A thermal unit is a set of devices and instruments that record energy, volume (mass) of a coolant, as well as register and control its parameters. The metering unit is structurally a collection of modules (elements) connected to the piping system.
Appointment
A heat energy metering unit is organized for the following purposes:
- Controlling the rational use of coolant and thermal energy.
- Monitoring of thermal and hydraulic modes of heat consumption and heat supply systems.
- Documentation of coolant parameters: pressure, temperature and volume (mass).
- Mutual financial settlement between the consumer and the organization involved in the supply of thermal energy.
Essential elements
The heat assembly consists of a set of metering devices and devices that provide the performance of both one and several functions at the same time: storage, storage, measurement, displaying information about the mass (volume), the amount of thermal energy, pressure, temperature of the circulating liquid, and also the operating time .
As a rule, a heat meter acts as a metering device, which includes a resistance thermoconverter, a heat meter, and a primary flow converter. In addition, the heat meter can be equipped with filters and pressure sensors (depending on the model of the primary converter). In heat meters, primary converters can be used with the following measurement options: vortex, ultrasound, electromagnetic and tachometric.
Accounting node device
The metering unit of thermal energy consists of the following main elements:
- Shutoff valves.
- Heat meter.
- Thermal converter.
- Sump.
- Flow meter
- Return temperature sensor.
- Optional equipment.
Heat meter
The heat meter is the main element of which the node of thermal energy should consist. It is installed at the heat input to the heating system in close proximity to the boundary of the balance sheet of the heating network.
When installing the metering device remotely from this boundary, heating networks add losses to the meter readings (to account for the heat that is released by the surface of pipelines in the area from the balance separation border to the heat meter).
Heat meter functions
Any type of device must perform the following tasks:
1. Automatic measurement:
- Duration of work in the error zone.
- Running hours at the applied supply voltage.
- Excessive pressure circulating in the fluid piping system.
- Water temperatures in pipelines of hot, cold water supply and heat supply systems.
- The flow rate of the coolant in the pipelines of hot water supply and heat supply.
2. Calculation:
- The amount of heat consumed.
- The volume of coolant flowing through the pipelines.
- Thermal power consumption.
- The temperature differences of the circulating liquid in the supply and return piping (cold water supply pipeline).
Stop valves and sump
Locking devices cut off the heating system of the house from the heating network. At the same time, the mud sump protects the elements of the heat meter and the heat network from the dirt that is present in the coolant.
Thermal converter
This device is installed after the sump and stop valves in an oil-filled sleeve. The sleeve is either threadedly fastened to the pipeline or welded into it.
Flow meter
The flow meter installed in the heat unit performs the function of a flow transducer. It is recommended to install special valves on the measuring section (before and after the flowmeter), due to which service and repair work will be simplified.
Having entered the supply pipe, the coolant is sent to the flow meter, and then goes into the heating system of the house. Further, the cooled liquid is returned in the opposite direction through the pipeline.
Thermal sensor
This device is mounted on the return pipe together with shutoff valves and a flowmeter. This arrangement allows not only to measure the temperature of the circulating liquid, but also its flow rate at the inlet and outlet.
Flow meters and temperature sensors are connected to heat meters, which allow calculating the consumed heat, storing and archiving data, recording parameters, as well as displaying them visually.
As a rule, the heat meter is located in a separate cabinet with free access. In addition, additional elements can be installed in the cabinet: uninterruptible power supply or modem. Additional devices allow you to process and control data that is transmitted remotely by the metering station.
Basic schemes of heating systems
So, before considering the schemes of thermal units, it is necessary to consider what are the schemes of heating systems. Among them, the most popular is the design of the upper wiring, in which the coolant flows along the main riser and goes to the main pipeline of the upper wiring. In most cases, the main riser is located in the attic, from where it branches into secondary risers, and then distributed to the heating elements. It is advisable to use a similar scheme in single-story buildings in order to save free space.
There are also schemes of heating systems with lower wiring. In this case, the heating unit is located in the basement room, from where the main pipeline with warm water comes out. It is worth paying attention that, regardless of the type of scheme, it is recommended to have an expansion tank in the attic of the building.
Schemes of thermal units
If we talk about the schemes of thermal points, it should be noted that the following types are the most common:
- Thermal unit - a circuit with parallel single-stage connection of hot water. This scheme is the most common and simple. In this case, the hot water supply is connected in parallel to the same network as the heating system of the building. The coolant is supplied to the heater from the external network, then the cooled liquid in the reverse order flows directly into the heat conduit. The main disadvantage of such a system, in comparison with other types, is the high consumption of network water, which is used to organize hot water supply.
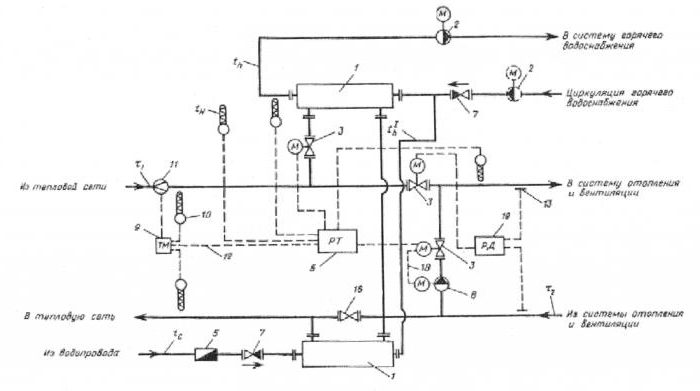
- Scheme of a heat point with a sequential two-stage connection of hot water. This scheme can be divided into two steps. The first stage is responsible for the return pipe of the heating system, the second - for the supply pipe. The main advantage possessed by thermal units connected according to such a scheme is the absence of a special supply of network water, which significantly reduces its consumption. As for the shortcomings - this is the need for the installation of an automatic control system to adjust and adjust the heat distribution. Such a connection is recommended to be used in the case of the ratio of the maximum heat consumption for heating and hot water supply, which is in the range from 0.2 to 1.
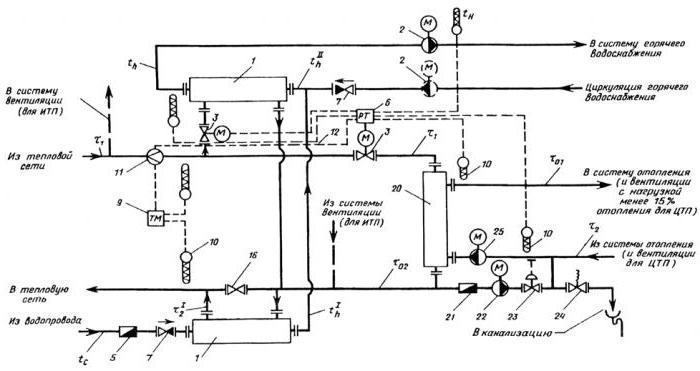
- Thermal unit - a scheme with a mixed two-stage connection of a hot water heater. This is the most versatile and flexible configuration scheme of the connection. It can be used not only for a normal temperature graph, but also for an increased one. The main distinguishing feature is the fact that the heat exchanger is connected to the supply pipe not in parallel, but in series. The further construction principle is similar to the second scheme of the heat point. Thermal units connected in accordance with the third scheme require additional consumption of network water for the heating element.
The procedure for installing the accounting node
Before installing the metering unit of thermal energy, it is important to conduct an inspection of the facility and develop design documentation. Specialists who are engaged in the design of heating systems make all the necessary calculations, select instrumentation, equipment and a suitable heat meter.
After the development of project documentation, it is necessary to obtain approval from the organization that supplies heat energy. This is required by the current rules for accounting for thermal energy and design standards.
Only after coordination can you easily install thermal metering units. Installation consists of inserting locking devices, modules into pipelines and electrical work. Electrical work is completed by connecting sensors, flow meters to the computer and then starting the computer to record heat energy.
After that, the thermal energy metering device is set up , which consists in checking the system’s operability and programming the calculator, and then the object is commissioned for commercial accounting, which is carried out by a special commission in the person of the heat supply company. It is worth noting that such a metering station should function for some time, which for different organizations ranges from 72 hours to 7 days.
To combine several metering nodes into a single dispatch network, it will be necessary to organize remote removal and monitoring of information accounting from heat meters.
Approval for use
With the admission of the heating unit to operation, the conformity of the serial number of the meter, which is indicated in its passport and the measurement range of the set parameters of the heat meter to the range of measured readings, as well as the presence of seals and installation quality, is checked.
Operation of the heating unit is prohibited in the following situations:
- The presence of inserts in pipelines that are not provided for in the design documentation.
- The operation of the meter beyond the limits of accuracy.
- The presence of mechanical damage on the device and its elements.
- Violation of seals on the device.
- Unauthorized interference with the operation of the heating unit.