Electricity meters are the most popular meter in the domestic spectrum. They are used in every home as a means of controlling consumed electricity. Another thing is that the technical design may be different. The traditional and still fairly common types of this device include an electric induction meter, which also provides for various forms of technical and structural implementation.
Definition of induction meters
Like all electricity meters, induction models provide for the passage of current through their conductors with the connection of sensitive measuring elements. They differ in bandwidth, size, maximum load, etc. First of all, the induction energy meter is a mechanical device provided with a counting mechanism. Again, technically, its “filling” may have a different design, but the basic principles are guided by the electromagnetic principle of operation, which allows fixing the behavior of eddy currents over a magnetic field.
Technical device and principle of operation of the device
The basis of the device is formed by two elements - coils for servicing voltage and current. The first is connected in parallel, and the second is connected in series. Together they create conditions for electromagnetic flows, in the environment of which, in principle, it becomes possible to fix and measure the necessary network parameters. Directly measuring operations are performed due to the aluminum disk. By means of a worm or gear transmission, this element is mated to a counting device, driving it. During operation, the disk rotation intensity will be determined by the power consumption. The modern device of the induction meter is also distinguished by the presence of electronic elements that make it possible to automatically record readings, remote control of individual accounting parameters and reduce the size of the panel with the display of information on consumption. But even in this case, the basic principles of electromagnetic metering by induction coils are preserved.
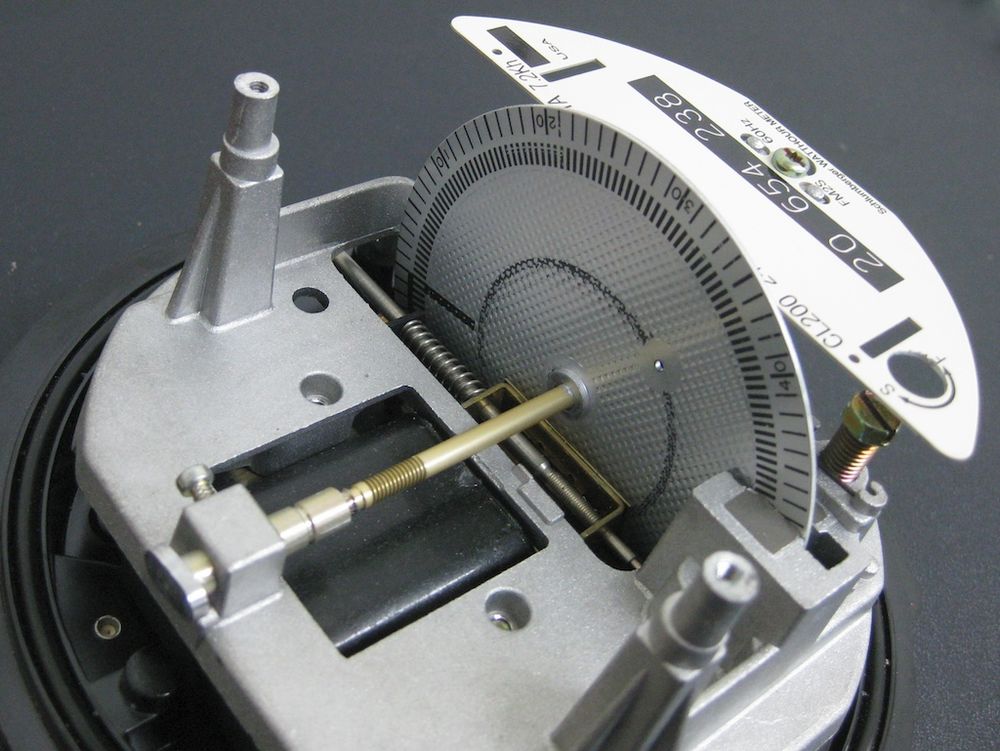

Counter creation
The first electromagnetic metering devices appeared at the end of the 19th century, when Italian engineers discovered the relationship between the different phases of the alternating current and magnet fields. In the manufacture of the simplest designs, a solid rotor was used like a cylinder and the same disk. He was driven by changing electrical characteristics. The next step was the development of a full-fledged screw mechanism, but so far without voltage control elements. Actually, at this stage the principles of the work and the technical device of a modern induction meter with self-induction coils and a rotating metal body were laid. In the future, the design was replenished with brake electromagnets, which allowed to expand the measurement range with a cyclometric register. Throughout the 20th century, there was a process of optimizing the case, which led not only to optimizing the size of the device, but also to increasing the reliability of the elements of the counting mechanism. Designs have become more resistant to temperature, humidity and physical influences. The accuracy of the readings also increased, which is especially manifested in devices of the latest generations with new functional capabilities and management approaches.

Classification Induction Counter
First of all, one-and three-phase models should be distinguished. The first relate to household measuring instruments intended for home use. They are powered by a single phase and provide for 4 terminals. You can connect such a device to a common main power network. As for three-phase induction meters, they have a higher level of reliability and are divided into groups depending on operating conditions. So, there are models for use at home, in industries and in public places. Moreover, in the domestic sphere they are usually used if a powerful energy consumption infrastructure is organized with the connection of productive equipment such as welding machines, compressor stations, pumping units, etc.
Within the general family of induction metering devices, the already mentioned mechanical and electronic types of models are distinguished. Mechanics has its advantages associated with low volatility and structural reliability. Electronics, in turn, makes it possible to differentially account for the energy consumed, which is convenient when using electricity at several tariffs depending on the consumer.
Instrument Specifications
Voltage is the main characteristic of electric metering devices. The standard range varies from 220 to 240 V, which corresponds to the capabilities of single-phase models. In the case of three-phase meters, we can talk about 380-400 V. Considered in the choice of induction device and the maximum load amperage. The rated indicator must exceed the amount of current allowed by the input circuit breaker. For example, if a transformer is used at 25-30 A, then it is advisable to install an induction meter at least 40 A. At the household level, the maximum performance on this characteristic rarely exceeds 100 A.
For a private house, it is quite possible to limit yourself to buying a model for 40-60 A. It will also be useful to pay attention to the accuracy class. In principle, the rules do not allow the operation of metering devices with a coefficient of more than 2.0. The best option is to purchase devices with an accuracy class of 1.0. This is important not only because of the receipt of more correct data on the consumed energy, but also for the objective control of the operation of a home or industrial power network.
Meter operation
After choosing the appropriate model, a place is selected for installing the device. It is desirable that it be protected from physical, thermal and electromagnetic external influences. Installation is usually carried out using a DIN rail and a complete set of hardware. Together with the rail, a terminal block is supplied, which can be separate or integrated. In any case, through it the device is integrated into the local power grid. Connection is made by employees of the power supply organization, who will also periodically check the status of the device.
The nuances of the work of induction metering devices
During the operation of measuring devices of this type, the following features of the working process should be borne in mind:
- At light loads in the network, a decrease in accuracy below the standard level is possible, therefore it is recommended to monitor the parameters of the same voltage using a stabilizer.
- Without mechanical means of protection, the operation of the induction meter can be physically adjusted. To fix such cases, the devices are sealed. By the way, electronic induction models of meters are protected from all kinds of “twists” programmatically.
- High maintainability. Even in case of damage to the internal elements of the energy control, it remains possible to restore full performance by replacing faulty components.
The future of induction metering technologies
Despite the moral obsolescence of the principles of electromagnetic metering, manufacturers do not abandon this segment, giving devices all the new functionality. Prospects for the development of an induction meter are primarily associated with digital means of processing and sending data. Already today there are models with GSM sensors that completely relieve the user of the analog fixation of accounting information. The range of basic functions is expanding. This set is replenished with the capabilities of recording frequency, voltage and external microclimatic indicators.
Conclusion
Induction measuring equipment today is widely used not only in the domestic and commercial fields, but also in industry. And this also applies to three-phase and single-phase induction meters with electronic "stuffing". Such a choice is determined by high requirements for the reliability and reliability of operating energy systems. However, the problems of using induction devices remain. Negative factors relate to a relatively low degree of accuracy, sensitivity to network loads and poor protection against theft of electricity.