In accordance with existing standards in modern suburban ownership should be present local treatment facilities. The building must be connected either to the main pipeline, or have its own filtration system. Next, we consider in more detail what constitutes a treatment plant for a private house and an industrial organization.
General information
If we talk about a well-maintained mansion, then certainly hot and cold water should be present in it. It is necessary for taking a bath or shower, washing, washing dishes, cleaning, watering. In this regard, sewage treatment plants are an integral part of the engineering communications of the building. Their device is one of the most important cases in the planning and construction. Of course, the best option would be to send wastewater to an appropriate common line. But it is not always possible to connect to it or it is completely absent. In some areas, owners arrange special cesspools. However, as practice shows, this option is extremely inconvenient. In addition, the pits are unsafe and very offensive. Today's realities dictate new standards for wastewater treatment.
Main characteristics
Local wastewater treatment plants are used to filter and discharge from the structure. Liquid waste in purified form enters the environment: river, ditch, soil and more. Local treatment facilities, in essence, are:
- Individualized. This means that the systems work directly for those objects for which they are designed.
- Gravity. In other words, the systems operate on the principle of gravity flow of liquid waste. But some local treatment facilities are equipped with pumps.
- Biological and mechanical. This means that local wastewater treatment plants operate in a comprehensive manner. At the same time, biological and mechanical methods of filtration and abduction are combined.
- Household. This characteristic suggests that the systems are designed exclusively for filtering liquid waste from personal subsidiary plots.
Of course, there are local treatment facilities for enterprises. Systems used for industrial purposes have a complex structure, since it is necessary to process sufficiently large volumes of waste.
Waste classification
Domestic wastewater is divided into two main types: black and gray. The latter include water used for washing, cleaning, washing or bathing. Black includes liquid waste from the toilet. They make up about 30% of the total volume of wastewater. At the same time, they contain 90% nitrogen, 50% phosphorus and many fecal bacteria. All this must be filtered and neutralized. Storm and drainage flows should not enter the sewage treatment plant for the home. Otherwise, serious system malfunctions are likely.
The principle of operation of installations
Local treatment facilities for enterprises and private households process waste in two stages. The first is pre-filtered, the second is final. Specialists also call the final stage "post-treatment". Next, we consider both stages in more detail.
Pre-filtering
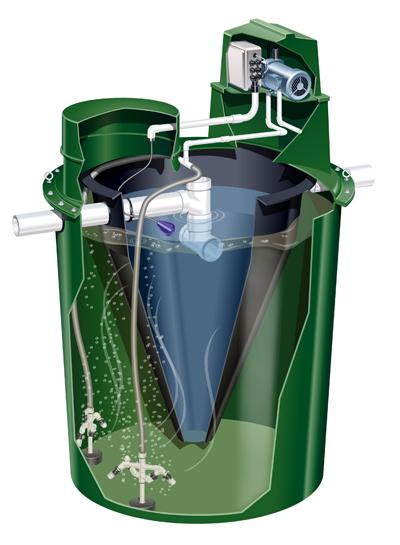
It is carried out in a special tank. It is called a sump, or septic tank. Particles that are present in the effluent accumulate at the bottom. This sediment undergoes slow fermentation over time. In the process, part of the pollution is dissolved in water. The remaining volume accumulates at the bottom in the form of mineral insoluble substances. In the septic tank, a foam or film is formed on the surface (usually from fats). To make the fermentation process more efficient, at least three days are needed. In this regard, a requirement is established for the size of sedimentation tanks, depending on the volume of effluents entering the preliminary treatment. In general, the tasks of a septic tank include separating a liquid with soluble components from insoluble fractions (in other words, mechanical sludge), as well as decomposing organic contaminants using anaerobic bacteria that are always present in waste (biological process). As a result, after preliminary filtration, sediment suspension and clarification of liquid waste occur. At the outlet of the septic tank, the effluents turn out to be approximately 65% purified.

Second phase
Post-treatment can occur in devices of various types. All these constructions are designed to form optimal conditions (the main one of which is oxygen access) for anaerobic bacteria, due to which the final filtering of waste flowing from the sump is carried out. The longer contact with O 2 is , the better the oxidation and subsequent decomposition of ammonia and organic nitrogen into nitrates and nitrites.
Biological Neutralization Systems
For post-treatment, sand and biological filters, soil drainage, and an absorbing well are used. Their working principle is borrowed from nature. It is based on the natural ability of the soil to self-clean. Its essence is the preliminary distribution of waste in small volumes on the filter surface. There they begin to interact with anaerobic bacteria. Then, mechanical and biological purification takes place gradually, but without "oxygen starvation". When leaving the system, waste is filtered at 95%. This indicator complies with established sanitary requirements. Then, the effluent is discharged into ditches, ditches, etc.
General recommendations for choosing VOCs
Local treatment facilities have this or that productivity. To determine the appropriate volume, it is necessary to multiply the consumption rate by the number of people living in the structure. For example, for the Moscow Region this indicator is from 680 to 1000 l / day (based on four people). As mentioned above, waste falling into wastewater treatment plants must be kept there for at least three days. As a result, the volume of the sump is about 2 m 3 . Then you need to choose the right material from which the septic tank is made. This is important because, firstly, sewage treatment plants for a private house are buried in the ground. Therefore, septic tanks must withstand the movement and stress of the soil. Secondly, an aggressive environment acts on it from the inside, which can be compared with seawater by its destructive effect. Thus, the materials from which sewage treatment plants are made should be strong and resistant to various negative factors, but at the same time light. As a rule, steel with a protective coating, reinforced concrete and polyethylene are used for the manufacture of equipment. The first material is quickly coated with corrosion. Some consumers choose steel structures. But this material is not resistant to aggressive environments. In this regard, attention should be paid to the quality of the coating. In addition, steel tanks have a fairly impressive weight and additional equipment is needed for their transportation. Reinforced concrete structures are hygroscopic. And, as buyers themselves note, this is fraught with the penetration of groundwater or, conversely, pollution with their waste. The most popular among consumers today is polyethylene. Buyers note its lightness, corrosion resistance, durability. Polyethylene provides reliable tightness in the joints. The only thing you need to pay attention to is the strength of the material.

Features of the site
When choosing a post-treatment system, special attention should be paid to the composition of the soil and the level of groundwater. Companies that are involved in the installation of filtration systems, as a rule, offer a full range of work. It includes hydrogeological research, design, installation of the station, assignment, as well as warranty and post-warranty maintenance of equipment. The cost of turnkey local treatment facilities depends on the type of soil and the volume of tanks. The cost of commissioning - from 7500 rubles., Installation of the installation - from 24 200 rubles.
Soil drainage
Many owners of suburban real estate choose this method of post-treatment, considering it the easiest. As users themselves note, soil drainage gives an excellent filtration result. This method is used in areas with low groundwater and sandy soil. Ground drainage is an integral part of local treatment facilities. In it, through a system of pipes, waste is fed to the place of their subsequent filtration. There they are cleaned with rubble and sand in the presence of anaerobic bacteria. Only after this, filtered effluents enter the soil. Among the shortcomings, consumers note the small capacity of the system and the need to ensure the receipt of small amounts of waste. Otherwise, they will not have time to effectively neutralize themselves. Therefore, the length of the drainage should be proportional to the permeability of the soil and the number of drains. The system is laid to a depth of 0.5-0.8 m. This is due to the fact that below 1.2 meters there are no anaerobic bacteria. The width of the ditch under the pipe is 1 meter. For 1 person, about 12 meters (linear) of drainage is taken (according to the standard). The total length of the system should be no more than 120 m. When installing this system, there should be no trees along the pipe. This is due to the fact that their roots will interfere with the normal functioning of the drainage.
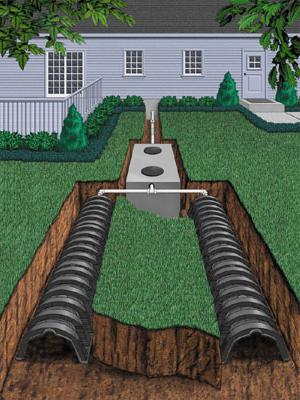
Absorbing well
This design is a small ventilated device. It is intended for the purification of a small volume of effluent in permeable soils. This device does not need drainage pipes. From the septic tank, the effluent is sent to a concrete well, which is loaded with gravel and sand. Then the waste is filtered and through the holes in the walls go into the ground. As a rule, absorbing wells are popular with owners of plots of a small area where drainage is not possible, or owners of buildings for 1-2 people.
Sand filter
It is designed for a sufficiently large load and may well become an alternative to soil drainage. The sand filter, according to many consumers, is the best solution on a site with difficult hydrogeological conditions. The design is a multilayer device. Inside installed drainage pipes in two floors. During the construction, a layer of soil is removed, and gravel and sand are laid instead. Waste from the top floor of the pipes passes the filter, and then, cleaned, are removed through the drainage of the first level into the receiving well. The depth of the trench is at least two meters.
Biological filter
Many owners of suburban real estate consider this system universal. This is evidenced by numerous user reviews. The biological filter can be used not only with a high level of clay soil and groundwater, but also with a small area of the site, when the drainage device is not possible. The so-called “load” enters the tank - a porous and fairly light material. As a rule, pozzolan, expanded clay, coke are used. These materials are both a filter and a place for the existence of anaerobic microorganisms. Pre-treated in the sump, the effluents are distributed over the surface and, filtered, enter the bottom. Further, the liquid accumulates in the intake well and then discharged into the ditch.