Polycarbonate from the point of view of chemistry is a synthetic polymer, it can be considered a complex polyester of carbonic acid and phenols. As you know, salts of carbonic acid are called carbonates, hence the name of the polymer popular today, formed from two parts - poly (which means a lot) and carbonate.
Some chemistry
The polycarbonate macromolecule has a linear structure. In general, its formula can be written as follows:
H - [- O — R — O— (C = O) —O — R—] n —OH.
Depending on the type of substituent R, all polycarbonates can be divided into aromatic, fatty aromatic and aliphatic. The largest of them today is the first group. Trade names for aromatic polycarbonates may be different, but they share similar values of physical and mechanical properties, such as high light transmission, low specific gravity, and relatively high melting point. Polycarbonates with these properties contain many benzene rings (aromatic substituents).
Polycarbonate Advantages
- Strength. One of the most famous properties and significant advantage of polycarbonate is its high resistance to mechanical shock.
- Transparency. Due to the high light transmission, polycarbonates have successfully replaced silicate glass in many areas of life and production, since they also have a relatively low weight.
- Thermal resistance. The values of the melting (softening) temperatures of polycarbonates are somewhat different from each other depending on the structural features of the macromolecule, but, as a rule, it exceeds 200 ° C.
- Thermoplasticity. Polycarbonate refers to this type of polymer that can be remelted many times. In this case, after hardening, it will restore its properties.
- Environmental friendliness. Due to the previous property, polycarbonate products can be recycled.
- Fire safety. The ignition temperature significantly exceeds the melting point of polycarbonate, it is about 570 ° C.
- Chemical resistance. Due to this property, the material is successfully used in various aggressive environments.

disadvantages
It is worth noting that polycarbonate has all the above advantages only if its macromolecules have a molecular weight of more than 25,000. Otherwise, it is very unstable and has a much lower melting point. A polycarbonate manufactured in violation of the technology may contain a rather high number of molecules with a reduced molecular weight, which negatively affects its strength and performance characteristics.
Another significant disadvantage of polycarbonates is their low resistance to ultraviolet radiation. However, today there are technologies that protect the polymer from direct exposure to UV rays. This is usually done using protective films, which are fused with polycarbonate at the stage of manufacture of the product. Another limiting factor in the use of polycarbonate is its high expansion value with increasing temperature.
Physical and mechanical properties
- The refractive index is 1.5850.
- Density (at 25 ° C) - 1.20 g / cm 3 .
- Glass transition temperature - 150 ° C.
- Softening point 220-230 ° C.
- Decomposition temperature> 320 ° C.
- Frost resistance, ° C <-100
- The tensile strength is 65-70 MPa.
- The bending strength is 95 MPa.
- The specific heat is 1090-1255 J / (g · K).
- Thermal conductivity - 0.20 W / (m · K).
- The coefficient of thermal linear expansion is -1 (5-6) · 10 -5 ° C.
- Brinell hardness - (784-980) · 10 5 Pa.
Cellular and monolithic polycarbonate
Cellular polycarbonate is a panel of several layers of plastic, between which longitudinal stiffeners are located. In the context, such a leaf vaguely resembles a honeycomb, for which it acquired its name. Such sheets can be easily bent in the cold state, achieving the smallest possible bending radius. Cellular polycarbonate is most often used for the construction of decorative partitions and the construction of transparent roofs.
Monolithic polycarbonate has higher impact resistance and transparency. An essential advantage is the high heat resistance of monolithic polycarbonate, the melting temperature is quite high, which allows it to be used without fear at temperatures reaching 120 ° C. An important property of it is frost resistance, which allows the use of products from this type of plastic at temperatures up to minus 50 ° C.
Polycarbonate Application
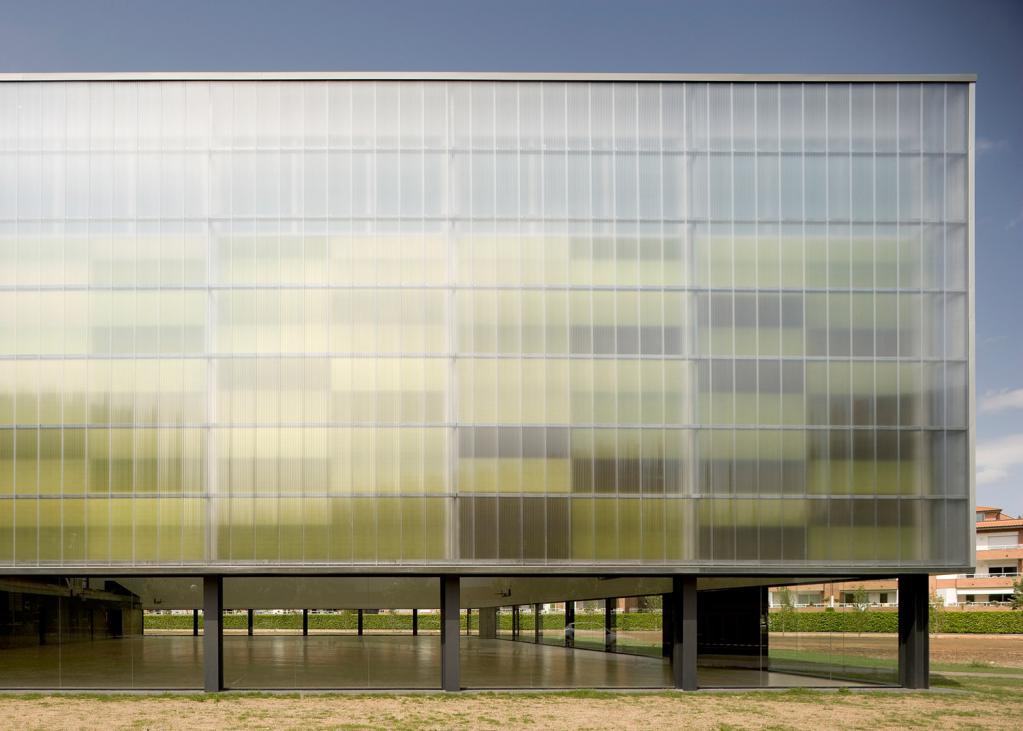
- Construction. Thanks to its high transparency and lightness, polycarbonate helps architects realize their most daring projects. At the same time, the weight of the structure, relative to the traditionally used glass, can significantly reduce the load on the foundations, and therefore save on materials. Moreover, polycarbonate also has thermal insulation properties, if we talk about its cellular variety. Translucent structures are made from it for swimming pools and stadiums, car parks and supermarkets, transitions between buildings and winter gardens. This material is popular among summer residents. Polycarbonate for greenhouses is increasingly being used. Its melting point is much higher than atmospheric even in the hottest summer, which means that the solar heat is not able to cause significant harm to this polymer.

- Electronics. Polycarbonate is used to make cases and protective coatings for laptops, smartphones, players, home computers, and much more. Thanks to this polymer, touch screen technology was able to reach the masses. It is used for the production of biometric passports.
- Advertising. From polycarbonate create light structures, signs, placards, three-dimensional letters and much more. All this can have very intricate extraordinary forms. Also, their sheets of monolithic plastic make anti-vandal protection of advertising structures.
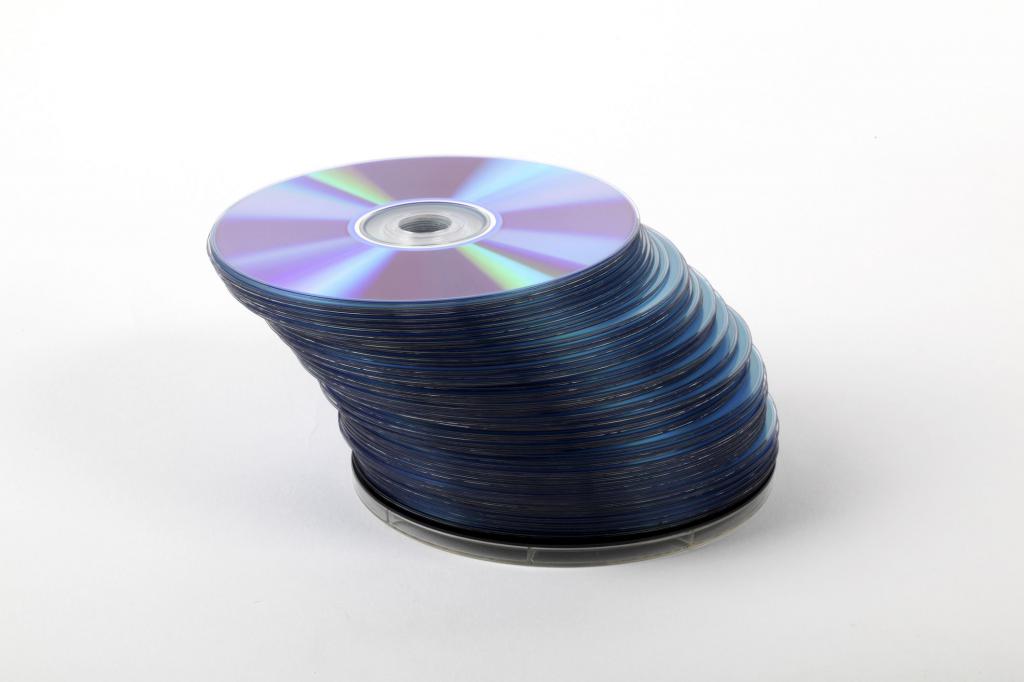
- Optical discs. Since the 1980s, polycarbonate has been used to create the base for CDs. Today, high-capacity DVDs are also made from it.
- Car– and aircraft industry. For the construction of aircraft traditionally use the latest materials with high strength and lightness, which is also characteristic of polycarbonate. It makes domes of fighter cabins and glass for helmets of astronauts and pilots. For cars, polycarbonate is made not only of glass, but also of headlights and hatches.
- The medicine. A very important area of application of polycarbonate was the manufacture of medical instruments. This was made possible thanks to such advantages of the material as non-toxicity and high biocompatibility, as well as the absence of the body's immune response to this plastic. And due to its strength and transparency, it competed with glass and metal alloys. Products and equipment made using this material are used to monitor tissues and body fluids. In addition, the high melting points of polycarbonates make it possible to subject them to the most modern sterilization methods - by heating, radiation, and UV rays.
- Optics. In 2000, polycarbonate lenses began to be made for industrial safety glasses, which protected the eyes when performing various tasks. Such products are tens of times stronger than other plastic lenses; if they are hit, they do not spread fragments, they are even more difficult to scratch. Gradually, polycarbonate also began to be used for everyday eyeglass lenses. Due to their safety qualities, such lenses are very often used for children's glasses, for the glasses of motorcycle helmets.
- Other areas. Today, polycarbonate has become so firmly entrenched in our lives that residents of not only megalopolises, but also of remote villages daily encounter products, of which this plastic is a part. Ball pens, flashlights, computer mice, irons and kettles, corks for wine bottles, furniture parts, containers for drinking liquids and even packaging film are made from it.