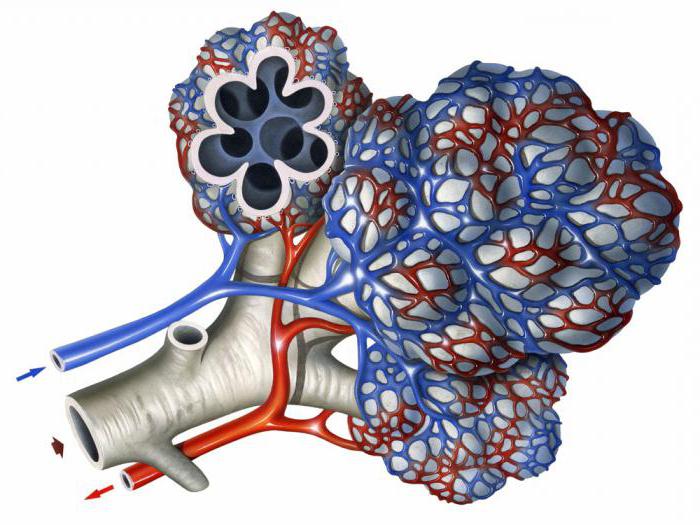
Airborne barrier
The portion of air received during inhalation enters the alveoli of the lungs, which are collected, like grapes, on the thinnest tubes - bronchioles. From the bloodstream they are separated by a three-component structure, 0.1-1.5 μm thick, called the airborne barrier. It includes membranes and cytoplasm of the alveolar elements, parts of the endothelium and its liquid contents. For a better understanding of what alveolus is and what its functions are, it must be remembered that gas diffusion in the lungs is impossible without structures such as the interalveolar septum, the airborne barrier, as well as interstitium, which contains fibroblasts, macrophages and white blood cells. An important function is performed by alveolar macrophages located inside the alveolar septa and near the capillaries. Here they break down harmful substances and particles that enter the lungs when inhaling. Macrophages can also phagocytose red blood cells that enter the alveolar vesicles if a person is diagnosed with heart failure, aggravated by symptoms of stagnation of blood in the lungs.
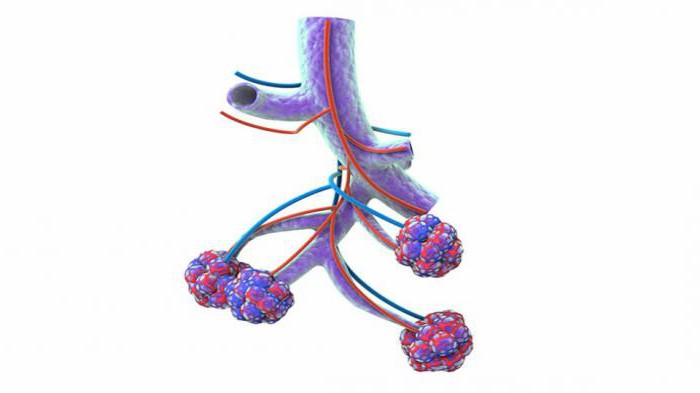
External respiration mechanism
The cells of the body are provided with oxygen and are released from carbon dioxide due to blood passing through the capillary network of the alveoli. Oxygen and carbon dioxide, liberated from carbonate acid and its salts by the enzyme carbonic anhydrase, continuously move through the aerogematic barrier in opposite directions. She is in red blood cells. The extent of diffusion can be judged from the following figures: about 300 million alveoli that form the lung tissue make up about 140 m 2 of the gas exchange surface and provide the process of external respiration. The above facts explain what alveolus is and what role it plays in the metabolism of our body. In fact, it is the main element that provides the breathing process.
The histological structure of the alveoli
Having examined the anatomy of lung tissue cells, let us now dwell on their species diversity. The alveoli consists of two types of elements, called cells of type I and II. The first are flat in shape, capable of adsorbing particles of dust, smoke and dirt in the inhaled air. An important function in them is played by pinocytotic vesicles filled with a protein substrate. They reduce the surface tension of the alveoli and prevent their subsidence during exhalation. Another element of type I cells is the closing structures, which serve as a buffer and do not allow intercellular fluid to penetrate into the alveolar cavity filled with air. Groups of oval cells of type II have a cytoplasm resembling a foam. They are found in the alveolar walls, are capable of active mitosis, this determines the regeneration and growth of lung tissue elements.
Alveola in dentistry
A deepening in the jaw in which the tooth root is located is what the alveolus is. Its wall is formed by a compact substance having the form of a plate. It contains osteocytes, as well as salts of calcium, phosphorus, zinc and fluorine, so it is quite solid and strong. The plate is attached to the bone beams of the jaw and has periodontal cords in the form of collagen fibers. It is also plentifully supplied with blood and braided by nerve endings. After tooth extraction, a strongly protruding wall of the external part of the hole and the bony septum remains. Alveoli of the teeth heal within 3-5 months by first forming granulation tissue, which changes to osteoid and then to mature bone tissue of the jaw.