The support and movement system, which includes bones, muscles and ligaments, functions in the human body as a whole. The skeleton, formed by a special type of connective tissue cells - osteocytes, consists of several departments. It includes the skull, spine, chest, free limbs and girdles, ensuring the connection of the bones of the upper and lower extremities with the spine.
In this paper, we will focus on the structure of the human scapula, which together with the clavicle forms the belt of the upper extremities. We also determine its role in the skeleton and get acquainted with the most common developmental pathologies.
Structural Features of Flat Bones
The supporting apparatus contains several types of bones: tubular, mixed and flat. They differ among themselves in both appearance and internal anatomical structure. For example, the compact substance of the bone may take the form of two thin plates, between which, as a layer in the cake, there is a spongy tissue penetrated by capillaries and containing red bone marrow.
It is this structure that the sternum, cranial vault, ribs, pelvic bones and human shoulder blade have. It is the best way to protect the underlying organs: lungs, heart and large blood vessels from mechanical shock and damage. In addition, a large number of muscles that perform static and dynamic work are attached to the vast flat surface of the bone by ligaments and tendons. And the red bone marrow inside the flat bone serves as the main hematopoietic organ supplying the shaped elements: red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets.
Human scapula anatomy
The bone has the shape of a triangle touching the back of the sternum. Its upper part has a cut edge, the medial section is turned towards the spine, the lateral angle contains the articular cavity. It includes the head of the tubular humerus. Another element of the upper limb belt - the clavicle, is connected to the scapula with the help of an acromioclavicular joint. The axis passing along the posterior surface of the scapula reaches the lateral surface, passing into the acromion. On it is the junction with the clavicle in the form of an articular surface. A more complete picture of the anatomical features of flat bones is given by the photo of the human scapula presented below.
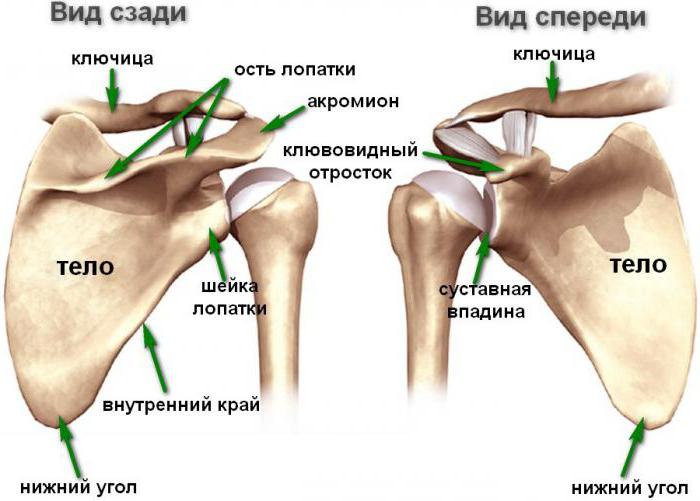
In embryogenesis, bone is formed from the mesoderm. In a newborn, ossification of the scapula is incomplete and osteocytes are contained only in the body and spine, the rest has a cartilaginous structure (enchondral ossification). In the first year of a child’s life, ossification points arise in the coracoid process, later in the acromion, the lateral end of the scapula. Complete ossification is completed by 18 years of human life.
How muscles attach to the scapula
The main way to connect bones and muscles in the musculoskeletal system is through tendons.
Thanks to collagen fibers, which is the end part of the biceps, the biceps of the shoulder is attached to the tubercle located above the upper edge of the articular cavity of the scapula. The lower edge has the same hilly surface, to which, with the help of a tendon, a muscle is attached that extends the arm in the shoulder joint - triceps (triceps muscle of the shoulder).
Thus, the human shoulder blade is directly involved in the flexion and extension of the upper limb and the maintenance of the muscular corset of the back. The bones of the belt of the upper extremities - the clavicle and scapula share a common system of ligaments, however, the scapula has three ligaments of its own, not related to the shoulder and acromioclavicular joints.
The value of the coracoid process
From the upper edge of the scapula, a part of the bone, representing the remainder of the vertebral coracoid and called the coracoid process, departs. It is located above the shoulder joint like a visor. The short head of the biceps, as well as the beak and shoulder and small pectoral muscles, are attached to the process with the help of tendons.
As part of the scapula - the bones of a person directly forming the belt of the upper extremities, the coracoid process participates in the work of antagonist muscles: the biceps and triceps, and its connection with the muscles of the shoulder ensures that the upper limb is led away to the side and up. As can be seen, the coracoid process is of no small importance in the structure of the scapula. What is its anatomical origin?
Coracoid and its role in vertebrate phylogenesis
Earlier, we focused on the fact that paired clavicle and scapula enter the upper limb belt. It is distinguished from other vertebrates, for example, from birds, reptiles, fish or amphibians, the reduction of the crow's bone - the coracoid. It is associated with the release of the upper limb from physically complex and diverse motor functions in the form of running, flying, swimming or crawling. Therefore, the presence of a third bone in the belt of the forelimbs has become impractical. The crow's bone was reduced in humans; only a part of it was preserved - the coracoid process, which was part of the scapula.
Pathology of the bones of the upper limb belt
The most common abnormalities in the structure of the human scapula arose as a result of a violation of organogenesis during fetal development, and in the form of complications after degenerative muscle damage or neuroinfections. These include, for example, pterygoid scapula syndrome , which is determined both during an external examination of the patient, and on an x-ray.
The disease is accompanied by debilitating pains in the shoulder and behind the sternum as a result of rapidly developing neuropathy. Remission occurs subject to treatment and preventive measures: dosed physical activity, massage, special exercises for the muscles of the shoulder and back.
Another pathology is congenital high standing of the scapula (Sprengel disease). This anomaly is combined with a violation of the structure of the vertebrae, anatomical defects of the ribs, for example, their fusion or partial absence. There are two forms of the disease: single and bilateral violation of the symmetry of the shoulder blades.
So, with a bilateral lesion, the left scapula is higher than the right. The anomaly is dangerous for the degeneration of myocytes in the main muscles: trapezius and rhomboid - large and small. A positive prognosis can be expected from surgery performed by a child under 8 years of age; at a later age, surgery is not resorted to due to the high degree of risk of complications, limited to therapeutic exercises and massage.