This article is devoted to the topic of the absorbed dose of radiation (radiation), ionizing radiation and their types. It contains information about diversity, nature, sources, methods of calculation, units of measurement of the absorbed radiation dose and much more.
The concept of absorbed radiation dose
The radiation dose is the value used by such sciences as physics and radiobiology in order to assess the degree of impact of ionizing radiation on the tissues of living organisms, their life processes, and also on substances. What is called the absorbed dose of radiation, what is its significance, form of exposure and variety of forms? It is mainly presented in the form of the interaction between the medium and ionizing radiation, and is called the ionization effect.
The absorbed dose of radiation has its own methods and units of measurement, and the complexity and diversity of the processes under the influence of radiation give rise to a certain species diversity in the forms of the absorbed dose.
Ionizing form of radiation
Ionizing radiation is a stream of various types of elementary particles, photons or fragments formed as a result of atomic fission and capable of causing ionization in a substance. Ultraviolet radiation, like the visible form of light, does not belong to this type of radiation, nor does it include infrared radiation emitted by radio bands, which is associated with their small amount of energy, which is not enough to create atomic and molecular ionization in the ground state.
Ionizing form of radiation, its nature and sources
The absorbed dose of ionizing radiation can be measured in different SI units, and depends on the nature of the radiation. The most significant types of radiation: gamma radiation, beta particles of positrons and electrons, neutron, ion (including alpha particles), X-ray, electromagnetic with short waves (high-energy photons) and muon.
The nature of the sources of ionizing radiation can be very diverse, for example: spontaneous radionuclide decay, thermonuclear reactions, cosmic rays, artificially created radionuclides, nuclear reactors, an elementary particle accelerator, and even an X-ray machine.
How is ionizing radiation affected
Depending on the mechanism by which the substance and ionizing radiation interact, a direct stream of particles of a charged type and radiation acting indirectly, in other words, a photon or proton stream, of neutral particles can be distinguished. The education device allows you to select the primary and secondary form of ionizing radiation. The power of the absorbed dose of radiation is determined in accordance with the type of radiation to which the substance is exposed, for example, the force of the effective dose of rays from space on the earth's surface, outside the shelter, is equal to 0.036 μSv / h. It should also be understood that the type of dose measurement and its indicator depends on the sum of a number of factors, speaking about cosmic rays, it also depends on the latitude of the geomagnetic form and the position of the cycle of the eleven-year activity of the sun.
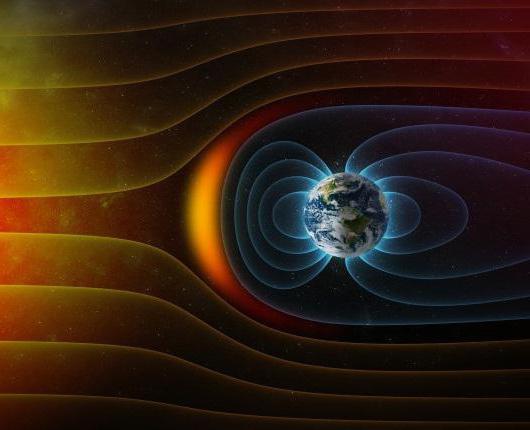
Ionizing particle energy range is in the range from a couple of indicators hundred eV and comes to indicators 10 15-20 electron volts. The length of the path and the ability to penetrate can vary greatly, and range from a few micrometers to thousands or more kilometers.
Exposure Exposure
The ionization effect is considered the main characteristic of the form of interaction of radiation with the medium. In the initial period of the development of radiation dosimetry, E-radiation was mainly studied, the electromagnetic waves of which lay within the range between ultraviolet and gamma radiation, due to the fact that it is widely distributed in air. Therefore, a quantitative measure of radiation for the field was the level of air ionization. Such a measure became the basis for creating an exposure dose determined by the ionization of air under ordinary atmospheric pressure, while the air itself must be dry.
The exposure absorbed dose of radiation serves as a means of determining the ionizing capabilities of the radiation of x-rays and gamma rays, shows the radiated energy, which, having undergone conversion, has become the kinetic energy of charged particles in a fraction of the air mass of the atmosphere.
The unit of measurement of the absorbed radiation dose for the exposure type is the pendant, the SI system component divided by kg (C / kg). The type of off-system unit is x-ray (P). One pendant / kg corresponds to 3876 X-rays.
Amount absorbed
The absorbed dose due to it, as a clear definition, has become necessary for man in connection with the variety of possible forms of exposure to a particular radiation on the tissues of living things and even inanimate structures. Expanding, the well-known circle of ionizing species of ini showed that the degree of influence and influence can be very diverse and not subject to the usual definition. Only a specific amount of absorbed radiation energy of the ionizing type can give rise to chemical-physical changes in tissues and substances exposed to radiation. The very number necessary to trigger such changes depends on the type of radiation. The absorbed dose of ini has arisen precisely for this reason. In fact, this is an energy quantity that has been absorbed by a unit of matter and corresponds to the ratio of the energy of the ionizing type, which was absorbed by the mass of the subject or object that absorbs radiation.
The absorbed dose is measured using a gray unit (Gy), an integral part of the Cu system. One gray is the amount of dose that can transmit one joule of ionizing radiation to 1 kilogram of mass. Rad - an off-system unit of measure, the size of 1 Gy corresponds to 100 rad.
Absorbed Dose in Biology
Artificial irradiation of animal and plant tissues has clearly demonstrated that different types of radiation, being in the same absorbed dose, can affect the body and all biological and chemical processes that occur in it in different ways. This is caused by the difference in the number of ions created by the lighter and heavier particles. During the same path along the tissue, a proton can create more ions than an electron. The denser the particles are collected as a result of ionization, the stronger will be the destructive effect of radiation on the body, under conditions of the same absorbed dose. It was in accordance with this phenomenon, the difference in the strength of the effects of various types of radiation on the tissue, that the designation of the equivalent dose of radiation was introduced. The equivalent dose of absorbed radiation is the data on the radiation received by the body, calculated by multiplying the absorbed dose indicator and a special coefficient, which is called the relative biological efficiency coefficient (RBE). But also it is often referred to as a quality factor.
Units of absorbed dose of radiation of equivalent type are measured in SI, namely in sievert (Sv). One Sv is equal to the corresponding dose of any radiation that is absorbed by one kilogram of tissue of biological origin and causes an effect equal to the effect of 1 Gy of photon-type radiation. Rem - used as an off-system measuring indicator of the biological (equivalent) absorbed dose. 1 Sv corresponds to one hundred rems.
Effective dosage form
The effective dose is an indicator of the value that is used as a measure of the risk of the long-term effects of human exposure, of its individual parts of the body, from tissues to organs. At the same time, its individual radiosensitivity is taken into account. The absorbed radiation dose is equal to the product of the biological dose in parts of the body by a certain weighted coefficient.
Different human tissues and organs have different radiation susceptibilities. Some organs may, at one value of the equivalent indicator of the absorbed dose, undergo cancer more likely than others, for example, the chance of such an illness in the thyroid is less than in the lungs. Therefore, a person uses the created radiation risk coefficient. CRC is a tool for determining the dose of an agent affecting organs or tissues. The total indicator of the degree of influence of the effective dose on the body is calculated by multiplying the number of the corresponding biological dose by CRC of a specific organ, tissue.
Collective dose concept
There is a concept of a group dose of absorption, which is the sum of an individual set of effective dose values in a specific group of subjects for a certain time period. Calculations can be made for any settlements, up to states or entire continents. For this, the average effective dose and the total number of subjects exposed to radiation are multiplied. This indicator of the absorbed dose is measured with the help of a man-sievert (person-Sv.).
In addition to the aforementioned forms of absorbed doses, there are also: committal, threshold, collective, preventable, maximum permissible, biological dose of gamma-neutron type of radiation, lethally minimal.
Dose Strength and Units
Exposure rate is the substitution of a specific dose under the influence of a specific radiation for a temporary measuring unit. This value is inherent in the dose difference (equivalent, absorbed, etc.) divided by the unit of time. There are many specially crafted units.
The absorbed dose of radiation is determined by the formula suitable for the specific radiation and the type of absorbed amount of radiation (biological, absorbed, exposure, etc.). There are many ways to calculate them, based on different mathematical principles, and various measurement units are used. Examples of measuring units are:
- The integral view is the gray kilogram in SI, outside the system it is measured in rad grams.
- The equivalent form is sievert in SI, outside the system it is measured in rems.
- Exposure view - pendant-kilogram in SI, measured outside the system - in X-rays.
There are other measuring units corresponding to other forms of absorbed radiation dose.
conclusions
Analyzing these articles, we can conclude that there are many types of both the ionizing ion itself and the forms of its effect on substances of animate and inanimate nature. All of them are measured, as a rule, in the SI system of units, and each type corresponds to a specific system and non-system measuring unit. Their source can be the most diverse, both natural and artificial, and the radiation itself plays an important biological role.