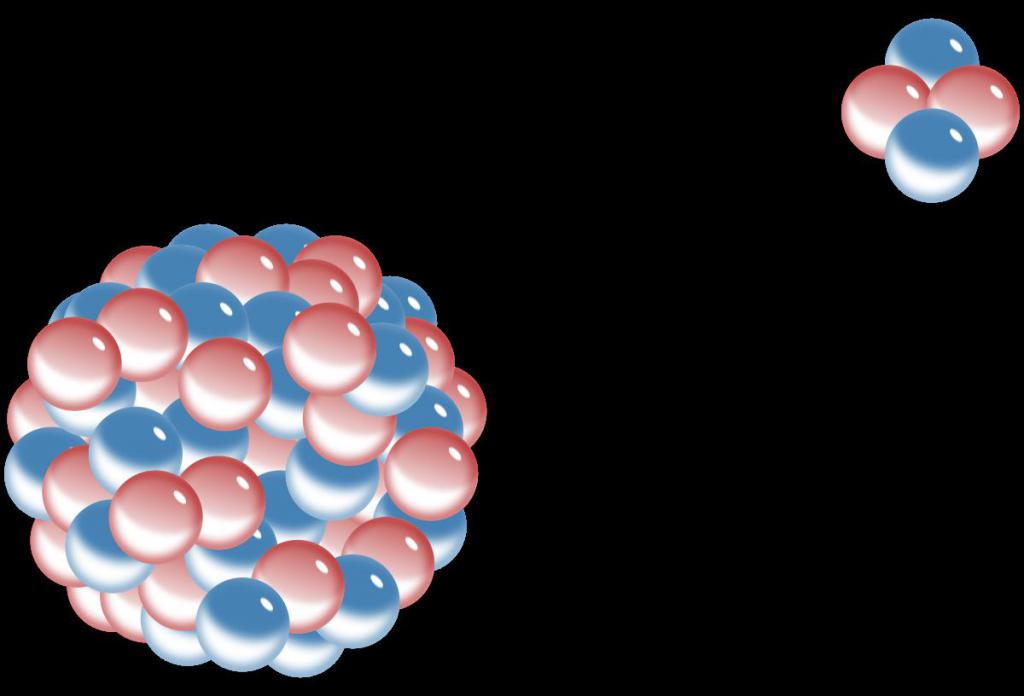
The alpha particle is the core of helium. If the electron shell is removed from the helium atom, this particle will remain. It consists of two protons and two neutrons, has a spherical shape with a radius of 10 -5 meters. The mass of the alpha particle is 6.68 * 10 -27 kilograms.
Discovery story
At the turn of the XIX-XX centuries, two world-famous physicists discovered the existence of alpha particles. These were New Zealand physicist Ernest Rutherford, who worked in Canada in the city of Montreal, and French chemist and physicist Paul Villard, who set up his experiments in Paris. These two scientists studied different types of radiation by their properties of penetrating through various environments, as well as by their interaction with an artificial magnetic field.
As a result of these experiments, Rutherford identified three types of radiation: alpha, beta, and gamma. Alpha rays were defined as rays having the lowest penetration through various objects among the studied types of radiation.
Elementary particles: protons and neutrons
In physics, it is customary to ascribe to any particle two basic characteristics - electric charge and mass, since these criteria largely determine its properties and behavior in specific physical conditions.
As mentioned above, an alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons. A proton is an elementary particle having a mass of 1.6726 * 10 -27 kg and a charge of 1.602 * 10 –19 C. As for the neutron, its mass is 1.00137 times greater than that of the proton, that is, 1.67489 * 10 -27 kg. The neutron charge is zero, that is, this particle is electrically neutral (hence the name - "neutron").
Alpha particles and their charge
The charge and mass of an alpha particle can be determined by taking into account the above figures, and also taking into account that the particle itself consists of two protons and two neutrons. The alpha particle charge is positive and is equal to +3.204 * 10 –19 C. We note that the value +1.602 * 10 –19 C is commonly called in physics an elementary charge, since it is equal in absolute value to the same quantities for the proton and the electron. Thus, the charge of an alpha particle is +2 elementary charges.
Alpha particle mass
If we take into account the additive property of the physical quantity "mass", then we can independently calculate how much the alpha particle weighs. The above figures for protons and neutrons say that the mass of an alpha particle is 6.69498 * 10 -27 kg. This figure is obtained if we add the masses at rest of two protons and two neutrons. As a result, the mass ratio of the proton and the alpha particle is approximately 1/4. That is, an alpha particle is four times heavier than a proton.
However, many experiments to establish the exact mass of this particle say that the rest mass of the alpha particle is 6.68 * 10 * 10 -27 kg, that is, it is less by 0.015 * 10 -27 kg of the value obtained above. Where does the difference go? The answer to this question is quite simple - it goes into energy. The fact is that during the formation of an alpha particle from protons and neutrons as a result of nuclear interactions between them, energy is released in the form of electromagnetic radiation, two protons and two neutrons pass into a more favorable energy state - our alpha particle.
Education energy
To calculate the alpha particle formation energy, one should use the famous Einstein equation, which connects mass and energy through one of the fundamental constants of our Universe - the speed of light. This equation has the form: E = mc 2 , where E is energy, m is mass, c is the speed of light in vacuum.
Knowing that during the formation of an alpha particle, the mass of its components decreases by 0.015 * 10 -27 kg, and also knowing that the speed of light is 3 * 10 8 m / s, we get the energy that is released during this process. It is equal to E = 0.015 * 10 -27 * 9 * 10 16 = 1.35 * 10 -12 J. In elementary particle physics, it is customary to write down the energy in electron volts (eV). One electron-volt is 1.602177 * 10 −19 J. Then the alpha-particle formation energy is 8.426 * 10 6 eV, or 8.426 MeV (megaelectron-volt).
To understand how large this energy is, a simple calculation can be made. Imagine that all the energy of formation of an alpha particle is transferred to its acceleration. Using the Lorentz equation for nonrelativistic velocities, that is, assuming that the kinetic energy-alpha of the particle is equal to mv 2/2, where v is the velocity of its motion, we obtain that this formation energy will be enough to accelerate the alpha particle to a speed of 2 * 10 7 m / s, which is 6.7% of the speed of light in vacuum. It should be noted that asking the question of how much the alpha particle mass increases at such speeds does not make sense, since the increase in its mass can be neglected, since it will be only 0.015 / 6.68 * 100 = 0.2%.
Basic physical properties
An alpha particle is 4 times heavier than a proton and 8000 times heavier than an electron, that is, it has a large mass for the world of elementary particles. Recall that the mass of one proton or one neutron in atomic units (amu) is 1, and the proton charge is +1 in units of elementary charge, that is, the alpha particle has a charge of +2, and the mass is 4. Then the ratio of the charge to the mass of the alpha particle is +1/2 = +0.5.
Since it has an electric charge, flying through an electric or magnetic field, it interacts with it. To determine the direction of the force that acts on the alpha particle in a magnetic field, it is necessary to use the so-called rule of the left hand: four fingers should be placed along the motion vector of the alpha particle, and the palm should be rotated so that the lines of magnetic induction enter it. Then the thumb protruding at a right angle will indicate the direction of the acting force on the moving charged particle.
Alpha particles can accelerate to high speeds, reaching 15 million km / s, that is, 5% of the speed of light. Due to the large mass and huge speeds, they acquire significant kinetic energy, which can be up to 10 MeV.
Penetrating ability
Since an alpha particle has a significant mass (compared to the mass of an electron), as well as an electric charge that is 2 times higher than the electron charge, its penetrating ability, that is, the ability to pass through a layer of matter, is insignificant.
During its movement, the alpha particle experiences collisions with atoms, transferring a significant amount of energy to them, which leads to ionization of atoms, that is, to the separation of electrons from them. For example, passing only 5 cm in air, an alpha particle experiences a huge number of collisions and almost completely loses its kinetic energy.
Any solid substance easily retains the alpha particle. So, it cannot pass through a layer of several sheets of paper, and an aluminum plate with a thickness of only 0.1 mm delays the flow of any intensity from alpha particles. Once again, although the penetrating ability of this particle is small, it very strongly ionizes any substance through which it moves.
Alpha particle is a product of radioactive decay.
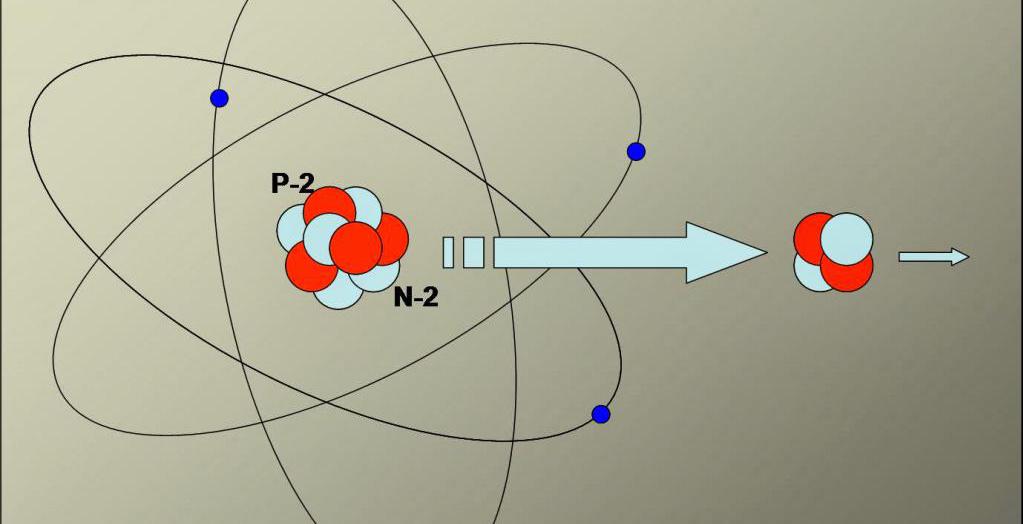
Despite the fact that an alpha particle consists of protons and neutrons, it does not form from these elementary particles in nature, but is obtained as a result of radioactive alpha decay of some chemical elements.
Alpha decay is a type of radioactive decay, as a result of which the atomic nucleus of a chemical element, emitting an alpha particle, turns into the nucleus of another element, whose mass is 4 amu less than this value in the parent nucleus, and the serial number in the periodic table is 2 units less than the original element.
Alpha decay is spontaneous (occurs arbitrarily in nature) and forced (caused as a result of any special effect on the atomic nucleus). Spontaneous decay is characteristic only of very heavy atomic nuclei. Thus, tellurium 106 is the lightest element that undergoes spontaneous alpha decay. Uranium 238 also undergoes alpha decay to form technetium 234.
Since an alpha particle has a double positive elementary charge, it quickly decays electrons upon decay of a radioactive nucleus, thus forming a helium atom. For this reason, in many rocks with a high content of alpha-radioactive elements there are cavities filled with helium gas, for example, in minerals rich in uranium or thorium. The main source of alpha particles on Earth is the noble gas radon, which is found in soil, water, air and various types of rocks.